BFS算法超时问题——标记已查找的元素与将其加入到下次需要查询的队列的先后顺序问题
问题引入
有一个n*m(1 <= n,m <= 500)的字符矩阵,仅包含'.' 和'#' 两种字符,保证'#' 所围起来的区域是一个封闭区域,且'#' 不在边缘区域,现在要求你将封闭区域内全部用符号'#' 填充
如图所示:将上面的矩阵转换成下面的矩阵

错误代码
我们可以使用BFS算法,因为'#' 不在矩阵的边缘,那么我们可以从 (0, 0) 开始,BFS到 (n-1, m-1)
const int MAXSIZE = 500; // 最大尺寸
int bfsPath[MAXSIZE][MAXSIZE]; // 记录是否搜索过该点
int mapp[MAXSIZE][MAXSIZE]; // 存储输入进来的图
const int SEARCHED = 999; // 搜索标记的常量
const int EXIST = 1; // 原图为‘#’
// 层序遍历,遍历未遍历过的区域
void bfs() {
queue<int> que;
que.push(0);
bfsPath[0][0] = SEARCHED;
while (que.size()) {
// printBfsPath();
queue<int> next;
while (que.size()) {
int index = que.front();
que.pop();
int i = index / cols;
int j = index % cols;
bfsPath[i][j] = SEARCHED; // 标记当前节点
if (i > 0 && bfsPath[i - 1][j] != SEARCHED && mapp[i - 1][j] != EXIST ) {
next.push(getIndex(i - 1, j)); // 加入到next队列
}
if (j > 0 && bfsPath[i][j - 1] != SEARCHED && mapp[i][j - 1] != EXIST ) {
next.push(getIndex(i, j - 1));
}
if (i + 1 < rows && bfsPath[i + 1][j] != SEARCHED && mapp[i + 1][j] != EXIST ) {
next.push(getIndex(i + 1, j));
}
if (j + 1 < cols && bfsPath[i][j + 1] != SEARCHED && mapp[i][j + 1] != EXIST ) {
next.push(getIndex(i, j + 1));
}
}
que = next;
}
}
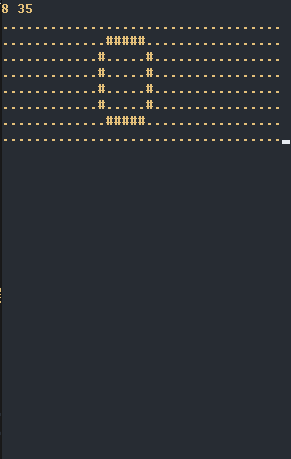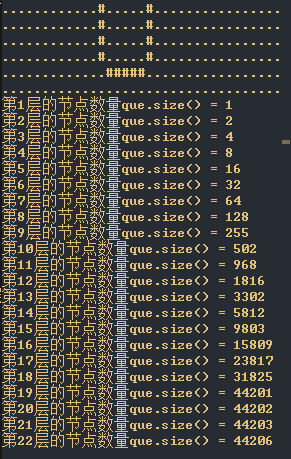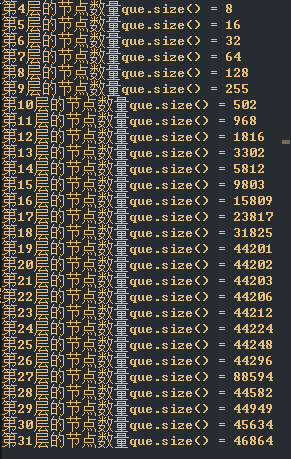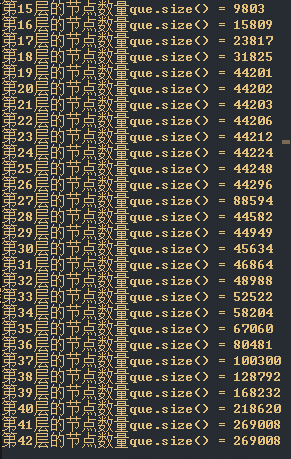
这个BFS模板当然很好写,通过维护两个队列,一层一层地遍历。但是经过测试后发现居然超时了,输出每一次遍历结果后发现是越搜索越慢!下面展示一下搜索过程:
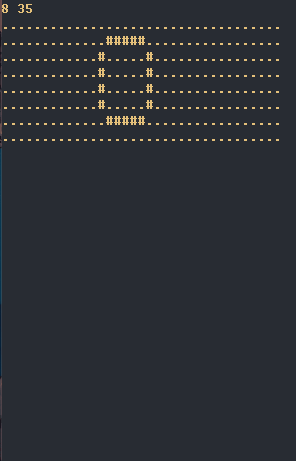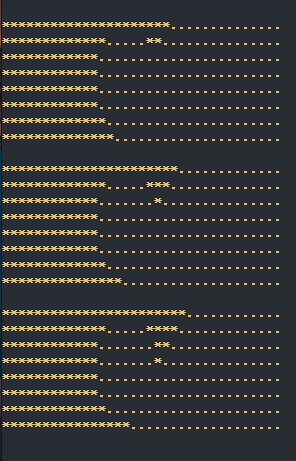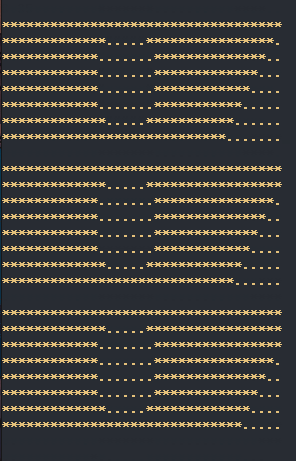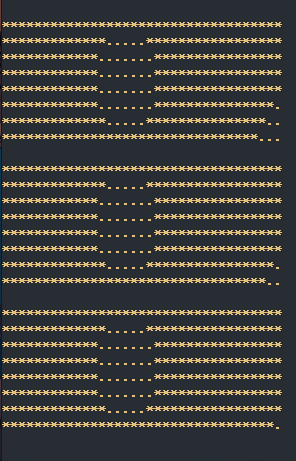
我其实蛮疑惑的,为什么会越来越慢呢?于是我将每一次向下一层遍历时,下一层的数量打印出来后,头皮发麻地看到最后一层竟然需要访问**40W+**的节点后,才恍然大悟!
原因解析
例如某过程中:
我们依次访问
curr队列(当前这一层节点的队列),里面有点A1、A2、A3。并将下一层节点放到next队列中。
- 我们首先访问点
A1(1, 2),我们将其标记为已访问。于是分别查找四个方向可以访问的节点,发现可以访问A1的下方这个点B(2, 2),于是将点B加入到next队列。- 我们继续访问点
A2(2, 3),我们将其标记为已访问。于是分别查找四个方向可以访问的节点,发现可以访问A2左边的这个点B(2, 2),于是将点B加入到next队列。- …
有没有发现我们竟然多次将点B加入到next队列?难怪我们会在访问第41层时居然需要依次访问 40W 个节点!
是的,如果我们将标记已查找的元素与将其加入到下次需要查询的队列的先后顺序调换一下,一旦加入到next队列中,那么就标记我们已经将该点处于待查找的队列中,虽然与已查找的含义不同,但是也能起到防止重复查找的效果。
我们再次将正确过程文字描述一遍:
我们依次访问
curr队列(当前这一层节点的队列),里面有点A1、A2、A3。并将下一层节点放到next队列中。
- 我们首先访问点
A1(1, 2),我们将其标记为已访问。于是分别查找四个方向可以访问的节点,发现可以访问A1的下方这个点B(2, 2),于是先将点B标记为已访问,再将点B加入到next队列。- 我们继续访问点
A2(2, 3),我们将其标记为已访问。于是分别查找四个方向可以访问的节点,发现可以访问A2左边的这个点B(2, 2)已经访问了,于是不考虑点B。- …
正确代码
当然只是将BFS函数单独拿出来举例:
const int MAXSIZE = 500; // 最大尺寸
int bfsPath[MAXSIZE][MAXSIZE]; // 记录是否搜索过该点
int mapp[MAXSIZE][MAXSIZE]; // 存储输入进来的图
const int SEARCHED = 999; // 搜索标记的常量
const int EXIST = 1; // 原图为‘#’
// 层序遍历,遍历未遍历过的区域
void bfs() {
queue<int> que;
que.push(0);
bfsPath[0][0] = SEARCHED;
while (que.size()) {
printBfsPath();
queue<int> next;
while (que.size()) {
int index = que.front();
que.pop();
int i = index / cols;
int j = index % cols;
if (i > 0 && bfsPath[i - 1][j] != SEARCHED && mapp[i - 1][j] != EXIST) {
bfsPath[i - 1][j] = SEARCHED; // 先标记
next.push(getIndex(i - 1, j)); // 再加入next队列
}
if (j > 0 && bfsPath[i][j - 1] != SEARCHED && mapp[i][j - 1] != EXIST) {
bfsPath[i][j - 1] = SEARCHED;
next.push(getIndex(i, j - 1));
}
if (i + 1 < rows && bfsPath[i + 1][j] != SEARCHED && mapp[i + 1][j] != EXIST) {
bfsPath[i + 1][j] = SEARCHED;
next.push(getIndex(i + 1, j));
}
if (j + 1 < cols && bfsPath[i][j + 1] != SEARCHED && mapp[i][j + 1] != EXIST) {
bfsPath[i][j + 1] = SEARCHED;
next.push(getIndex(i, j + 1));
}
}
que = next;
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:Coder-Jiang,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/coderjiang/p/18118096


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号