剑指offer-树(JavaScript)
树
7. 重建二叉树
题目描述
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
例如,给出
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
返回如下的二叉树:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} preorder
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
if(preorder.length==0 || inorder.length==0) return null;
var root=preorder[0];
var index = inorder.indexOf(root);
var left = inorder.slice(0, index);
var right = inorder.slice(index+1);
var node = new TreeNode(root);
node.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1,index+1), left);
node.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index+1), right);
return node;
};
8. 二叉树的下一个节点
题目描述
给定一个二叉树其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的next指针。下图为一棵有9个节点的二叉树。树中从父节点指向子节点的指针用实线表示,从子节点指向父节点的用虚线表示。
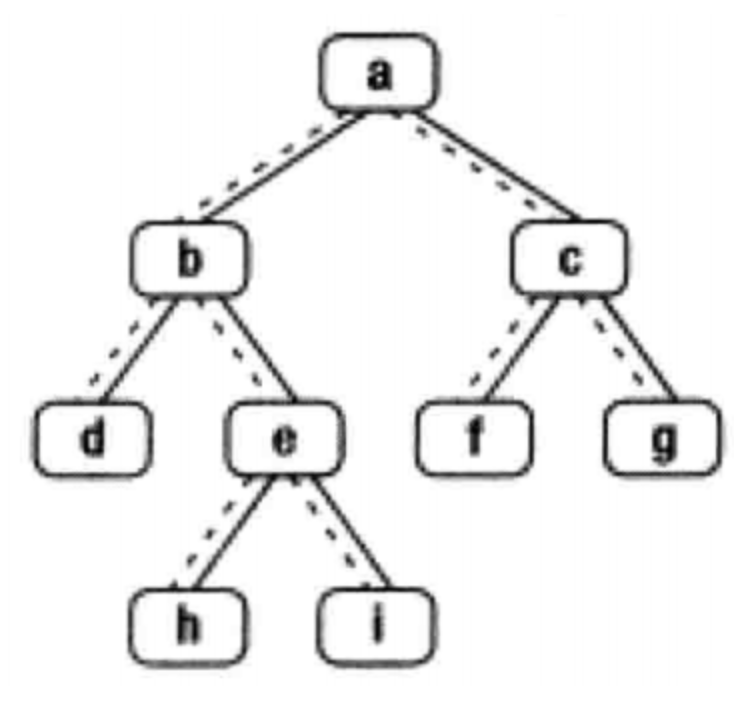
例如
输入:{8,6,10,5,7,9,11},8
返回:9
解析:这个组装传入的子树根节点,其实就是整颗树,中序遍历{5,6,7,8,9,10,11},根节点8的下一个节点就是9,应该返回{9,10,11},后台只打印子树的下一个节点,所以只会打印9,如下图,其实都有指向左右孩子的指针,还有指向父节点的指针,下图没有画出来
代码
/*function TreeLinkNode(x){
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.next = null;
}*/
function GetNext(pNode) {
// write code here
if (pNode === null) return null; //空结点
var p = null;
if (pNode.right) {
//有右子树,则下一个结点在右子树最左边的结点
p = pNode.right;
while (p.left !== null) {
p = p.left;
}
return p;
} else {
//没有右子树
p = pNode.next;
if (p && p.right === pNode) {
while (p.next && p.next.right === p) {
p = p.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
return p;
}
return null;
}
26. 树的子结构
题目描述
输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
B是A的子结构, 即 A中有出现和B相同的结构和节点值。
例如:
给定的树 A:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
给定的树 B:
4
/
1
返回 true,因为 B 与 A 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
示例 1:
输入:A = [1,2,3], B = [3,1]
输出:false
示例 2:
输入:A = [3,4,5,1,2], B = [4,1]
输出:true
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} A
* @param {TreeNode} B
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSubStructure = function(A, B) {
if(!A || !B) return false;
return isSame(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B);
};
var isSame = function(A, B){
if(!B) return true;
if(!A) return false;
if(A.val != B.val) return false;
return isSame(A.left, B.left) && isSame(A.right, B.right);
}
27.二叉树的镜像
题目描述
请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。
例如输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
镜像输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mirrorTree = function(root) {
if(!root) return root;
[root.left, root.right] = [root.right, root.left];
mirrorTree(root.left);
mirrorTree(root.right);
return root
};
28.对称的二叉树
题目描述
请实现一个函数,用来判断一棵二叉树是不是对称的。如果一棵二叉树和它的镜像一样,那么它是对称的。
例如,二叉树 [1,2,2,3,4,4,3] 是对称的。
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
但是[1,2,2,null,3,null,3] 则不是镜像对称的:
1
/ \
2 2
\ \
3 3
示例 1:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
if(!root) return true;
return isSame(root.left, root.right)
};
var isSame = function(A, B){
if(!A && !B) return true;
if(!A) return false;
if(!B) return false;
if(A.val != B.val) return false;
return isSame(A.left, B.right) && isSame(A.right, B.left);
}
32-I.从上到下打印二叉树
从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。
例如:
给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回:
[3,9,20,15,7]
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
let nodes = [];
nodes.push(root);
let res = [];
while(nodes.length > 0){
node = nodes.shift();
res.push(node.val);
node.left && nodes.push(node.left);
node.right && nodes.push(node.right);
}
return res;
};
32-II.从上到下打印二叉树II
题目描述
从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层的节点按从左到右的顺序打印,每一层打印到一行。
例如:
给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return []
let nodes = [] // 存放当前节点
let layer = 0 // 表示当前层数
let res = []
nodes.push(root)
while(nodes.length){
res[layer] = []
let num = nodes.length
while(num--){
let node = nodes.shift()
res[layer].push(node.val)
node.left && nodes.push(node.left)
node.right && nodes.push(node.right)
}
layer++
}
return res
};
33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
题目描述
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 true,否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
参考以下这颗二叉搜索树:
5
/ \
2 6
/ \
1 3
示例 1:
输入: [1,6,3,2,5]
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: [1,3,2,6,5]
输出: true
代码
/*
在二叉搜索树中:
1.若任意结点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均不大于它的根结点的值。
2. 若任意结点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均不小于它的根结点的值。
3.任意结点的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树。
*/
function VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence) {
// write code here
if (!sequence || !sequence.length) {
return false;
}
return __VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence);
}
function __VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence) {
const len = sequence.length;
if (len < 2) return true;
const root = sequence[len - 1];
let i = 0;
for (; i < len - 1 && sequence[i] < root; i++) {} //left的数量是i,0 -> i-1
for (let j = i; j < len - 1; j++) {
if (sequence[j] < root) {
return false;
}
}
return __VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence.slice(0, i)) && __VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence.slice(i, len - 1));
}
34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述
输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根节点开始往下一直到叶节点所经过的节点形成一条路径。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 target = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
返回:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
代码
/* function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
} */
function FindPath(root, expectNumber) {
// write code here
var result = [];
if (root === null) {
return result;
}
dfsFind(root, expectNumber, [], 0, result);
return result;
}
function dfsFind(root, expectNumber, path, sum, result) {
sum += root.val;
path.push(root.val);
if (sum === expectNumber && root.left === null && root.right === null) {
result.push(path.slice(0)); // 为什么不能直接push(path),因为在深度优先搜索的时候path都是指向的同一个
}
if (root.left !== null) {
dfsFind(root.left, expectNumber, path, sum, result);
}
if (root.right !== null) {
dfsFind(root.right, expectNumber, path, sum, result);
}
path.pop();
}
36. 二叉搜索树和双向链表
题目描述
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的循环双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的节点,只能调整树中节点指针的指向。
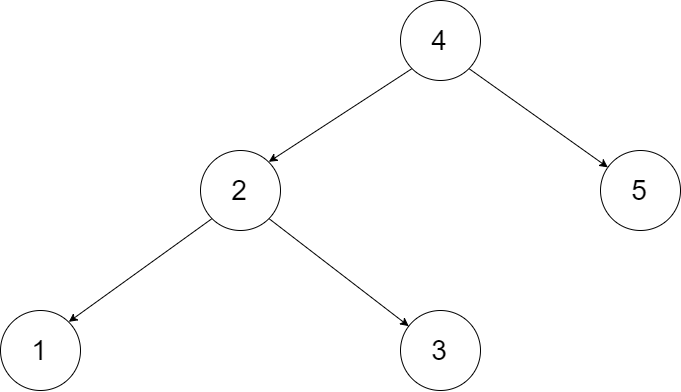
我们希望将这个二叉搜索树转化为双向循环链表。链表中的每个节点都有一个前驱和后继指针。对于双向循环链表,第一个节点的前驱是最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继是第一个节点。
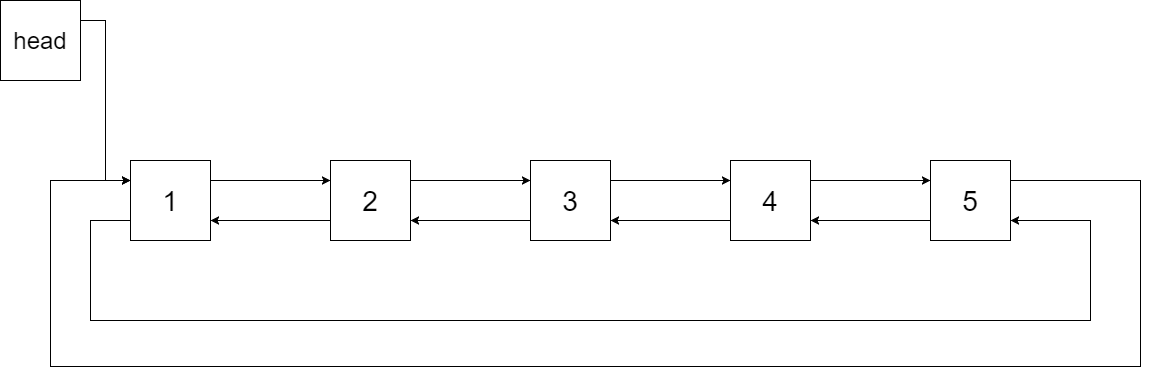
下图展示了上面的二叉搜索树转化成的链表。“head” 表示指向链表中有最小元素的节点。
特别地,我们希望可以就地完成转换操作。当转化完成以后,树中节点的左指针需要指向前驱,树中节点的右指针需要指向后继。还需要返回链表中的第一个节点的指针。
代码
方法一:递归+数组
解题思路:
- 中序遍历一遍二叉搜索树,将节点保存在一个数组中。
- 遍历数组,更改每个节点的 left 和 right
- 返回数组第一个元素
时间复杂度是 O(N),空间复杂度是 O(N)。相较于方法二,多开辟了 O(N)的数组空间。
/* function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
} */
function Convert(pRootOfTree) {
// write code here
if (!pRootOfTree) {
return null;
}
const nodes = [];
midTravel(pRootOfTree, nodes);
const len = nodes.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
nodes[i].right = nodes[i + 1] || null;
nodes[i].left = nodes[i - 1] || null;
}
return nodes[0];
}
//中序遍历,将所有节点存在nodes中
function midTravel(node, nodes) {
if (node.left) {
midTravel(node.left, nodes);
}
nodes.push(node);
if (node.right) {
midTravel(node.right, nodes);
}
}
方法二:一次递归
二叉搜索树的性质是:左节点 < 当前节点 < 右节点。转换后的双向链表是有序的,这里采用中序递归遍历保证有序性。
设计的递归函数返回的是:已转换好的双向链表的尾结点,也就是当前节点的 left 指针应该指向的地方。递归函数的实现思路:
- 检查 left 是否为空,不为空,那么递归调用(传入左子树)
- 将 left 指针指向已转换好的双向链表的尾结点,并将尾节点的 right 指向当前节点
- 更新双向链表尾节点(变为当前节点),检查 right 是否为空,不为空,递归调用传入右子树)
- 返回转换后的双向链表尾节点
整个过程的要递归遍历一遍二叉树,时间复杂度是 O(N),空间复杂度是 O(N)。
/* function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
} */
function Convert(pRootOfTree) {
if (!pRootOfTree) {
return null;
}
__Convert(pRootOfTree, null);
let node = pRootOfTree;
while (node.left) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
function __Convert(pRootOfTree, lastNodeInList = null) {
if (!pRootOfTree) {
return null;
}
// step1:左子树
if (pRootOfTree.left) {
lastNodeInList = __Convert(pRootOfTree.left, lastNodeInList);
}
// step2:当前节点
pRootOfTree.left = lastNodeInList;
if (lastNodeInList) {
lastNodeInList.right = pRootOfTree;
}
// step3:右子树
lastNodeInList = pRootOfTree;
if (pRootOfTree.right) {
lastNodeInList = __Convert(pRootOfTree.right, lastNodeInList);
}
return lastNodeInList;
}
37. 序列化二叉树
题目描述
请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树
二叉树的序列化是指:把一棵二叉树按照某种遍历方式的结果以某种格式保存为字符串,从而使得内存中建立起来的二叉树可以持久保存。序列化可以基于先序、中序、后序、层序的二叉树遍历方式来进行修改,序列化的结果是一个字符串,序列化时通过 某种符号表示空节点(#),以 ! 表示一个结点值的结束(value!)。
二叉树的反序列化是指:根据某种遍历顺序得到的序列化字符串结果 str,重构二叉树。
代码
/* function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
} */
var arr = [];
function Serialize(pRoot) {
// write code here
if (!pRoot) {
arr.push("#");
} else {
arr.push(pRoot.val);
Serialize(pRoot.left);
Serialize(pRoot.right);
}
}
function Deserialize(s) {
// write code here
if (arr === null) return null;
if (arr.length < 1) return null;
var root = null;
var temp = arr.shift();
if (typeof temp === "number") {
root = new TreeNode(temp);
root.left = Deserialize(arr);
root.right = Deserialize(arr);
}
return root;
}
54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
题目描述
给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中第k大的节点。
示例 1:
输入: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
3
/ \
1 4
\
2
输出: 4
示例 2:
输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \
2 4
/
1
输出: 4
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var kthLargest = function(root, k) {
let res
let num = 0
const dfs = function(root){
if(root === null){
return
}
dfs(root.right)
num++
if(num === k){
res = root.val
}
dfs(root.left)
}
dfs(root)
return res
};
55-I. 二叉树的深度
题目描述
输入一棵二叉树的根节点,求该树的深度。从根节点到叶节点依次经过的节点(含根、叶节点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
例如:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
if(root === null) return 0
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right))+1
};
55-II. 平衡二叉树
题目描述
输入一棵二叉树的根节点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。如果某二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
示例 1:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回 true 。
代码
function IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot) {
return depth(pRoot) !== -1;
}
// 用递归来判断root是不是平衡二叉树,如果不是则返回最大的深度,如果不是则返回-1
function depth(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
var left = depth(root.left);
if (left === -1) return -1;
var right = depth(root.right);
if (right === -1) return -1;
if (Math.abs(left - right) > 1) {
return -1;
} else {
return 1 + Math.max(left, right);
}
}
68-I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题目描述
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
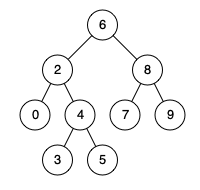
示例 :
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
while(root){
if(root.val<p.val && root.val<q.val){
root = root.right
} else if(root.val>p.val && root.val>q.val) {
root = root.left
} else {
break
}
}
return root
};
68-II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
题目描述
例如,给定如下二叉树: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
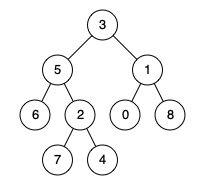
示例 1:
输出: 3
解释: 节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3。```
示例 2:
输出: 5
解释: 节点 5 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是节点 5。因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。```
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if (!root || root === p || root === q) return root;
const left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
const right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
// 左子树找不到,返回右子树
if (!left) return right;
// 右子树找不到,返回左子树
if (!right) return left;
// 左右子树都找到了,那么root就是要找的
return root;
};




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号