自定义持久层框架
自定义持久层框架
1、 JDBC的弊端
我们话不多说,直接看一段JDBC代码。想必学过Java的人一看下面的代码都已经非常熟悉了吧,毕竟JDBC怎么写都是那样了。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//加载驱动类
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 获取连接
connection =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?
characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 定义sql语句
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// ឴预处理对象
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数,尤其注意下标从1开始
preparedStatement.setString(1, "tom");
// 执行语句
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 封装结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
// 封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
}
System.out.println(user);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
想必上面的代码,大家是不是非常熟悉了呢?
那么这样的代码有没有问题?答案是肯定有的,不然为啥会有框架呢?那么有什么问题?
JDBC问题分析:
- 我们每次使用jdbc是不是都要自己去创建连接,最后都要去手动关闭连接。想一想,如果我在100个地方都要执行增删改查jdbc操作那么我每次都要去创建资源,然后释放资源。是不是非常耗时间且浪费资源。思考一下,数据库连接频繁创建释放有什么解决办法?
- sql语句是硬编码,如果我的项目需要改变一个需求,我不查询User了,我要查询Product,那么你就得回来改这个java代码,再重新编译。是不是非常麻烦?
- 同样的道理,使用预编译传参数也是硬编码,如果我要查询的id不是1了而是2,或者我不按照id查询了,我按照name查询,那么你又得改代码。哎,心累是不是?
- 继续这个逻辑不要停,我查询出来这个结果集是不是硬编码?我的id和name都自己写的,只有两个字段还能接受吧,如果有20个字段,那么你很有可能就写掉了一个也是可能的。
JDBC问题解决:
- 频繁创建数据库连接是不是可以用连接池。
- sql语句和预编译硬编码,是不是可以启动配置文件。
- 手动封装结果集,是不是可以反射来自动封装。
2、自定义框架设计
咱们先来捋一捋平时是怎么用框架的。以mybatis为例,是不是得有这么几个步骤:
- 添加mybatis坐标
- 创建对应数据库表的实体类
- 得有一个mapper.xml
- 得有一个配置数据源的sqlMapConfig.xml
那么设计这个框架,咱们是不是也得分两个部分:使用端和框架端。使用端导入框架,可以拿来使用,框架端封装jdbc。
2.1 框架端
2.1.1 Configuration配置
mybatis中sqlSessionFactoryBuilder就根据这样的解析配置来生成sqlsessionfactory从而产生sqlsession。
关于这几个类我们在后面会基础到,继续往下。
public class Configuration {
// 数据源
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* key: statementId (唯一标识: namespace + id)
* value: 封装好的mappedstatement对象
*/
Map<String,MappedStatement> mappedStatementMap = new HashMap<>();
// 省略get set 方法
}
2.1.2 MappedStatement
对应mapper.xml中的各种属性,包括id,resultType,parameterType,和sql语句。
public class MappedStatement {
// id标识
private String id;
// 返回值类型
private String resultType;
// 参数值类型
private String paramterType;
// sql语句
private String sql;
// 省略get set 方法
}
2.1.3 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
建造者模式。
提供一个build方法,根据xml的输入字节流来根据不同的配置来建造不同的sqlSessionfactory工厂。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream in) throws PropertyVetoException, DocumentException {
// 第一:使用dom4j解析配置文件,将解析出来的内容封装到Configuration
XmlConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = new XmlConfigBuilder();
Configuration configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.parseConfig(in);
// 第二: 创建sqlSessionFactory对象:工厂类:生产sqlSession
DefaultSqlSessionFactory defaultSqlSessionFactory = new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(configuration);
return defaultSqlSessionFactory;
}
}
2.1.4 XMLConfigBuilder
主要功能就是对配置文件进行解析,然后封装到configuration
public class XmlConfigBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public XmlConfigBuilder() {
this.configuration = new Configuration();
}
/**
* 该方法就是使用dom4j对配置文件进行解析,封装成configuration的方法
* @param inputStream
* @return
*/
public Configuration parseConfig(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException, PropertyVetoException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
// 匹配所有property的节点
List<Element> list = rootElement.selectNodes("//property");
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 遍历获取他们的属性值封装到 properties
for (Element element : list) {
String name = element.attributeValue("name");
String value = element.attributeValue("value");
properties.setProperty(name,value);
}
// c3p0连接池
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(properties.getProperty("driverClass"));
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl"));
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(properties.getProperty("username"));
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(properties.getProperty("password"));
configuration.setDataSource(comboPooledDataSource);
// maper.xml解析 --- 拿到路径---字节输入流--dom4j进行解析
List<Element> mapperList = rootElement.selectNodes("//mapper");
for (Element element : mapperList) {
String mapperPath = element.attributeValue("resource");
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(mapperPath);
// 解析mapper.xml
XmlMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XmlMapperBuilder(configuration);
xmlMapperBuilder.parse(resourceAsStream);
}
return configuration;
}
}
2.1.5 XMLMapperBuilder
主要对mapper.xml进行解析
public class XmlMapperBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public XmlMapperBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void parse(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
// 获取命名空间值
String namespace = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
// 获取select节点
List<Element> list = rootElement.selectNodes("//select");
for (Element element : list) {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
String paramterType = element.attributeValue("paramterType");
String sqlText = element.getTextTrim();
// 将select的id,返回类型,参数类型都封装到mappedStatement
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
mappedStatement.setId(id);
mappedStatement.setResultType(resultType);
mappedStatement.setParamterType(paramterType);
mappedStatement.setSql(sqlText);
String key = namespace+"."+id;
configuration.getMappedStatementMap().put(key,mappedStatement);
}
}
}
2.1.6 sqlSessionFactoryളݗ݊DefaultSqlSessionFactory实现类
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
public SqlSession openSession();
}
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration);
}
}
2.1.7 sqlSessionളݗ݊DefaultSqlSession实现类
public interface SqlSession {
// 查询所有
<E> List<E> selectList(String statementId,Object... param) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException;
// 根据条件查询单个
<T> T selectOne(String statementId,Object... param) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException;
// 为dao接口生成代理实现类
<T> T getMapper(Class<?> mapperClass);
}
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statementId, Object... param) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 完成对simpleExecutor的query方法调用
SimpleExecutor simpleExecutor = new SimpleExecutor();
Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatementMap = configuration.getMappedStatementMap();
MappedStatement mappedStatement = mappedStatementMap.get(statementId);
List<Object> list = simpleExecutor.query(configuration, mappedStatement, param);
return (List<E>) list;
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statementId, Object... param) throws SQLException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, NoSuchFieldException {
List<Object> objects = selectList(statementId, param);
if (objects.size() == 1){
return (T) objects.get(0);
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("查询结果为空或者返回结果过多");
}
}
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<?> mapperClass) {
// 使用jdk动态代理来为dao接口生成代理对象并返回
Object proxyInstance = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperClass},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 底层还是jdbc代码
// 根据不同情况,来调用selectOne或者selectList
// 准备参数。1. statementId: sql 语句的唯一标识符: namespace.id = 接口全限定名.方法名
String methodName = method.getName();
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String statementId = className + "." + methodName;
// 准备参数 2. params:args
// 获取被调用方法的返回值类型
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
// 判断是否进行了 泛型类型参数化
if (genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
List<Object> objects = selectList(statementId, args);
return objects;
}
return selectOne(statementId,args);
}
});
return (T) proxyInstance;
}
}
2.1.8 Executor和SimpleExecutor实现类
public interface Excutor {
<E> List<E> query(Configuration configuration,MappedStatement mappedStatement,Object... params) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException;
}
public class SimpleExecutor implements Excutor {
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object... params) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
// 1.注册驱动,获取连接
Connection connection = configuration.getDataSource().getConnection();
// 2. 获取sql语句 select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
// 转换sql语句 select * from user where id = ? and username = ?
// 转换的过程中还需要对#{}的值进行解析存储
String sql = mappedStatement.getSql();
BoundSql boundSql = getBoundSql(sql);
// 3. 获取预处理对象 preparestatement
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(boundSql.getSqlText());
// 4. 设置参数
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList = boundSql.getParameterMappingList();
String paramterType = mappedStatement.getParamterType();
Class<?> paramterTypeClass = getClassType(paramterType);
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappingList.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappingList.get(i);
String content = parameterMapping.getContent();
// 反射
Field declaredField = paramterTypeClass.getDeclaredField(content);
// 设置暴力访问
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
Object o = declaredField.get(params[0]);
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,o);
}
// 5. 执行sql
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType();
Class<?> resultTypeClass = getClassType(resultType);
ArrayList<Object> objects = new ArrayList<>();
// 6. 封装返回结果集
while (resultSet.next()){
Object o = resultTypeClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
// 元数据
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
for (int i = 1; i <= metaData.getColumnCount(); i++) {
// 获取到字段名
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
// 字段的值
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnName);
// 使用反射根据数据库表和实体的对应关系完成封装
PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName, resultTypeClass);
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
writeMethod.invoke(o,value);
}
objects.add(o);
}
return (List<E>) objects;
}
private Class<?> getClassType(String paramterType) throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (paramterType != null){
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(paramterType);
return aClass;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 完成对#{}的解析工作,
* 1. 将#{} 使用 ? 进行代替
* 2. 将#{} 立面的值进行存储
* @param sql
* @return
*/
private BoundSql getBoundSql(String sql) {
// 标记处理类,配置标记解析器来完成对占位符的解析处理工作
ParameterMappingTokenHandler parameterMappingTokenHandler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler();
GenericTokenParser genericTokenParser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", parameterMappingTokenHandler);
// 解析出来的sql
String parseSql = genericTokenParser.parse(sql);
// #{} 里面解析出来的参数名称
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = parameterMappingTokenHandler.getParameterMappings();
BoundSql boundSql = new BoundSql(parseSql,parameterMappings);
return boundSql;
}
}
2.1.9 BoundSql
包含解析后的sql和参数列表。
解析过后的参数?比如:mybatis写法 select * from user where id = #{}
解析为jdbc能认识的 select * from user where id = ?
然后再把参数填入? 完成执行
public class BoundSql {
// 解析过后的sql
private String sqlText;
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList = new ArrayList<>();
public BoundSql(String sqlText, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList) {
this.sqlText = sqlText;
this.parameterMappingList = parameterMappingList;
}
// 省略get set
}
2.2 使用端
在写好了框架端后,maven install打包,然后依赖到使用端就可以使用了。
2.2.1 sqlMapConfig.xml
<configuration>
<!-- 数据库配置信息 -->
<dataSource>
<property name ="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name ="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///zdy_mybatis"></property>
<property name = "username" value="root"></property>
<property name ="password" value="123456"></property>
</dataSource>
<!-- 存放mapper.xml全路径-->
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</configuration>
2.2.2 UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.lagou.dao.IUserDao">
<!-- sql的唯一标识:namespace.id来组成 : statementId-->
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.lagou.pojo.User">
select * from user
</select>
<!--
User user = new User()
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("zhangsan")
-->
<select id="findByCondition" resultType="com.lagou.pojo.User" paramterType="com.lagou.pojo.User">
select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
</select>
</mapper>
2.2.3 IUserDao
public interface IUserDao {
// 查询所有用户
List<User> findAll() throws IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, SQLException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException, PropertyVetoException, DocumentException;
// 根据条件进行查询
public User findByCondition(User user) throws IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, SQLException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException, PropertyVetoException, DocumentException;
}
2.2.4 User
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
// 省略 get set toString
}
2.2.5 Test
public class IPersistenceTest {
@Test
public void test() throws PropertyVetoException, DocumentException, SQLException, IllegalAccessException, IntrospectionException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, ClassNotFoundException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 调用
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("张三");
// 返回代理对象
//IUserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
User condition = userDao.findByCondition(user);
System.out.println(condition);
List<User> all = userDao.findAll();
for (User user1 : all) {
System.out.println(user1);
}
}
}
3、总结
通过这个小案例学到了工厂设计模式,代理设计模式,建造者设计模式,解析XML方法,反射和内省技术。
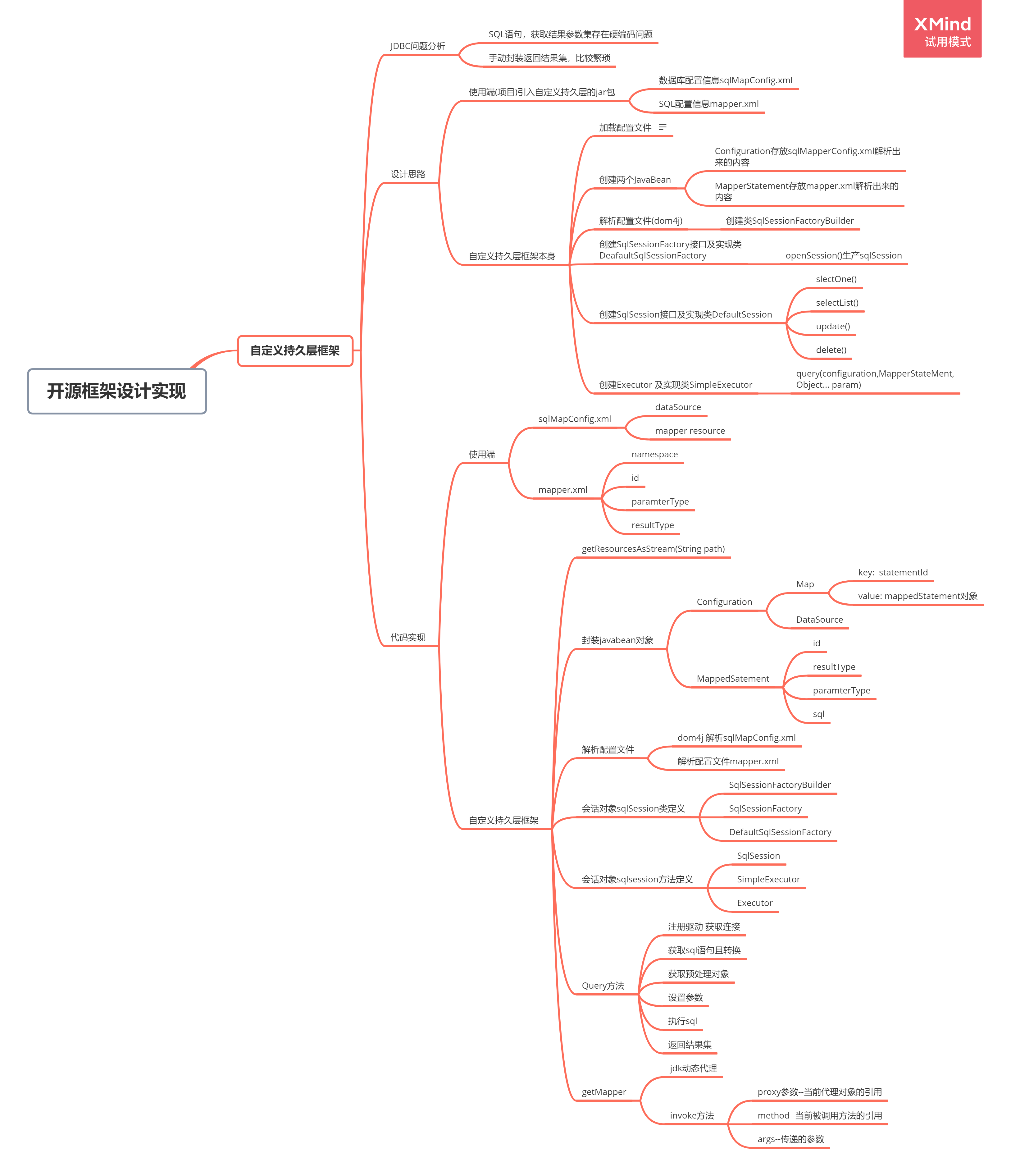
总的来说,收获非常大。最后附上一张xmind思维导图有助于理解整个demo。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号