160. 相交链表
示例 1:
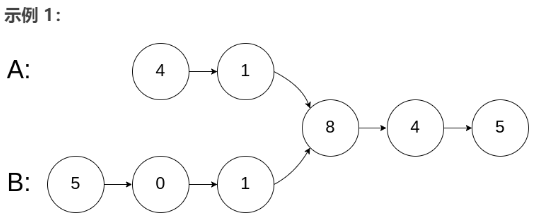
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
package aboutLinkList; class MyLinkList{ ListNode head = new ListNode(0); public void add(ListNode listnode) { ListNode tmp = head; while(tmp.next!=null) { tmp =tmp.next; } tmp.next =listnode; } } public class GetIntersectionNode { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ListNode node8= new ListNode(8); ListNode node4= new ListNode(4); ListNode node5= new ListNode(5); MyLinkList list = new MyLinkList(); list.add(new ListNode(4)); list.add(new ListNode(1)); list.add(node8); list.add(node4); list.add(node5); MyLinkList list1 = new MyLinkList(); list1.add(new ListNode(5)); list1.add(new ListNode(0)); list1.add(new ListNode(1)); list1.add(node8); ListNode node = getIntersectionNode(list.head,list1.head); System.out.println(node); } public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if(headA == null || headB == null) return null; ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB; // 在这里第一轮体现在pA和pB第一次到达尾部会移向另一链表的表头, 而第二轮体现在如果pA或pB相交就返回交点, 不相交最后就是null==null while(pA != pB) { pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next; pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next; } return pA; } }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号