并发队列介绍
本文主要介绍并发队列相关的知识。
概述
简单介绍各个并发并发队列的关系,并发队列是指线程安全的队列,包含:阻塞队列和非阻塞队列,区别如下。
阻塞队列:满了之后不能再插入,当队列为空的时候,读不到会阻塞
非阻塞队列:和阻塞队列完全不一样的
部分类图如下所示:
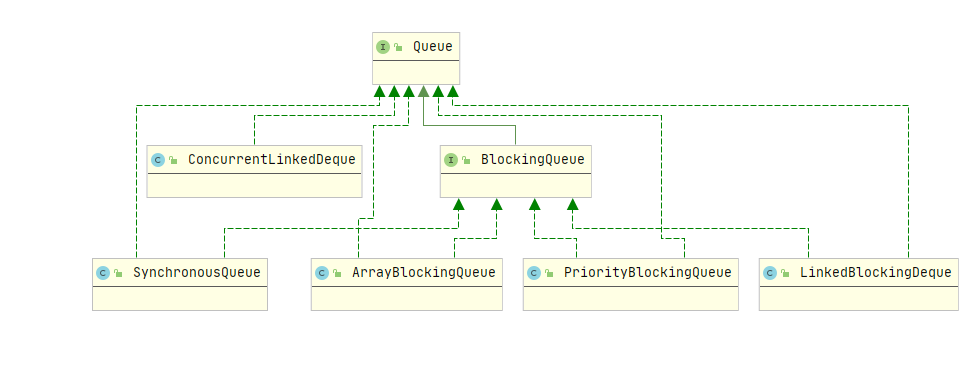
阻塞队列
对阻塞队列进行介绍,阻塞队列自身是线程安全的。一端给生产者,一端给消费者。
最重要的两个方法
1.take()方法:当队列为空的时候需要阻塞
2.put()方法:当队列满的时候需要阻塞
是否有界
1.有些队列是无界的,取整型的最大值
2.有界,可定制
三类方法介绍
1.put、take
2.add,remove,element(头元素)-->会抛出异常
3.offer,poll,peek-->比前两种更加的优雅,peek取出不删除,poll,peek当队列为空时,取到的是null,
阻塞队列实现
ArrayBlockingQueue
下面演示ArrayBlockQueue的基本用法,我们模拟生产者和消费者,最后我们看下put方法的源码。
package com.yang.concurrent;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
/**
* 本实例模拟生产者和消费者如何基于BlockingQueue去生产和消费
*/
public class ArrayBLockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(2);
ConsumerRunnable consumer = new ConsumerRunnable(queue);
ProviderRunnable provider = new ProviderRunnable(queue);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(consumer);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(provider);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
}
}
class ConsumerRunnable implements Runnable {
private ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
ConsumerRunnable(ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
String msg = queue.take();
if ("end".equals(msg)) break;
System.out.println(msg+"消费了");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("结束了");
System.out.println("结束了");
}
}
class ProviderRunnable implements Runnable {
private ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue;
ProviderRunnable(ArrayBlockingQueue<String> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
queue.put("Rrovider-" + i);
System.out.println("Provider-"+i+"生产好了");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
queue.put("end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
接下来我们查看put方法的实现:我们发现此方法中添加了一个可被打断的一个锁,若队列满了一直会阻塞,直到队列不满
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
LinkedBlockingQueue
针对LinkedBlockingQueue我们重点关注了加了两把锁,对读和写都加了锁,如下所示。
/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号