一、概述
流是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。“集合讲的是数据,流讲的是计算!”
注意:
- Stream 自己不会存储元素
- Stream 不会改变源对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream
- Stream 操作是延迟执行的。这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行
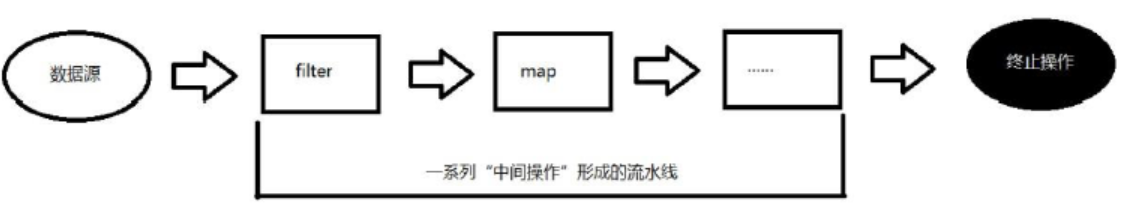
二、Stream操作的三个步骤
1、创建Stream
一个数据源(如:集合、数组),获取一个流
2、中间操作
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理
3、终止操作(终端操作)
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果
三、创建stream
四种方法:
//创建Stream方式一:通过集合 Stream<Employee> listStream = emps.stream(); //创建Stream方式二:通过数组 int[] intArr = new int[] {1,2,3,4,7}; IntStream arrayStream = Arrays.stream(intArr); //创建Stream方式三:通过Stream.of Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 5, 9, 10); //创建Stream方式四:创建无限流: Stream.iterate或Stream.generate Stream.iterate(1, i -> i + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
四、Stream的中间操作
多个中间操作可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理!而在终止操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”
1、筛选与切片:
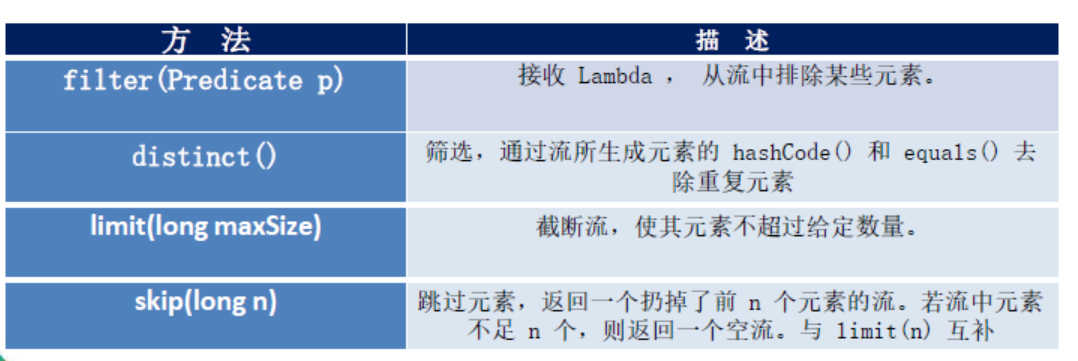
举例:filter
private static List<Employee> emps = Arrays.asList( new Employee(101, "张三", 18, 9999.99), new Employee(102, "李四", 59, 6666.66), new Employee(103, "王五", 28, 3333.33), new Employee(104, "赵六", 8, 7777.77), new Employee(104, "赵六", 8, 7777.77), new Employee(104, "赵六", 8, 7777.77), new Employee(105, "田七", 38, 5555.55) ); Stream<Employee> listStream = emps.stream(); //filter:过滤元素 listStream.filter(employee -> employee.getSalary() > 8000).forEach(System.out::println);
返回:Employee [id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=null]
distinct
//distinct 根据equals和hashcode去重 listStream.distinct().forEach(System.out::println); 返回: Employee [id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=null] Employee [id=102, name=李四, age=59, salary=6666.66, status=null] Employee [id=103, name=王五, age=28, salary=3333.33, status=null] Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=105, name=田七, age=38, salary=5555.55, status=null]
limit
listStream.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println); 返回: Employee [id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=null] Employee [id=102, name=李四, age=59, salary=6666.66, status=null] Employee [id=103, name=王五, age=28, salary=3333.33, status=null]
skip
listStream.skip(3).forEach(System.out::println); 返回: Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=105, name=田七, age=38, salary=5555.55, status=null]
2、映射
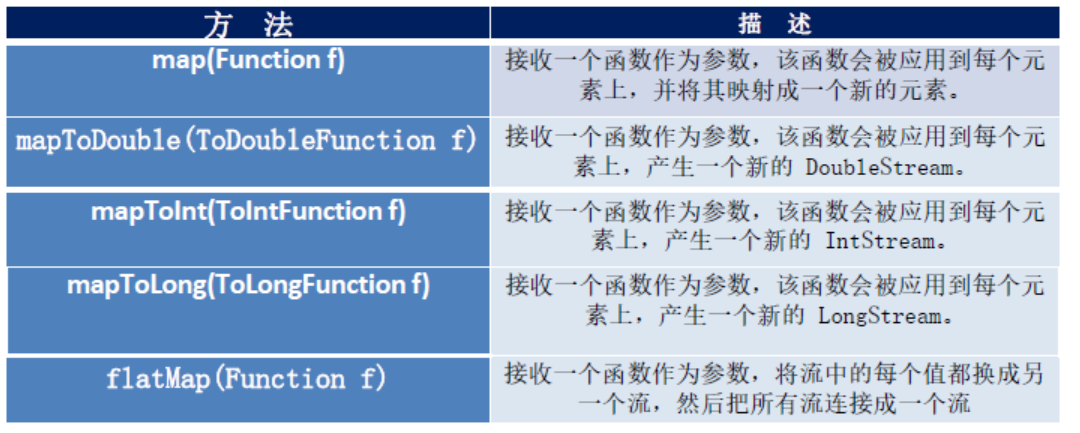
map
//获取员工姓名年龄大于30的姓名 listStream.filter(employee -> employee.getAge() > 30).map(Employee::getName).forEach(System.out::println);
返回:
李四
田七
flatmap (接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流)
String[] strArr = new String[]{"aa","bb","cc","dd"};
Arrays.stream(strArr).flatMap(TestStream1::stringToStream).forEach(System.out::print); 返回: a a b b c c d d
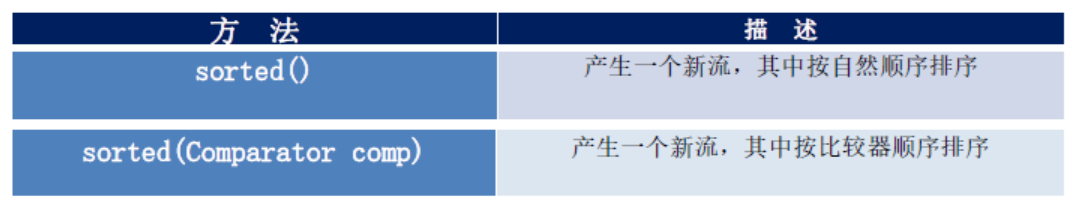
3、排序
listStream.sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge())).forEach(System.out::println); 返回: Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=104, name=赵六, age=8, salary=7777.77, status=null] Employee [id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=null] Employee [id=103, name=王五, age=28, salary=3333.33, status=null] Employee [id=105, name=田七, age=38, salary=5555.55, status=null] Employee [id=102, name=李四, age=59, salary=6666.66, status=null]
五、Stream的终止操作
终端操作会从流的流水线生成结果。其结果可以是任何不是流的值,例如:List 、IntegerInteger Integer Integer,甚至是void
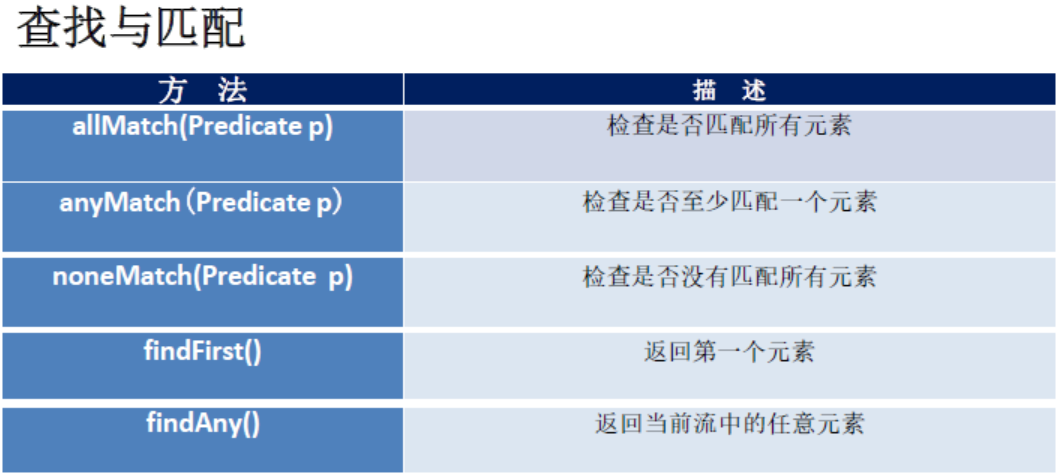
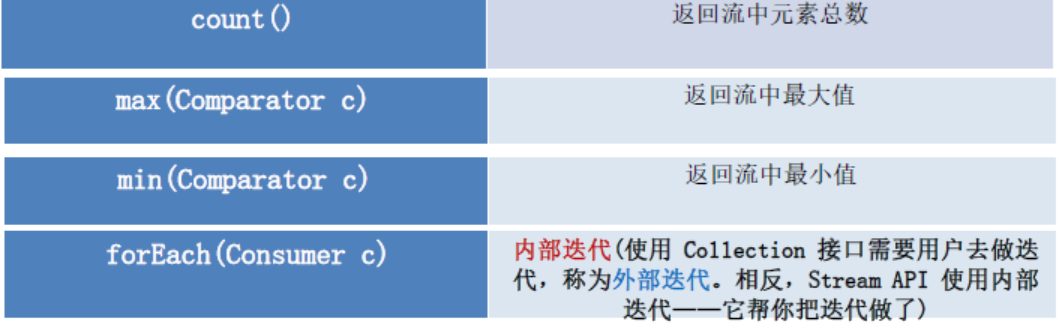
//是否所有员工年龄都大于5 boolean r = listStream.allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 5); //返回:true //是否存在员工年龄大于60 boolean r = listStream.anyMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 60); //返回false //是否没有员工年龄大于60 boolean r = listStream.noneMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 60); //返回true //返回第一个元素 Optional<Employee> first = listStream.findFirst(); //返回: Employee [id=101, name=张三, age=18, salary=9999.99, status=null] //员工总数 long count = listStream.count(); //返回:7 //年龄最大的员工 Optional<Employee> max = listStream.max((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge())); //返回:Employee [id=102, name=李四, age=59, salary=6666.66, status=null]

//计算年龄总和 Optional<Integer> reduce = listStream.map(Employee::getAge).reduce((s1, s2) -> s1 + s2);//或使用方法引用Integer::sum System.out.println(reduce.get());
//返回结果 167
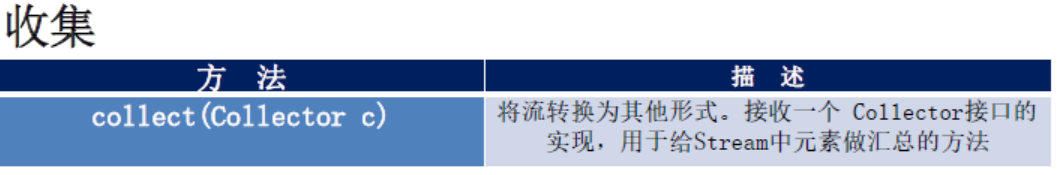

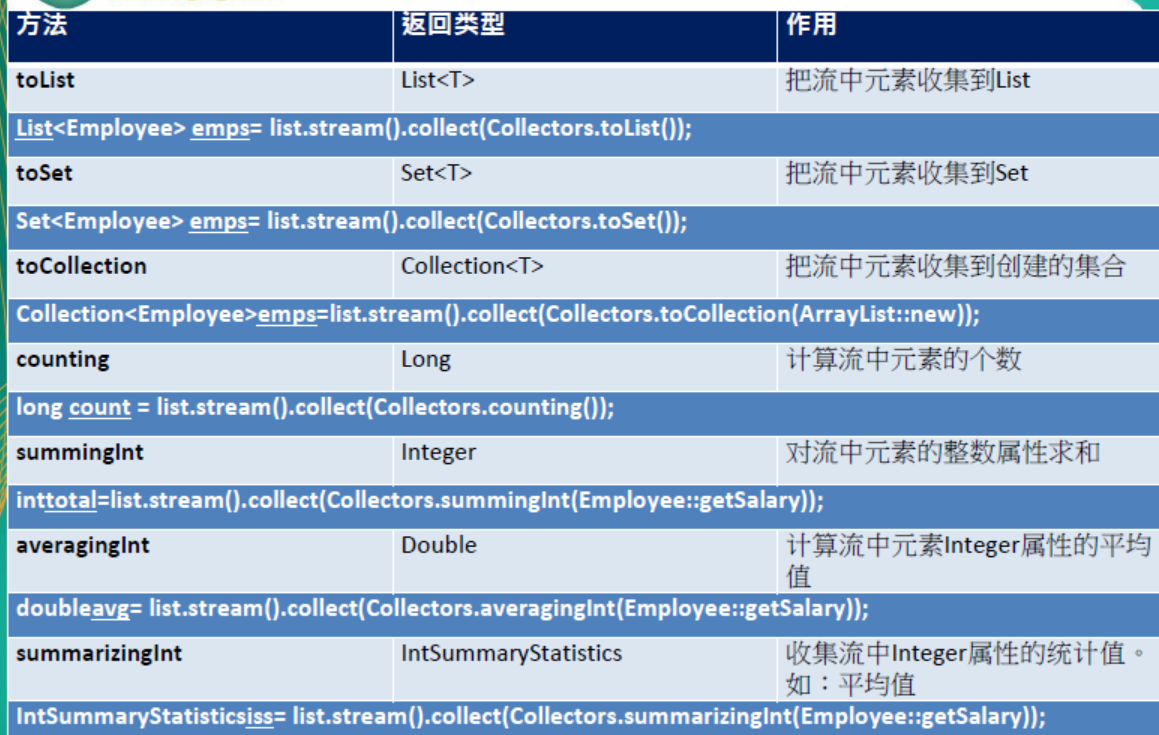

List<Integer> collect = listStream.map(Employee::getAge).collect(Collectors.toList()); //将员工所有年龄字段转成int集合
Map<Integer, List<Employee>> map = listStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getAge)); //将员工按年龄进行分组
IntSummaryStatistics statistics = listStream.collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Employee::getAge)); //统计所有年龄
System.out.println(statistics.getAverage()); //根据统计结果计算平均值


