day_17~19:IO流
IO流
File类
代表文件或目录路径(文件夹)的抽象表示
File只关注文本本身信息,不能操作文本里的内容(要想操作就要IO流的技术)
绝对路径:指定盘符
相对路径:相对于当前项目的路径
主要方法

public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建出文件的对象 File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\test.txt"); System.out.println("获取文件绝对路径:" + file.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("获取文件名:" + file.getName()); System.out.println("文件内容是否可读:" + file.canRead()); System.out.println("文件内容是否可写:" + file.canWrite()); System.out.println("文件内容是否隐藏:" + file.isHidden()); System.out.println("获取文件长度(字节):" + file.length()); SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); String format = sdf.format(file.lastModified()); System.out.println("获取文件最后修改时间:" + format); System.out.println("判断此文件或文件夹是否存在:" + file.exists()); System.out.println("获取父路径的字符串表示:" + file.getParent()); System.out.println("获取父路径的文件对象表示:" + file.getParentFile()); System.out.println("判断该对象是否是文件:" + file.isFile()); System.out.println("判断该对象是否是文件夹:" + file.isDirectory()); } }
绝对路径、相对路径

public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //绝对路径:指定盘符 // File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\hhy.txt"); // System.out.println("获取路径:" + file.getPath()); // System.out.println("获取绝对路径:" + file.getAbsolutePath()); //相对路径:相对于当前项目的路径 File file = new File("hhy.txt"); System.out.println("获取路径:" + file.getPath()); System.out.println("获取绝对路径:" + file.getAbsolutePath()); } }
应用

public class Test03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /** * 需求2:通过程序,判断指定路径的文件是否存在,如果不存在,则创建该文件 下面按各种情况来解决该问题 */ } private static void method03() throws IOException { //3)有多个层级的目录不存在的情况 File file = new File("file1\\file2\\file3\\test.txt"); //创建文件夹 File parentFile = file.getParentFile();//获取到父路径的文件对象 if(!parentFile.exists()){//不存在 parentFile.mkdirs();//创建多层目录 } //创建文件 if(!file.exists()){//不存在 file.createNewFile();//创建文件 } } private static void method02() throws IOException { //2)有一个层级的目录不存在的情况 File file = new File("file\\test.txt"); //创建文件夹 File parentFile = file.getParentFile();//获取到父路径的文件对象 if(!parentFile.exists()){//不存在 parentFile.mkdir();//创建一层目录 } //创建文件 if(!file.exists()){//不存在 file.createNewFile();//创建文件 } } private static void method01() throws IOException { //1)目录已存在的情况 File file = new File("file\\test.txt"); if(!file.exists()){//文件不存在 file.createNewFile();//创建文件 } } } public class Test04 { @Test public void method01(){ /** * 需求3:输出指定目录下的所有文件信息(只考虑当前目录,不考虑子目录) */ File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\资源"); String[] list = file.list();//把当前目录下的所有文件的名字放入list数组中 for (String fileName : list) { System.out.println(fileName); } } @Test public void method02(){ /** * 需求3:输出指定目录下的所有文件信息(只考虑当前目录,不考虑子目录) */ File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\资源"); File[] listFiles = file.listFiles();//把当前目录下的所有文件对象放入listFiles数组中 for (File f : listFiles) { System.out.println(f.getName() + " : " + f.getAbsolutePath()); } } @Test public void method03(){ /** * 需求3:输出指定目录下的所有文件信息(只考虑当前目录,不考虑子目录) * 1)要求只输出文件后缀名为txt的文件 */ File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\资源"); File[] listFiles = file.listFiles();//把当前目录下的所有文件对象放入listFiles数组中 for (File f : listFiles) { if(f.getName().endsWith(".txt")){ System.out.println(f.getName() + " : " + f.getAbsolutePath()); } } } @Test public void method04(){ /** * 需求3:输出指定目录下的所有文件信息(只考虑当前目录,不考虑子目录) * 1)要求只输出文件后缀名为txt的文件 * 2)根据API的过滤器来完成该功能 */ File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\资源"); String[] list = file.list(new FilenameFilter() { @Override public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {//依次遍历文件夹中所有的文件,true-加载到list数组中,false-不加载 if(name.endsWith(".txt")){ return true; }else{ return false; } } }); for (String fileName : list) { System.out.println(fileName); } } @Test public void method05(){ /** * 需求3:输出指定目录下的所有文件信息(只考虑当前目录,不考虑子目录) * 1)要求只输出文件后缀名为txt的文件 * 2)根据API的过滤器来完成该功能 * 3)需求继续跟进,列出当前目录及子目录中符合该条件的文件信息(递归) */ File file = new File("C:\\Users\\hehanyu\\Desktop\\资源"); getFile(file,".jpg"); } public static void getFile(File file,String str){ File[] listFiles = file.listFiles(); for (File f : listFiles) { if(f.isDirectory()){//文件夹 getFile(f, str); }else if(f.isFile()){//文件 if(f.getName().endsWith(str)){ System.out.println(f.getName() + " : " + f.getAbsolutePath()); } } } } }
IO流
IO:两个方向(输出流-out-写 输入流-in-读)
分流:
按方向分流:输出流、输入流
按单位分流:字节流、字符流
按功能分流:基础流\节点流、处理流(在基础流的基础上包装了,使得流的功能变强大了)
学习路线:按照IO流的发展历史
ps:注意流与流之间的继承关系
字节流(二进制信息)
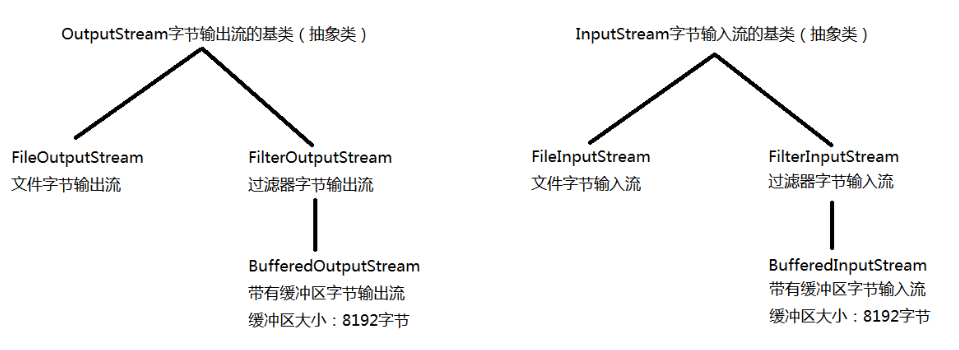
OutputStream -- 字节输出流的基类(抽象类)
InputStream -- 字节输入流的基类(抽象类)
FileOutputStream extends OutputStream -- 文件字节输出流
FileInputStream extends InputStream -- 文件字节输入流
FilterOutputStream extends OutputStream -- 过滤器字节输出流
FilterInputStream extends InputStream -- 过滤器字节输入流
BufferedOutputStream extends FilterOutputStream -- 带有缓冲区的字节输出流
BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream -- 带有缓冲区的字节输入流
ps:缓冲区大小为8192字节(8*1024)
FilterOutputStream和FileInputStream实现copy

public class Copy01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //读取源文件,并写入目标文件 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt"); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.txt"); //读取一个字节的数据,写入一个字节的数据 int read; while((read=fis.read()) != -1){ fos.write(read); } fis.close(); fos.close(); } } public class Copy02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //读取源文件,并写入目标文件 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("上原亚衣.avi"); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.avi"); //读取1024个字节的数据,写入1024个字节的数据 byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = fis.read(b)) != -1){ fos.write(b, 0, len); } fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
BufferedOutputStream 和BufferedInputStream 实现copy

public class Copy { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("上原亚衣.avi")); BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy.avi")); byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = bis.read(b)) != -1){ bos.write(b, 0, len); } bis.close(); bos.close(); } }
字符流(文本信息)
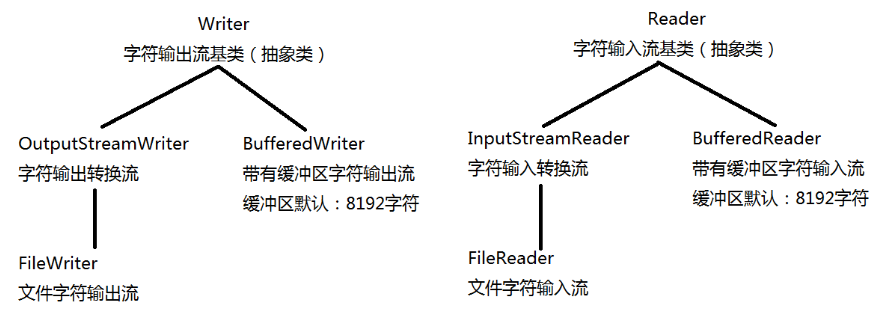
Writer -- 字符输出流的基类(抽象类)
Reader -- 字符输入流的基类(抽象类)
OutputStreamWriter extends Writer -- 字符输出转换流
InputStreamReader extends Reader -- 字符输入转换流
ps:将字节流转换为字符流
应用场景:Java很多类给我们提供的流对象都是字节流,如果需求要操作文本信息,
可以将字节流对象转换为字符流对象,所以要用到转换流
FileWriter extends OutputStreamWriter -- 文件字符输出流
FileReader extends InputStreamReader -- 文件字符输入流
BufferedWriter extends Writer -- 带有缓冲区的字符输出流
BufferedReader extends Reader -- 带有缓冲区的字符输入流
ps:缓冲区大小为8192字符(8*1024)
InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter实现copy

public class Copy { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("С˵.txt"), "GBK"); OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("copy.txt"), "GBK"); char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; int len; while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ osw.write(cbuf, 0, len); } isr.close(); osw.close(); } }
FileReader和FileWriter实现copy

public class Copy { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ FileReader fr = new FileReader("С˵.txt"); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("copy.txt"); char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; int len; while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){ fw.write(cbuf, 0, len); } fr.close(); fw.close(); } }
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现copy ---- 其中copy的方式有两种

public class Copy { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("小说.txt")); BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("copy.txt")); copy02(br, bw); br.close(); bw.close(); } private static void copy02(BufferedReader br, BufferedWriter bw) throws IOException { String str; while((str = br.readLine()) != null){//读取一行数据 bw.write(str); bw.newLine();//新的一行(换行) } } private static void copy01(BufferedReader br, BufferedWriter bw) throws IOException { char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; int len; while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){ bw.write(cbuf, 0, len); } } }
注意:
1.输出流文件不存在时,会自动创建文件对象
2.输入流文件不存在时,会报错
3.read():逐个读取字节,并返回字节数,读取到文件末尾返回-1
read(byte数据):读取数组长度的数据,并返回读取的到有效字节数的长度,读取到末尾返回-1
各种流
对象流:
ObjectOutputStream -- 对象输出流
ObjectInputStream -- 对象输入流
序列化:程序(对象) --> 文件
反序列化:文件(对象) --> 程序
ps:
1.对象所属的类必须实现Serializable(序列化接口)
2.Serializable序列化接口没有实现任何方法,这种接口叫做标记型接口
3.对象中的属性不想被写入文件,就用transient修饰属性
利用ObjectOutputStream向文件写入对象

public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ /** * 利用ObjectOutputStream向文件写入对象 */ ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt")); oos.writeInt(3); oos.writeObject(new String("木头人")); oos.writeObject(new String("木头人")); oos.writeObject(new String("木头人")); oos.close(); } private static void method01(ObjectOutputStream oos) throws IOException { oos.writeObject(new String("木头人")); oos.writeObject(new String("木头人")); oos.writeObject(new String("木头人")); oos.writeObject(null); } }
利用ObjectInputStream读取文件中的对象

public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ /** * 利用ObjectInputStream读取文件中的对象 */ ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt")); //取出顺序必须和存入顺序一致 int num = ois.readInt(); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { Object readObject = ois.readObject(); System.out.println(readObject); } ois.close(); } //给Test01类里的method01方法对应 private static void method01(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { Object obj; while((obj = ois.readObject()) != null){ System.out.println(obj); } } }
自定义对象

public class User implements Serializable{ //生成固定的版本号 private static final long serialVersionUID = 5219224685895297646L; //序列化操作的时候系统会把当前类的serialVersionUID写入到序列化文件中, //当反序列化时系统会去检测文件中的serialVersionUID, //判断它是否与当前类的serialVersionUID一致, //如果一致就说明序列化类的版本与当前类版本是一样的,可以反序列化成功,否则失败。 private String username; private transient String password;//不会被存入的文件中 private static String info;//此属性就不在对象中,自然就不会被存入到文件中 private char sex; private int age; public User() { } public User(String username, String password, String info) { this.username = username; this.password = password; this.info = info; } public User(String username, String password, String info, char sex) { this.username = username; this.password = password; this.info = info; this.sex = sex; } public User(String username, String password, String info, char sex, int age) { super(); this.username = username; this.password = password; this.info = info; this.sex = sex; this.age = age; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String getInfo() { return info; } public void setInfo(String info) { this.info = info; } public char getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(char sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", info=" + info + ", sex=" + sex + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }
利用ObjectOutputStream向文件写入自定义类的对象

public class Test03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ /** * 利用ObjectOutputStream向文件写入自定义类的对象 */ ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt")); oos.writeObject(new User("hhy", "123123", "我是最帅的...", '男', 18)); oos.close(); } }
利用ObjectInputStream读取文件内容

public class Test04 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ /** * 利用ObjectInputStream读取文件内容 */ ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.txt")); User user = (User) ois.readObject(); System.out.println(user); ois.close(); } }
打印流:(方向:程序 --> 文件)
PrintStream:将字节流转换为打印流
PrintWriter:将字节流、字符流转换为打印流
应用:

public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("test.txt"); PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true)); ps.println("木头人..."); ps.close(); } } public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("test.txt"); // PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("test.txt",true)); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("test.txt", true)); pw.println("木头人..."); pw.close(); } }
重定向:重新定义系统标准的输出输入流的方向
系统标准的输入流-System.in:控制台->程序
//重新定义系统标准的输入流:文件->程序
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
系统标准的输出流-System.out:程序->控制台
//重新定义系统标准的输出流方向:程序->文件
System.setOut(new PrintStream("test.txt"));
重新定义系统标准的输入流:程序 --> 文件

public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ /** * 系统标准的输入流:控制台->程序 * InputStream in = System.in; */ //重新定义系统标准的输入流 System.setIn(new FileInputStream("test.txt")); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String next = scan.next(); System.out.println(next); next = scan.next(); System.out.println(next); scan.close(); } }
重新定义系统标准的输出流方向:程序->文件

public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //重新定义系统标准的输出流方向:程序->文件 System.setOut(new PrintStream("test.txt")); System.out.println("xxxxx"); } }
重新定义系统标准的输出流的应用

public class Test03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ System.setOut(new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("log.txt", true))); method01(); method02(); method03(); method04(); method05(); } public static void method01(){ System.out.println(getDate()); System.out.println("扫描二维码"); } public static void method02(){ System.out.println(getDate()); System.out.println("确认金额"); } public static void method03(){ System.out.println(getDate()); System.out.println("输入密码"); } public static void method04(){ System.out.println(getDate()); System.out.println("密码验证成功"); } public static void method05(){ System.out.println(getDate()); System.out.println("支付成功"); } public static String getDate(){ SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); return sdf.format(new Date()); } }
随机访问流:
RandomAccessFile:此类的实例支持对随机访问文件的读取和写入。随机访问文件的行为类似存储在文件系统中的一个大型 byte 数组。存在指向该隐含数组的光标和索引,称为文件指针;输入操作从文件指针开始读取字节,并随着对字节的读取而前移此文件指针。如果随机访问文件以读取/写入模式创建,则输出操作也可用;输出操作从文件指针开始,并随着对字节的写入而前移此文件指针。写入隐函数组的当前末尾之后的输出操作导致该数组扩展。该文件指针可以通过getFilePointer 方法获取,并通过seek 方法设置。
1.认为文件中的数据为大型的byte数组,有隐含的文件指针
2.读取或写入从文件指针出开始,文件指针默认从0开始
3.r-读的模式 rw-读写的模式
4.断点续传
应用:

public class Test01 { // 写入数据 @Test public void method1() throws Exception { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("test.txt", "rw"); raf.write("123abc木头人".getBytes()); ; raf.close(); } // 读取数据 @Test public void method2() throws Exception { RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("test.txt", "r"); byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len; while ((len = raf.read(b)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len)); } raf.close(); } // 指定位置读取 @Test public void method3() throws Exception { RandomAccessFile rdf = new RandomAccessFile("test.txt", "r"); rdf.seek(3); byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len; while ((len = rdf.read(b)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(b, 0, len)); } rdf.close(); } // 文件末尾追加 @Test public void method4() throws Exception { File file = new File("test.txt"); RandomAccessFile rdf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw"); rdf.seek(file.length()); rdf.write("1314赤名莉香mmd".getBytes()); rdf.close(); } }

//用随机访问流copy文件实现断点续传的功能 public class Test02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { RandomAccessFile r = new RandomAccessFile("上原亚衣.avi", "r"); RandomAccessFile w = new RandomAccessFile("copy.avi", "rw"); long pointer = w.length(); r.seek(pointer); w.seek(pointer); byte[] bys = new byte[102]; int len; while((len = r.read(bys)) != -1) { w.write(bys, 0, len); } r.close(); w.close(); } }
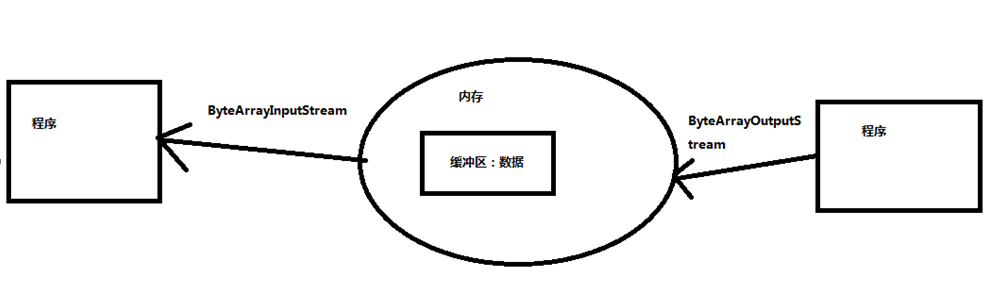
内存流:
ByteArrayOutputStream
ByteArrayInputStream
应用场景:频繁使用过的数据如果存在文件中,效率不高,因为内存频繁和硬盘交互,效率很低,所以我们可以把一些不重要但又要频繁使用的数据放在内存中。
ps:1.之前的流都是程序<->文件,但是内存流是此程序<->内存
2.内存流不用关闭,你关也关不了

public class Test01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { method3(); } //使用读写操作 private static void method3() throws IOException { ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("天空没有翅膀的痕迹,而我已经飞过。".getBytes()); ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) { bos.write(bys, 0, len); } // String string = bos.toString(); // System.out.println(string); byte[] array = bos.toByteArray(); System.out.println(new String(array)); } //写入数据 private static void method2() throws IOException { ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); bos.write("123木头人".getBytes()); byte[] array = bos.toByteArray(); System.out.println(new String(array)); // System.out.println(bos.toString()); } //读取数据 private static void method1() throws IOException { // 创建内存输入流,并输入内容 ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream("赤名莉香mmd1314".getBytes()); // 读取数据 byte[] bys = new byte[1024]; int len; while ((len = bis.read(bys)) != -1) { System.out.println(new String(bys, 0, len)); } } }
NIO - BewIo
由以下几个核心部分组成:
Buffers -- 缓冲区:针对系统的缓冲区
Channels -- 通道:类型于BIO里面的流 主要是FileChannel:文件通道
Selectors -- 选择器
Channels 和Buffer
基本上,所有的IO在NIO中都从一个Channel开始。Channel有点像流,数据可以从Channel读到Buffer中,也可以从Buffer写入到Channel中。
通过BIO的流(fos)获取到NIO里的通道:FileChannel channel = fos.getChannel();
创建缓冲区:ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
获得指针:allocate.position()
获得限制:allocate.limit()
获得容量:allocate.capacity()
写入数据:put(byte) or put(byte[])
反转:flip() -------- 指针归零,限制指针到原指针位置,容量不变
remaining()获取到指针与限制之间的元素数量
Ps:反转此缓冲区:将指针初始化,限制为数据的长度

public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); System.out.println("指针:" + buffer.position());//0 System.out.println("限制:" + buffer.limit());//10 System.out.println("容量:" + buffer.capacity());//10 System.out.println("-----------------"); //写入数据 buffer.put("abc".getBytes()); System.out.println("指针:" + buffer.position());//0 System.out.println("限制:" + buffer.limit());//10 System.out.println("容量:" + buffer.capacity());//10 System.out.println("-----------------"); //翻转指针:指针归零,限制到原来的位置,容量不变 buffer.flip(); System.out.println("指针:" + buffer.position());//0 System.out.println("限制:" + buffer.limit());//3 System.out.println("容量:" + buffer.capacity());//10 System.out.println("-----------------"); System.out.println("获取指针到限制之间的数据个数:" + buffer.remaining());//3 for(int i=0;i<buffer.remaining();i++) { byte b = buffer.get(i); System.out.println((char)b); } } }

//一次性拷贝 public class copy01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 获取BIO对象 File file = new File("上原亚衣.avi"); long length = file.length(); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("东京爱情故事.avi"); // 获取Channel通道 FileChannel rChannel = fis.getChannel(); FileChannel wChannel = fos.getChannel(); // 创建Buffer缓冲区 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) length); // 拷贝 rChannel.read(buffer); buffer.flip(); wChannel.write(buffer); // 关流 fis.close(); fos.close(); } }

//1024个字节拷贝 public class copy02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("上原亚衣.avi"); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("东京爱情故事.avi"); FileChannel rChannel = fis.getChannel(); FileChannel wChannel = fos.getChannel(); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); while (rChannel.read(buffer) != -1) { buffer.flip(); wChannel.write(buffer); buffer.clear(); } fos.close(); fis.close(); } }

//Map映射拷贝 public class Copy03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建BIO对象 File file = new File("东京爱情故事.avi"); long length = file.length(); RandomAccessFile r = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r"); RandomAccessFile w = new RandomAccessFile("赤名莉香.avi", "rw"); // 获取通道 FileChannel rChannel = r.getChannel(); FileChannel wChannel = w.getChannel(); // 创建缓冲区 MappedByteBuffer rMap = rChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, length); MappedByteBuffer wMap = wChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, length); // 拷贝 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { byte b = rMap.get(i); rMap.put(b); } // 关流 r.close(); w.close(); } }
BIO VS NIO
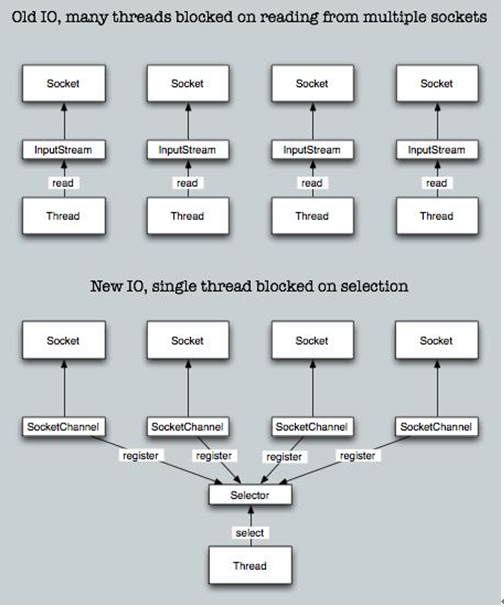
BIO:面向流 阻塞IO 无
NIO:面向缓存 非阻塞IO 选择器
了解
BIO是一个连接一个线程
NIO是一个请求一个线程
AIO是一个有效请求一个线程



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号