【JAVA 进阶】Spring Boot 自动部署原理与自定义 Starter 实战

文章目录
0. 导读与目标
0.1 背景与主题
0.1.1 为什么选“自动配置”
自动配置是 Spring Boot 的核心竞争力之一。它通过条件化装配在启动阶段自动注册合适的 Bean,使应用在“约定优于配置”的前提下保持可自定义与可扩展。理解自动配置原理、条件化注入与属性绑定,是写好生产级应用与构建高质量 Starter 的关键。
0.1.2 本文目标
- 搭建清晰的自动配置知识框架。
- 掌握条件化注入的常用技巧与组合方式。
- 结合
@ConfigurationProperties完成类型安全的外部化配置。 - 动手实现一个可用的自定义 Starter,并学会调试与优化。
0.2 阅读预备与受众
0.2.1 预备知识
- 熟悉 Spring 容器与 Bean 的基本概念。
- 能读懂简单的 Java、Maven、YAML。
- 知道
@SpringBootApplication的作用。
0.2.2 适用读者
- 想从“会用”升级到“会扩展”的开发者。
- 需要为团队封装通用能力的架构与平台工程师。
1. 自动配置总览
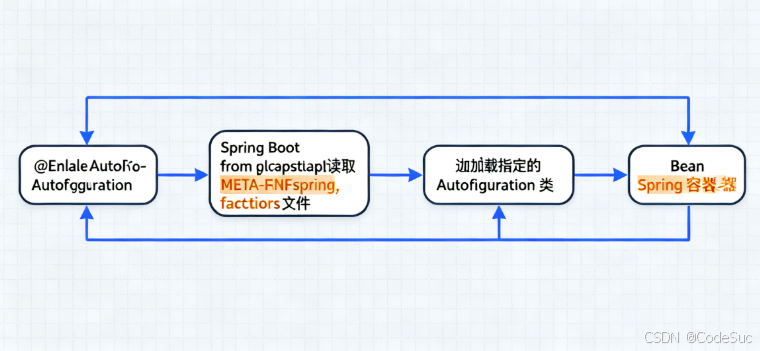
1.1 自动配置的设计哲学
1.1.1 与传统 Spring 的对比
传统 Spring 以显式 XML 或注解配置为主,开发者要为每个子系统逐一声明 Bean。Spring Boot 则通过扫描与条件化匹配在启动时自动导入“合理默认”的 Bean 集合,并保留用户覆盖入口,显著降低样板代码与配置复杂度。
1.1.2 三个关键点
- 入口:
@SpringBootApplication组合了@EnableAutoConfiguration。 - 载体:一组
AutoConfiguration类是可被导入的配置集合。 - 规则:条件注解族决定是否装配某个 Bean。
1.2 重要组件速览
1.2.1 @SpringBootApplication 与 @EnableAutoConfiguration
@SpringBootApplication 等价于 @Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 的组合。@EnableAutoConfiguration 负责发现并导入所有候选自动配置类。
1.2.2 AutoConfiguration 类
每个自动配置类都是一个普通的 @Configuration 类,内部基于条件注解注册 Bean,并常结合 @EnableConfigurationProperties 完成属性绑定。
1.2.3 条件注解族
常见注解包括 @ConditionalOnClass、@ConditionalOnMissingBean、@ConditionalOnProperty、@ConditionalOnBean、@ConditionalOnWebApplication 等,其组合决定了某个配置是否生效。
2. 自动配置加载流程
2.1 从应用启动看入口
2.1.1 SpringApplication.run
应用启动后,SpringApplication 初始化上下文并触发自动配置导入流程,随后进行条件评估与 Bean 注册。
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApp.class, args);
}
}2.2 自动配置发现与导入
2.2.1 Spring Boot 3 机制:AutoConfiguration.imports
在 Spring Boot 3 中,自动配置候选通过 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 列表声明。框架读取该文件,批量导入对应的配置类。
# META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
com.example.starter.DemoFeatureAutoConfiguration2.2.2 Spring Boot 2.x 机制:spring.factories
在 2.x 版本,自动配置候选通过 META-INF/spring.factories 的 EnableAutoConfiguration 键声明。
# META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.example.starter.DemoFeatureAutoConfiguration2.3 条件评估与 Bean 注册
框架在导入每个自动配置类时,会对其上的条件注解逐一评估,满足条件才继续注册相关 Bean。评估顺序、默认值与缺省匹配是理解装配结果的关键。
3. 条件化注入精讲
3.1 常见条件注解与语义
3.1.1 @ConditionalOnClass
当某个类存在于类路径时生效,常用来在可选依赖出现时启用对应功能。
@AutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnClass(name = "com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource")
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration { }3.1.2 @ConditionalOnMissingBean
当容器中不存在某种类型或名称的 Bean 时才注册默认 Bean,支持用户覆盖默认行为。
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyService();
}3.1.3 @ConditionalOnProperty
基于外部化配置的值决定启用与否,支持默认开启和显式关闭。
@AutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "demo.feature", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class DemoFeatureAutoConfiguration { }3.2 组合条件与顺序控制
3.2.1 顺序控制
借助 @AutoConfiguration(before = ...) 与 @AutoConfiguration(after = ...) 可以调整不同自动配置之间的先后关系,确保依赖的 Bean 已准备就绪。
@AutoConfiguration(before = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class MetricsAutoConfiguration { }3.2.2 自定义条件
当内置注解无法满足复杂场景时,可通过 @Conditional 搭配自定义 Condition 扩展匹配规则。
public class OnProdProfileCondition implements Condition {
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
String[] profiles = context.getEnvironment().getActiveProfiles();
for (String p : profiles) {
if ("prod".equalsIgnoreCase(p)) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
@AutoConfiguration
@Conditional(OnProdProfileCondition.class)
public class ProdOnlyAutoConfiguration { }4. 外部化配置与 @ConfigurationProperties
4.1 类型安全属性绑定
@ConfigurationProperties 用于将层级化配置绑定到强类型对象,提升可读性与可维护性,同时与自动配置无缝配合。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "demo.feature")
public class DemoFeatureProperties {
private boolean enabled = true;
private String endpoint = "/demo";
public boolean isEnabled() { return enabled; }
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) { this.enabled = enabled; }
public String getEndpoint() { return endpoint; }
public void setEndpoint(String endpoint) { this.endpoint = endpoint; }
}4.2 属性验证与默认值
配合 JSR-303 注解可做约束校验;合理设置默认值能让功能“开箱即用”。绑定后的对象可被自动配置类注入使用。
demo:
feature:
enabled: true
endpoint: /demo4.3 与自动配置联动
自动配置类通常通过 @EnableConfigurationProperties 使属性类生效,并根据属性值决定是否注册 Bean。
@AutoConfiguration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DemoFeatureProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "demo.feature", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class DemoFeatureAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DemoService demoService(DemoFeatureProperties props) {
return new DemoService(props.getEndpoint());
}
}5. 实战:构建一个自定义 Starter
5.1 需求与设计
5.1.1 目标功能
实现一个提供简单 HTTP 端点处理的 DemoService,支持通过属性开关启停,并允许用户覆盖默认 Bean。
5.2 模块与依赖
5.2.1 Maven 依赖
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>5.3 编码实现
5.3.1 业务服务
public class DemoService {
private final String endpoint;
public DemoService(String endpoint) { this.endpoint = endpoint; }
public String handle(String name) { return "Hello, " + name + " via " + endpoint; }
}5.3.2 属性类与自动配置
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "demo.feature")
public class DemoFeatureProperties {
private boolean enabled = true;
private String endpoint = "/demo";
public boolean isEnabled() { return enabled; }
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) { this.enabled = enabled; }
public String getEndpoint() { return endpoint; }
public void setEndpoint(String endpoint) { this.endpoint = endpoint; }
}@AutoConfiguration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DemoFeatureProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "demo.feature", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class DemoFeatureAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public DemoService demoService(DemoFeatureProperties props) {
return new DemoService(props.getEndpoint());
}
}5.3.3 注册导入文件
Spring Boot 3 的导入文件:
# META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports
com.example.starter.DemoFeatureAutoConfigurationSpring Boot 2.x 的工厂文件:
# META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.example.starter.DemoFeatureAutoConfiguration5.4 应用接入与覆盖
5.4.1 在应用中使用
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoConsumerApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoConsumerApp.class, args);
}
}demo:
feature:
enabled: true
endpoint: /api/demo@RestController
public class DemoController {
private final DemoService demoService;
public DemoController(DemoService demoService) { this.demoService = demoService; }
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam String name) {
return demoService.handle(name);
}
}5.4.2 覆盖默认 Bean
@Configuration
public class CustomConfig {
@Bean
public DemoService demoService() {
return new DemoService("/custom");
}
}6. 调试、可观察性与性能
6.1 自动配置条件报告
6.1.1 查看匹配详情
开启条件报告便于定位某个自动配置为何未生效。
debug=true在日志中可看到各自动配置的条件匹配结果,包括满足与未满足的原因。
6.2 Actuator 端点辅助诊断
6.2.1 常用端点
env 显示环境与属性来源,configprops 展示 @ConfigurationProperties 绑定结果,conditions 汇总条件评估。
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=env,configprops,conditions6.3 启动性能优化建议
- 合理拆分自动配置模块,避免不必要的类加载。
- 使用精确的条件注解,减少无效匹配与 Bean 创建。
- 避免在自动配置阶段做耗时初始化,延迟到使用时。
7. 常见问题与最佳实践
7.1 Bean 重复与覆盖
- 默认使用
@ConditionalOnMissingBean防止重复定义。 - 当必须覆盖时,用户侧显式声明 Bean 即可生效。
7.2 属性绑定失败排查
- 检查前缀与层级是否正确。
- 类型与格式需与属性类字段匹配。
- 使用
configprops端点验证绑定结果。
7.3 Starter 发布建议
- 独立维护版本并适配目标 Boot 版本。
- 提供清晰的使用说明与属性文档。
- 保持默认安全与最小侵入原则。
8. 总结与扩展
8.1 知识点回顾与扩展
本文围绕“自动配置原理与自定义 Starter 实战”展开:总览了 @EnableAutoConfiguration 的角色、自动配置发现机制与条件化注入的核心注解;讲解了类型安全的 @ConfigurationProperties;完成了从需求到编码、从注册到接入的 Starter 实战;并提供了调试、诊断与性能优化建议。扩展方向包括:更复杂的条件组合、利用 AOT 与原生镜像优化启动、在平台层统一治理 Starter。
8.2 更多阅读资料
8.3 新问题与其它方案
- 如何在多模块项目中组织与治理自动配置的边界与依赖?
- 在高并发场景下,哪些自动配置应延迟初始化以降低启动成本?
- 是否需要在团队内制定 Starter 设计规范与质量门禁?
8.4 号召行动
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,欢迎收藏与点赞,并分享给同事与朋友。也欢迎在评论区提出你的思考与问题,我们一起深入讨论、共同进步。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号