图的存储方式
-
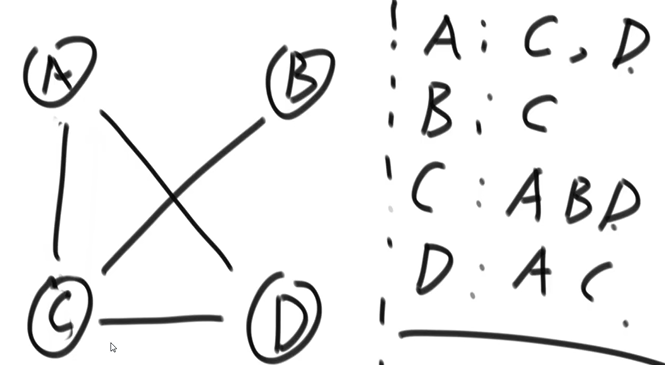
邻接表
![]()
-
邻接矩阵
正方形矩阵
A B C D
A 0 - 7 3
B - 0 2 -
C 7 2 0 5
D 3 - 5 0
表达图。。。 生成图
有向图 无向图 权值
点 + 边
点如下
public class Node {
// 点集
public int value; // 编号,值
public int in; // 入度 ,有多少个进入这个点, 无向图,入度和出度一样。
public int out; // 出度 ,
public ArrayList<Node> nexts; // 从当前点出发,发散出去的点,直接邻居。
public ArrayList<Edge> edges; // 属于我的边 有哪些。 A→B from 是 当前node.
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in = 0;
out = 0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
边如下
public class Edge {
public int weight; // 权重
public Node from; // 从哪个node 出发
public Node to; // 到哪个node
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
图结构如下
public class Graph {
public HashMap<Integer, Node> nodes;
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public Graph() {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
edges = new HashSet<>();
}
}
生成图, 其他结构类型的图,生成 自己的这个图
public static Graph generatorGraph(Integer[][] matrix) {
// matrix 二维数组,
// matrix[0][0] = from,
// matrix[0][1] = to,
// matrix[0][2] = weight
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
Integer from = matrix[i][0];
Integer to = matrix[i][1];
Integer weight = matrix[i][2];
// 判断当前点是否已经加入nodes
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(from)) {
graph.nodes.put(from, new Node(from));
}
if (!graph.nodes.containsKey(to)) {
graph.nodes.put(to, new Node(to));
}
Node fromNode = graph.nodes.get(from);
Node toNode = graph.nodes.get(to);
Edge edge = new Edge(weight, fromNode, toNode);
fromNode.out ++;
toNode.in ++;
fromNode.nexts.add(toNode);
graph.edges.add(edge);
}
return graph;
}
图的宽度优先遍历
1) 宽度,都是队列
2) 从源节点开始依次按照宽度 进 队列, 然后弹出
3) 每弹出一个点,把该节点所有没有进过队列的 邻接点 放入队列
4) 直到队列为空
和二叉树的区别,可能有环 。要注意,使用一个set保存已经进入过队列的 node
public static void graphBFS(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>(); // 保存已经进入过 queue的node
// 节点入队
queue.add(node);
set.add(node);
Node cur = null;
// 开始循环 出队
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
cur = queue.poll();
// 打印处理
System.out.println(cur.value);
// 把当前节点 的邻接点 都入队
for (Node tmpNode : cur.nexts) {
// 判断是否已经进入过队列
if (set.contains(tmpNode)) {
continue;
}
queue.add(tmpNode);
set.add(tmpNode);
}
}
}
图的深度优先遍历
1)深度,使用栈
2)从源节点开始把节点按照深度放入栈, 然后弹出,
3)每弹出一个点,把该节点 下一个 没有进过栈的邻接点 放入栈 , 只放一个。还要把当前节点也压进去。处理next节点。
如果都已经进过栈了。开始弹上一个
栈永远保存当前深度路劲
4)直到栈为空
public static void graphDFS(Node node){
if(node == null){
return;
}
HashSet<Node> set = new HashSet<>();
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(node);
set.add(node);
//先处理 第一个节点
System.out.println(node.value);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
// 开始出栈
Node cur = stack.pop();
// 遍历 当前节点的 nexts
for (Node nextNode : cur.nexts) {
if(!set.contains(nextNode)){
//如果当前下一个节点 没 入过栈 ,开始处理当前节点,
// 又因为栈要一直保存当前 深度,所以要把当前节点再压进去
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(nextNode);
// 当前nextNode 加入到 set
set.add(nextNode);
//打印处理 nextNode
System.out.println(nextNode);
// 只走一条路,所以直接break
break;
}
}
// 如果当前节点的下一个节点都 进入过栈,就开始依次弹出上面的节点。
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号