java基础语法
基本Dos命令
切换盘符 C: E:
切换目录 cd test || cd /d E:/test
清理屏幕 cls
创建文件夹 md test
创建文件 cd>a.txt
删除文件夹 rd test
删除文件 del a.txt
查看当前目录内容 dir
java基础语法
基本数据类型
标识符只能以:字母、美元符、下划线开始,之后可以是任意的字母,美元符,下划线,数字的组合
byte e = 10
int a = 5;
char b = 'a';
String str = "中国";
short c = 10;
// 二进制 0b 八进制 0 十六进制0X
//尽量不要用浮点数进行比较 float用f结尾
类型转换
强制转换 由高到低 byte b = (int)a
自动转换 由低到高
注意: 不能进行布尔转换、注意内存溢出
System.out.println((int)15.78F);
输出: 15
变量作用域

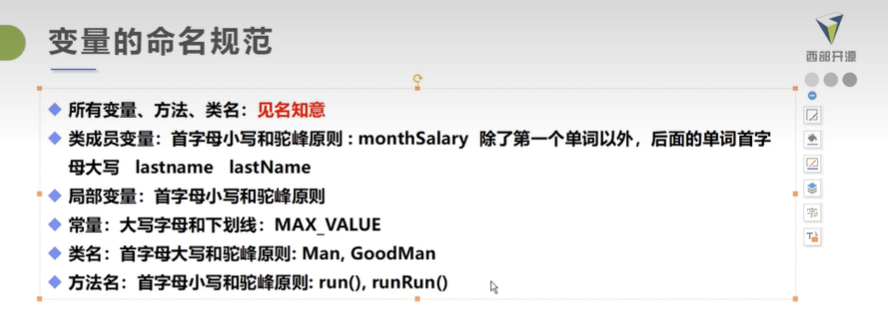
变量命名规范
字符串连接符
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10,b=20;
System.out.println(""+a+b);
System.out.println(a+b+"");
}
}
输出:
1020
30
Scanner的使用
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要输入的字符串:");
String str = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("你输入的字符是:"+str);
}
}
注意: next和nextline的区别 next是以空格为结尾的,既不能输入带空格的字符串;nextline是以回车为结尾的,可以输入带空格的字符串
方法重载
规则:方法名称相同、参数列表必须不同
可变长参数
规则:普通变量只能在可变参数之前 在指定的参数后面加 ...
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1 test1 = new test1();
test1.printMax(1,5,2,8,6,4,50);
}
public static void printMax(int ...num){
int r=num[0];
if (num.length==0){
System.out.println("什么也没输入啊");
}
for (int i =0;i<num.length;i++){
if (num[i]>r)r=num[i];
}
System.out.println(r);
}
}
函数的递归调用
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1 test1 = new test1();
int n = test1.jieCcheng(5);
System.out.println(n);
}
//阶乘
public static int jieCcheng(int n ){
if (n==1)return 1;
else return n*jieCcheng(n-1);
}
}
数组
int[] num;
num = new int[10];
//或者
int[] nums = new int[10];
二维数组
int[][] arry = {{},{},{}}
int[][] arry = new int[10][10];
数组中的常用类
int[] arry = {8,5,6,2,5,4,2,65,2};
Arrays.sort(arry); //排序
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(arry)); // 打印数组
稀疏数组
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr1 = new int[11][11];
arr1[1][2]=1;
arr1[2][3]=2;
int sum = get_sum(arr1);
System.out.println("这是原始数组");
System.out.println("========================");
print(arr1);
System.out.println("转化为稀疏数组");
System.out.println("========================");
int[][] arr2 = new int[sum+1][3];
arr2[0][0]=11;
arr2[0][1]=11;
arr2[0][2]=sum;
vlaue(arr1,arr2);
print(arr2);
System.out.println("还原");
System.out.println("========================");
int[][] arr3 = new int[11][11];
back(arr3,arr2);
print(arr3);
}
//打印数组
public static void print(int[][] arr){
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for (int j=0;j<arr[0].length;j++){
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//获取有效数据的个数
public static int get_sum(int[][] arr){
int sum=0;
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
for (int j=0;j<arr[0].length;j++){
if (arr[i][j]!=0){sum++;}
}
}
return sum;
}
//为稀疏数组赋值
public static void vlaue(int[][] arr1,int[][] arr2){
int count = 1;
for (int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
for (int j=0;j<arr1[0].length;j++){
if (arr1[i][j]!=0){
arr2[count][0]=i;
arr2[count][1]=j;
arr2[count][2]=arr1[i][j];
count++;
}
}
}
}
//还原
public static void back(int[][] arr1,int[][] arr2){
for (int i=1;i<arr2.length;i++){
arr1[arr2[i][0]][arr2[i][1]]=arr2[i][2];
}
}
}
输出:
这是原始数组
========================
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
转化为稀疏数组
========================
11 11 2
1 2 1
2 3 2
还原
========================
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Process finished with exit code 0
面向对象
本质:以类的方式组织代码,以对象的组织(封装)数据
static方法可以直接调用,普通的方法只能对象化调用
构造器
每一个定义的类中都有一个默认的方法,这个方法就叫构造器,构造器没有返回值类型和void,它主要用于初始化对象的值,只要new对象就会生成默认的构造器,构造器还可以方法重载。
注意:进行构造器的方法重载的时候,一定要显示的定义一个无参的构造,不然机会会报错
快捷生成: alt+insert 生成构造器
创建对象的过程
封装
封装是将代码隐藏起来,仅仅暴露一个访问接口来使用,在操作上使用get/set方法
好处:
- 提高程序的安全性,保护数据
- 隐藏代码的实现细节
- 统一接口
- 系统可维护性大大增加
package oop;
public class student {
private String name;
private int age;
private char sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
if (age> 0 ){this.age=age;}
else {this.age=8;}
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
package oop;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student s1 = new student();
s1.setName("小明");
System.out.println(s1.getName());
s1.setAge(1);
System.out.println(s1.getAge());
}
}
继承
继承是子类可以自动的继承父类的全部方法!使用关键字 extends
注:
- java中所有的类都默认继承object类
- java中只有单继承没有多继承,单继承就是一个子类只能有一个父类,而一个父类可以用多个子类
Super关键字:
- super调用父类的构造方法,必须在构造方法的第一个
- super必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中
- super和this不能同时调用构造方法
与this的区别:
- this本身调用的是自身的对象
- super代表的是父类对象的应用
- this没继承只能使用,super只能在继承的条件下才能使用
- this()是本类的构造
- super()是父类的构造
方法的重写
- 方法名必须相同
- 参数列表必须相同
- 修饰符范围可以扩大不能缩小
- 抛出的异常可以缩小但不能扩大
- 一定是在继承中子类重写父类的方法 override
- 重写只是方法体的不同
多态
多态是指子类自身的类型是确定的,但是子类指向的引用类型是不确定的。father A = new son();
多态存在的条件:
- 有继承关系
- 子类重写了父类的方法
- 父类引用指向子类的对象
package oop;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化两个对象
student s1 = new student();
Teacher s2 = new student();
//s1可以使用父子的方法
s1.say();
s1.run();
//s2只能使用父类的方法
s2.say();
//进行强制类型转换后,就可以使用父子的方法
((student)s2).run();
((student)s2).say();
//注意:由高到低需要强制类型转换,而由低到高则不需要
}
}
Static修饰符
package oop;
import static java.lang.Math.random;
public class Application {
//匿名代码块
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public Application(){
System.out.println("构造方法被执行了");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Application ap = new Application();
System.out.println(random());
}
}
输出:
静态代码块
匿名代码块
构造方法被执行了
0.3654148250439865
Process finished with exit code 0
抽象类abstract
抽象类就是类的抽象,作用于一个类只需要变一部分内容时,这部分内容就可以定义为抽象的方法,交由子类来完成,当子类继承了抽象类的时候,相当于需要强制重写一下父类的抽象方法,不然就会报错。
//定义了一个抽象类
public abstract class demo1 {
//定义了一个抽象方法
public abstract void fun();
//定义了一个普通方法
public void f(){
System.out.println("111");
}
}
public class student extends demo1{
@Override
public void fun() {
}
}
接口
接口是一组约束,可以定义一些方法,让不同的人来实现
注:所有的属性都是常量都是public static final、所有的方法都是public abstract ,接口中没有构造方法不能被实例化、实现接口的时候必须要把接口中所有的方法重写,实现接口用implements
public interface testInter {
public abstract void fun1();
void fun2();
void fun3();
void fun4();
}
package oop;
public class student implements testInter{
@Override
public void fun1() {
}
@Override
public void fun2() {
}
@Override
public void fun3() {
}
@Override
public void fun4() {
}
}
异常
关键字:try catch throw throws final
try和catch要必须初选,final可以不出现
快捷键:ctrl+alt+t
package oop;
import static java.lang.Math.random;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new Application().run();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("程序出现异常啦");
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(1/0);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号