java慕课第三季
java慕课第三季
1.1java异常
处理异常:
package comm.imooc.test;
public class java {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java sc= new java();
int c = sc.test1();
System.out.println(c);
}
public int test1(){
int a = 10;
int result = 0;
try {
while (a > -1){
a--;
result = result + result/a;
return result;
}
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("出现异常了啊!!!");
}
return 100;
}}
字符串
字符串的定义
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义字符串
String hobby = "爱慕课";
String url = "www.imooc.com";
//输出字符串
System.out.println("hobby:" + hobby );
System.out.println("url:" + url );
}
}
java中字符串的不变性
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "imooc";
String s2 = "imooc";
//定义字符串s3,保存“I love”和s1拼接后的内容
String s3 = "I love"+s1;
// 比较字符串s1和s2
// imooc为常量字符串,多次出现时会被编译器优化,只创建一个对象
System.out.println("s1和s2内存地址相同吗?" + (s1 == s2));
//比较字符串s1和s3
System.out.println("s1和s3内存地址相同吗?" + (s1 == s3) );
String s4 = "I love " + s1;
//比较字符串s4和s3
// s1是变量,s4在运行时才知道具体值,所以s3和s4是不同的对象
System.out.println("s3和s4内存地址相同吗?" + (s4 == s3));
}
}
java中string类的常用方法
判断文件名与邮箱名是否合法:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Java文件名
String fileName = "HelloWorld.java";
// 邮箱
String email = "laurenyang@imooc.com";
// 判断.java文件名是否正确:合法的文件名应该以.java结尾
/*
参考步骤:
1、获取文件名中最后一次出现"."号的位置
2、根据"."号的位置,获取文件的后缀
3、判断"."号位置及文件后缀名
*/
//获取文件名中最后一次出现"."号的位置
int index = fileName.lastindexOf(".");
// 获取文件的后缀
String prefix = fileName.substring(index+1);
// 判断必须包含"."号,且不能出现在首位,同时后缀名为"java"
if ( index != 0 && index != -1 && prefix.equals("java") ) {
System.out.println("Java文件名正确");
} else {
System.out.println("Java文件名无效");
}
// 判断邮箱格式是否正确:合法的邮箱名中至少要包含"@", 并且"@"是在"."之前
/*
参考步骤:
1、获取文件名中"@"符号的位置
2、获取邮箱中"."号的位置
3、判断必须包含"@"符号,且"@"必须在"."之前
*/
// 获取邮箱中"@"符号的位置
int index2 = email.indexOf("@");
// 获取邮箱中"."号的位置
int index3 = email.indexOf('.');
// 判断必须包含"@"符号,且"@"必须在"."之前
if (index2 != -1 && index3 > index2) {
System.out.println("邮箱格式正确");
} else {
System.out.println("邮箱格式无效");
}
}
}
统计字符串中a出现的次数
package comm.imooc.test;
public class ChainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个字符串
String s = "aljlkdsflkjsadjfklhasdkjlflkajdflwoiudsafhaasdasd";
// 出现次数
int num = 0;
// 循环遍历每个字符,判断是否是字符 a ,如果是,累加次数
for ( int i =0; i< s.length() ;i++ )
{
// 获取每个字符,判断是否是字符a
if ( s.charAt(i) == 'a' ) {
// 累加统计次数
num++;
}
}
System.out.println("字符a出现的次数:" + num);
}
}
认识java中的StringBuilder类
从运行结果中我们可以看到,程序运行时会额外创建一个对象,保存 "helloworld"。当频繁操作字符串时,就会额外产生很多临时变量。使用 StringBuilder 或 StringBuffer 就可以避免这个问题。至于 StringBuilder 和StringBuffer ,它们基本相似,不同之处,StringBuffer 是线程安全的,而 StringBuilder 则没有实现线程安全功能,所以性能略高。因此一般情况下,如果需要创建一个内容可变的字符串对象,应优先考虑使用 StringBuilder 类。
创建一个StringBuilder类的对象:
StringBuilder hobby=new StringBuilder("爱慕课");
从右边开始每三个字母用逗号分隔开来:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个空的StringBuilder对象
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
// 追加字符串
str.append("jaewkjldfxmopzdm");
// 从后往前每隔三位插入逗号
for(int i = str.length()-3;i >0;i = i -3){
str.insert(i,',');
}
// 将StringBuilder对象转换为String对象并输出
System.out.print(str.toString());
}
}
java中的包装类
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义int类型变量,值为86
int score1 = 86;
// 创建Integer包装类对象,表示变量score1的值
Integer score2=new Integer(score1);
// 将Integer包装类转换为double类型
double score3=score2.doubleValue();
// 将Integer包装类转换为float类型
float score4=score2.floatValue();
// 将Integer包装类转换为int类型
int score5 =score2.intValue();
System.out.println("Integer包装类:" + score2);
System.out.println("double类型:" + score3);
System.out.println("float类型:" + score4);
System.out.println("int类型:" + score5);
}
}
装箱与拆箱
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义double类型变量
double a = 91.5;
// 手动装箱
Double b = new Double(a);
// 自动装箱
Double c = a;
System.out.println("装箱后的结果为:" + b + "和" + c);
// 定义一个Double包装类对象,值为8
Double d = new Double(87.0);
// 手动拆箱
double e = d.doubleValue(); ;
// 自动拆箱
double f = d ;
System.out.println("拆箱后的结果为:" + e + "和" + f);
}
}
java中基本类型呃字符串之间的转换
基本类型转换为字符串有三种方法:
1.使用包装类的toString()方法
2.使用String类的valueOf()方法
3.用一个空字符串加上基本类型,得到的就是基本类型数据相对应的字符串
double m = 78.5;
//将基本类型转换为字符串
String str1 = m + ""; ;
System.out.println("m 转换为String型后与整数20的求和结果为: "+(str1+20));
String str = "180.20";
// 将字符串转换为基本类型
Double a = Double.valueOf(str) ;
System.out.println("str 转换为double型后与整数20的求和结果为: "+(a+20));
}
基本类型与包装类之间的区别:基本类型不能调用方法,二包装类提供了在不同类型之间进行转换的方法
使用Date和SimpleDateFormat类表示时间
在程序开发中,经常需要处理日期和时间的相关数据,此时我们可以用java.utl包中的Date类。这个类最主要的作用就是获取当前的时间。
使用Date类的默认无参的构造方法创建出的对象就代表的是当前的时间。
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// 使用format()方法将日期转换为指定格式的文本
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒");
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm");
SimpleDateFormat sdf3 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// 创建Date对象,表示当前时间
Date now = new Date();
// 调用format()方法,将日期转换为字符串并输出
System.out.println( sdf1.format(now) );
System.out.println(sdf2.format(now));
System.out.println(sdf3.format(now));
// 使用parse()方法将文本转换为日期
String d = "2014-6-1 21:05:36";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// 调用parse()方法,将字符串转换为日期
Date date = sdf.parse(d);
System.out.println(date);
}
}
声明一个内存为10的数组: int[] sc = new int[10];
随机生成十以内的随机数: sc = (int)(Math.random()*10);
用foreach循环打印数组:
for(num : sc){system.out.println(num)}
```
//通过循环给数组赋值
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 产生10以内的随机数
int x = (int)(Math.random()*10);
nums[i] = x;// 为元素赋值
}
```
集合框架
集合框架概述
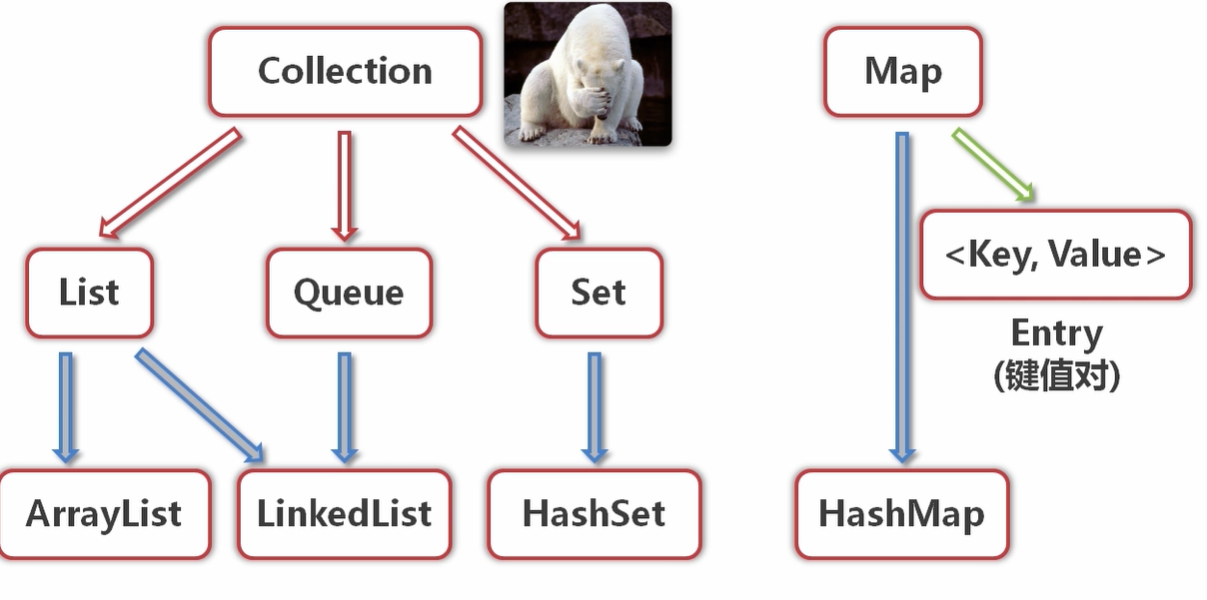
声明一个集合:
public List coursesToSelecTest;
将集合实例化:
public ListTest(){
this.coursesToSelecTest = new ArrayList();
}
创造一个Course类:
package projcet_test;
public class Course {
public String id ;
public String name ;
public Course(String id,String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
给Course添加课程:
public void testAdd() {
Course cr1 = new Course("1", "数据结构");
coursesToSelecTest.add(cr1);
Course temp = (Course )coursesToSelecTest.get(0);
System.out.println("添加了课程:"+ temp.id +":"+temp.name);
批量向Course中添加课程:
Course[] course1 = {new Course("3","大学英语"),new Course("4","离散数学")};
coursesToSelecTest.addAll(2,Arrays.asList(course1));
Course temp3 = (Course)coursesToSelecTest.get(2);
Course temp4 = (Course)coursesToSelecTest.get(3);
System.out.println("添加了课程:"+ temp3.id +":"+temp3.name+";"+
temp4.id +":"+temp4.name);
通过set修改列表中的元素:
public void testModify() {
coursesToSelecTest.set(2, new Course("9","嘿嘿嘿"));
}
通过迭代器来遍历list
public void testGet() {
int size = coursesToSelecTest.size();
System.out.println("有如下课程可供选择:");
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++) {
Course cr = (Course)coursesToSelecTest.get(i);
System.out.println(cr.id + ":"+ cr.name);
}
通过for each 方法访问集合元素:
public void testForEach() {
System.out.println("有如下课程待选择(for each打印输出)");
for (Object obj : coursesToSelecTest) {
Course sc = (Course) obj;
System.out.println(sc.id + ":"+ sc.name);
}
}
通过remove删除元素
public void testremove() {
Course cr0 = (Course)coursesToSelecTest.get(3);
System.out.println("我即将被删除了啊"+cr0.id+":"+cr0.name);
coursesToSelecTest.remove(3);
testForEach();
}
应用泛型来管理课程
集合中的元素,可以是任意类型的对象:如果把某个对象放入集合,则会忽略它的类型,而把他当作Object处理
泛型则是规定了某个集合只可以存放特定类型的对象,并且会在编译期间进行类型的检查


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号