【序列化与反序列化】Java原生 & Hessian & protobuf
序列化应用场景:网络传输;将发送端信息序列化为二进制,通过流的方式发送到接收端后,反序列化还原对象
序列化方案:Java原生
待序列化对象必须implements Serializable
//序列化对象 ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./objectFile.obj")); Customer customer = new Customer(); out.writeObject("你好!"); //写入字面值常量 out.writeObject(new Date()); //写入匿名Date对象 out.writeObject(customer); //写入customer对象 out.close(); //反序列化对象 ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./objectFile.obj")); System.out.println("obj1 " + (String) in.readObject()); //读取字面值常量 System.out.println("obj2 " + (Date) in.readObject()); //读取匿名Date对象 Customer obj3 = (Customer) in.readObject(); //读取customer对象 System.out.println("obj3 " + obj3); in.close();
序列化方案:Hessian
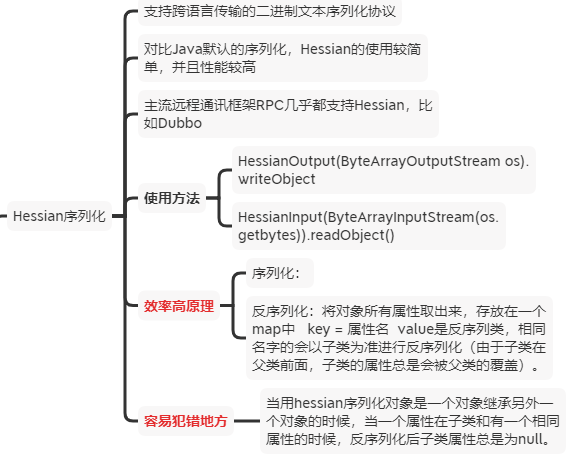
代码样例:
// 序列化
public static <T extends Serializable> byte[] serialize(T t){ HessianOutput hessianOutput = null; try(ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream()){ hessianOutput = new HessianOutput(os); hessianOutput.writeObject(t); return os.toByteArray(); }catch(Exception e){ LOGGER.error("serialize", e); }finally { if(hessianOutput!=null){ try { hessianOutput.close(); } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("serialize", e); } } } return null; } // 反序列化 public static <T extends Serializable> T deserialize(byte[] bytes){ HessianInput hessianInput = null; try(ByteArrayInputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes)){ hessianInput = new HessianInput(is); return (T) hessianInput.readObject(); }catch(Exception e){ LOGGER.error("deserialize", e); }finally { if(hessianInput!=null){ hessianInput.close(); } } return null; }
序列化方案: protobuf(谷歌出品)
待补充
几种序列化方式对比



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号