航空公司客户价值分析
import pandas as pd datafile = 'E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/air_data.csv'#航空公司原始数据,第一行是属性名 resultfile = 'E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/explore.xlsx' data = pd.read_csv(datafile, encoding='utf-8') explore = data.describe( percentiles = [],include = 'all').T explore['null'] = len(data)-explore['count'] explore1 = explore[['null','max','min']] explore1.columns = [u'空值数',u'最大值',u'最小值']#重命名列名 explore1.to_excel(resultfile)
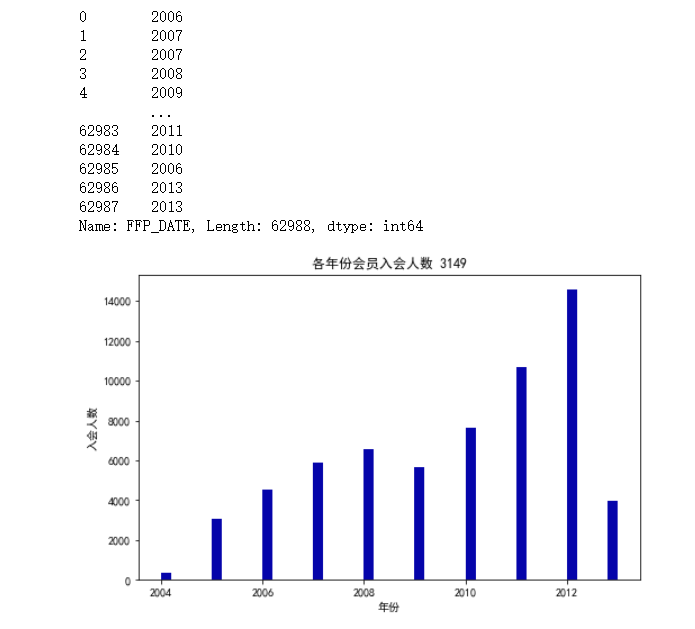
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from datetime import datetime #客户信息类别 #提取会员入会年份 ffp = data['FFP_DATE'].apply(lambda x:datetime.strptime(x, '%Y/%m/%d')) ffp_year = ffp.map(lambda x : x.year) print(ffp_year) #绘制各年份会员入会人数直方图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5)) #设置画布大小 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] #用来正常显示中文标签 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False #用来正常显示负号#探索客户的基本信息分布情况 plt.hist(ffp_year, bins='auto', color='#0504aa') plt.xlabel('年份') plt.ylabel('入会人数') plt.title('各年份会员入会人数 3149') plt.show() plt.close()
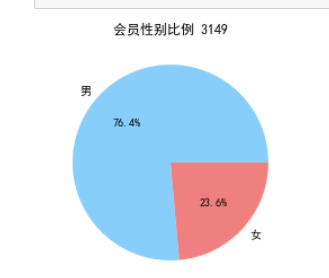
#提取会员不同性别人数 male = pd.value_counts(data['GENDER'])['男'] female = pd.value_counts(data['GENDER'])['女'] #绘制会员性别比例饼图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 4)) #设置画布大小 plt.pie([male, female], labels=['男', '女'], colors=['lightskyblue', 'lightcoral'], autopct='%1.1f%%') plt.title('会员性别比例 3149') plt.show() plt.close()
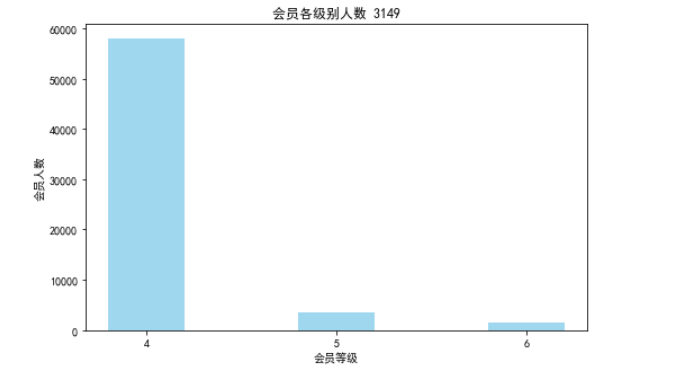
#提取不同级别会员的人数 lv_four = pd.value_counts(data['FFP_TIER'])[4] lv_five = pd.value_counts(data['FFP_TIER'])[5] lv_six = pd.value_counts(data['FFP_TIER'])[6] #绘制会员各级别人数条形图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,5)) #设置画布大小 plt.bar(range(3), [lv_four, lv_five, lv_six], width=0.4, alpha=0.8, color='skyblue') #left:x轴的位置序列,一般采用arange函数产生一个序列; #height:y轴的数值序列,也就是柱形图的高度,一般就是我们需要展示的数据; #alpha:透明度 #width:为柱形图的宽度,一般这是为0.8即可; #color或facecolor:柱形图填充的颜色; plt.xticks([index for index in range(3)], ['4', '5', '6']) plt.xlabel('会员等级') plt.ylabel('会员人数') plt.title('会员各级别人数 3149') plt.show() plt.close()
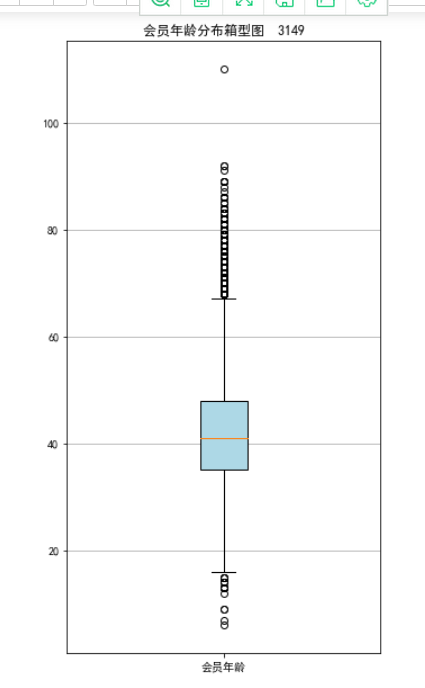
#提取会员年龄 age = data['AGE'].dropna() age = age.astype('int64') #绘制会员年龄分布箱型图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,10)) plt.boxplot(age, patch_artist=True, labels=['会员年龄'], boxprops={'facecolor': 'lightblue'}) #设置填充颜色 plt.title('会员年龄分布箱型图 3149') #显示y坐标轴的底线 plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close()
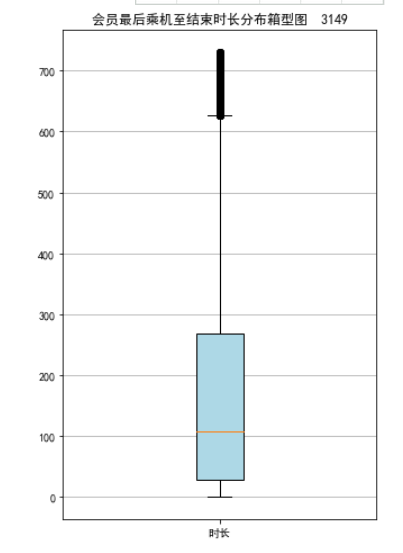
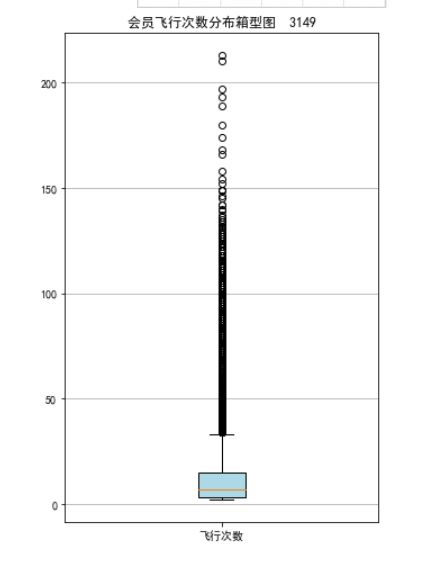
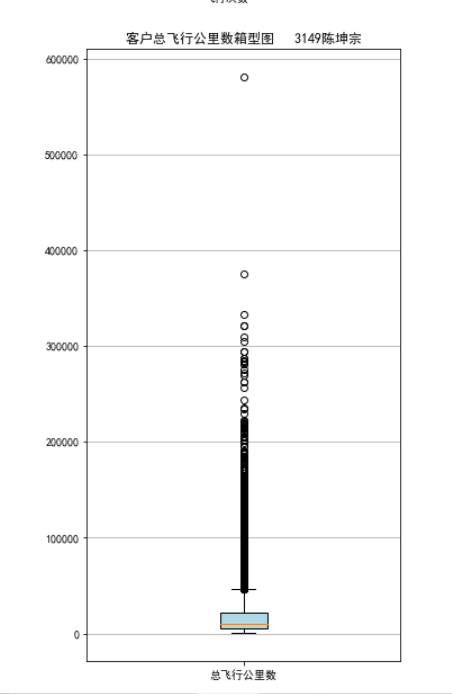
#7-3 lte=data['LAST_TO_END'] fc=data['FLIGHT_COUNT'] sks=data['SEG_KM_SUM'] fig=plt.figure(figsize=(5,8)) plt.boxplot(lte, patch_artist=True, labels=['时长'], boxprops={'facecolor':'lightblue'}) plt.title('会员最后乘机至结束时长分布箱型图 3149') plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close fig=plt.figure(figsize=(5,8)) plt.boxplot(fc, patch_artist=True, labels=['飞行次数'], boxprops={'facecolor':'lightblue'}) plt.title('会员飞行次数分布箱型图 3149') plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close fig=plt.figure(figsize=(5,10)) plt.boxplot(sks, patch_artist=True, labels=['总飞行公里数'], boxprops={'facecolor':'lightblue'}) plt.title('客户总飞行公里数箱型图 3149陈坤宗') plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close
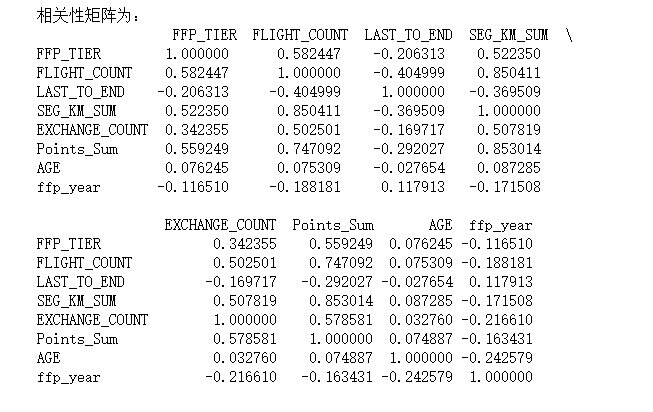
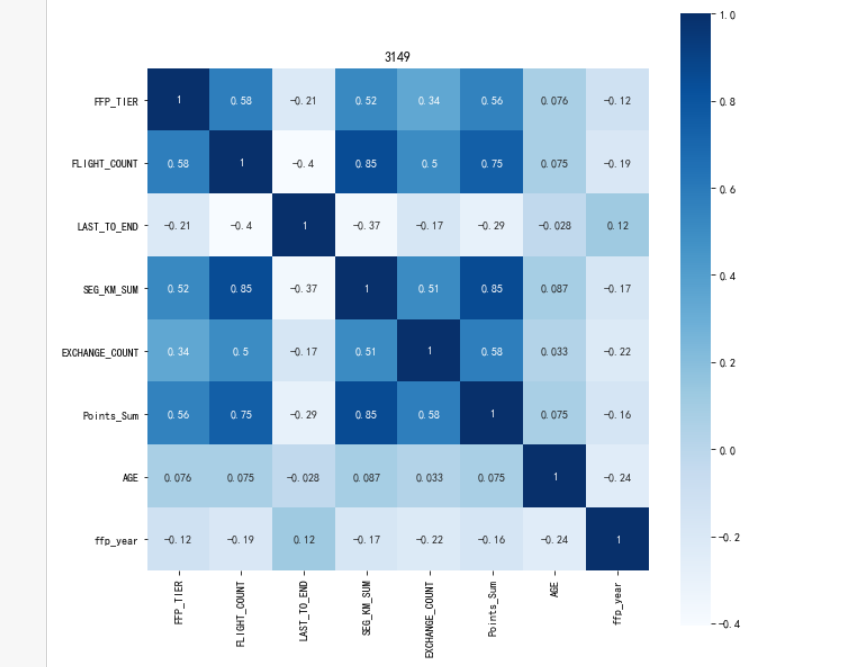
#3相关性分析 #提取属性并合并为新的数据集 data_corr = data.loc[:,['FFP_TIER', 'FLIGHT_COUNT', 'LAST_TO_END', 'SEG_KM_SUM', 'EXCHANGE_COUNT', 'Points_Sum']] age1 = data['AGE'].fillna(0) data_corr['AGE'] = age1.astype('int64') data_corr['ffp_year'] = ffp_year #计算相关性矩阵 dt_corr = data_corr.corr(method='pearson') print('相关性矩阵为:\n', dt_corr) #绘制热力图 import seaborn as sns plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10)) #设置画面大小 ## data:数据 square:是否是正方形 vmax:最大值 vmin:最小值 robust:排除极端值影响 sns.heatmap(dt_corr, annot=True, vmax=1, square=True, cmap='Blues') plt.title('3149') plt.show() plt.close()
datafile = 'E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/air_data.csv'#航空公司原始数据,第一行是属性名 # 去除票价为空的记录 cleanedfile = 'E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/cleaned.csv' airline_data = pd.read_csv(datafile, encoding='utf-8') airline_notnull = airline_data.loc[airline_data['SUM_YR_1'].notnull() & airline_data['SUM_YR_2'].notnull(),:] print('3149 \n删除缺失记录后数据的形状为:',airline_notnull.shape) # 只保留票价非零的,或者平均折扣率不为0且总飞行公里数大于0的记录。 index1 = airline_notnull['SUM_YR_1'] != 0 index2 = airline_notnull['SUM_YR_2'] != 0 index3 = (airline_notnull['SEG_KM_SUM']> 0) & (airline_notnull['avg_discount'] != 0) index4 = airline_notnull['AGE'] > 100 # 去除年龄大于100的记录 airline = airline_notnull[(index1 | index2) & index3 & ~index4] print('数据清洗后数据的形状为:',airline.shape) airline.to_csv(cleanedfile) # 保存清洗后的数据

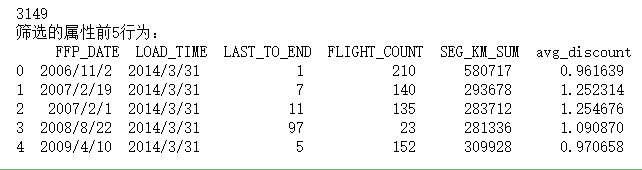
import pandas as pd import numpy as np # 读取数据清洗后的数据 cleanedfile = 'E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/cleaned.csv' # 数据清洗后保存的文件路径 airline = pd.read_csv(cleanedfile, encoding='utf-8') # 选取需求属性 airline_selection = airline[['FFP_DATE', 'LOAD_TIME', 'LAST_TO_END', 'FLIGHT_COUNT', 'SEG_KM_SUM', 'avg_discount']] print('3149 \n筛选的属性前5行为:\n', airline_selection.head())
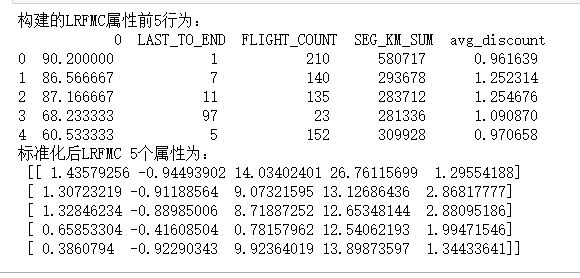
# 7-8 属性构造与数据标准化 # 构造属性L L = pd.to_datetime(airline_selection['LOAD_TIME']) - pd.to_datetime(airline_selection['FFP_DATE']) L = L.astype('str').str.split().str[0] L = L.astype('int')/30 # 合并属性 airline_features = pd.concat([L,airline_selection.iloc[:,2:]],axis=1) print('构建的LRFMC属性前5行为:\n', airline_features.head()) # 数据标准化 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler data = StandardScaler().fit_transform(airline_features) np.savez('E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/airline_scale.npz', data) print('标准化后LRFMC 5个属性为:\n', data[:5,:])
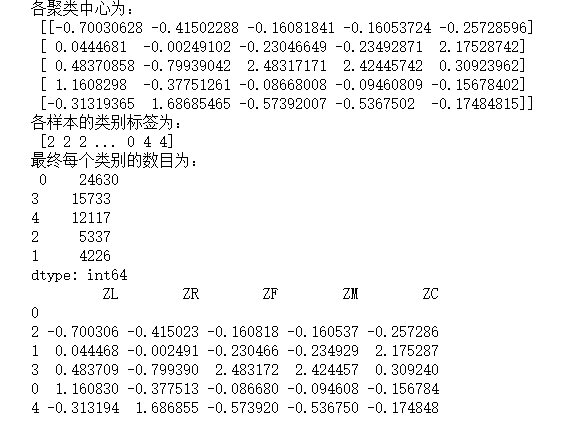
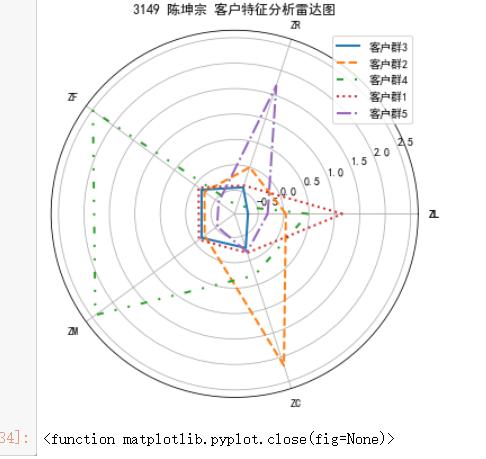
#代码7-9 K-Meas聚类标准化后的数据 import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.cluster import KMeans #导入K-Mmeans算法 #读取标准化后的数据 airline_scale = np.load('E:\py mathph\JupyterLab-Portable-3.1.0-3.9\shujuwajue/airline_scale.npz')['arr_0'] k = 5 #确定聚类中心数 #构建模型,随机种子设为123 kmeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=k,n_jobs=4,random_state=123) fit_kmeans = kmeans_model.fit(airline_scale) #模型训练 #查看聚类结果 kmeans_cc = kmeans_model.cluster_centers_ #聚类中心 print('各聚类中心为:\n',kmeans_cc) kmeans_labels = kmeans_model.labels_ #样本的类别标签 print('各样本的类别标签为:\n',kmeans_labels) r1 = pd.Series(kmeans_model.labels_).value_counts() #统计不同类别样本的数目 print('最终每个类别的数目为:\n',r1) #输出聚类分群的结果 cluster_center = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.cluster_centers_,\ columns = ['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC']) #将聚类中心放在数据中 cluster_center.index = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.labels_).\ drop_duplicates().iloc[:,0] #将样本类别作为数据框索引 print(cluster_center)
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 客户分群雷达图 labels = ['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC'] legen = ['客户群' + str(i + 1) for i in cluster_center.index] # 客户群命名,作为雷达图的图例 lstype = ['-','--',(0, (3, 5, 1, 5, 1, 5)),':','-.'] kinds = list(cluster_center.iloc[:, 0]) # 由于雷达图要保证数据闭合,因此再添加L列,并转换为 np.ndarray cluster_center = pd.concat([cluster_center, cluster_center[['ZL']]], axis=1) centers = np.array(cluster_center.iloc[:, 0:]) # 分割圆周长,并让其闭合 n = len(labels) angle = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, n, endpoint=False) angle = np.concatenate((angle, [angle[0]])) labels = np.concatenate((labels, [labels[0]])) # 绘图 fig = plt.figure(figsize = (8,6)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True) # 以极坐标的形式绘制图形 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 # 画线 for i in range(len(kinds)): ax.plot(angle, centers[i], linestyle=lstype[i], linewidth=2, label=kinds[i]) # 添加属性标签 ax.set_thetagrids(angle * 180 / np.pi, labels) plt.title('3149 陈坤宗 客户特征分析雷达图') plt.legend(legen) plt.show() plt.close



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号