blog第二次作业
一.前言
1.三次题目集中所考察的知识点:
(1)正则表达式的运用;
(2)类的基本运用;
(3)字符数据类型和操作;
(4)String类型和操作;
(5)类的继承与多态;
(6)接口与抽象类;
2.三次题目集中题量、难度等情况
(1)题目集四题量较少,但题目总体难度较大,其中的7-2和7-3难度适中,而7-1难度较大,没有课外进行大量地学习很难能够独立自主地完成这道题;
(2)题目集五和题目集六虽然题量都变多了,但是总体难度并不高,只有个别难度较大的题目;
二.设计与分析
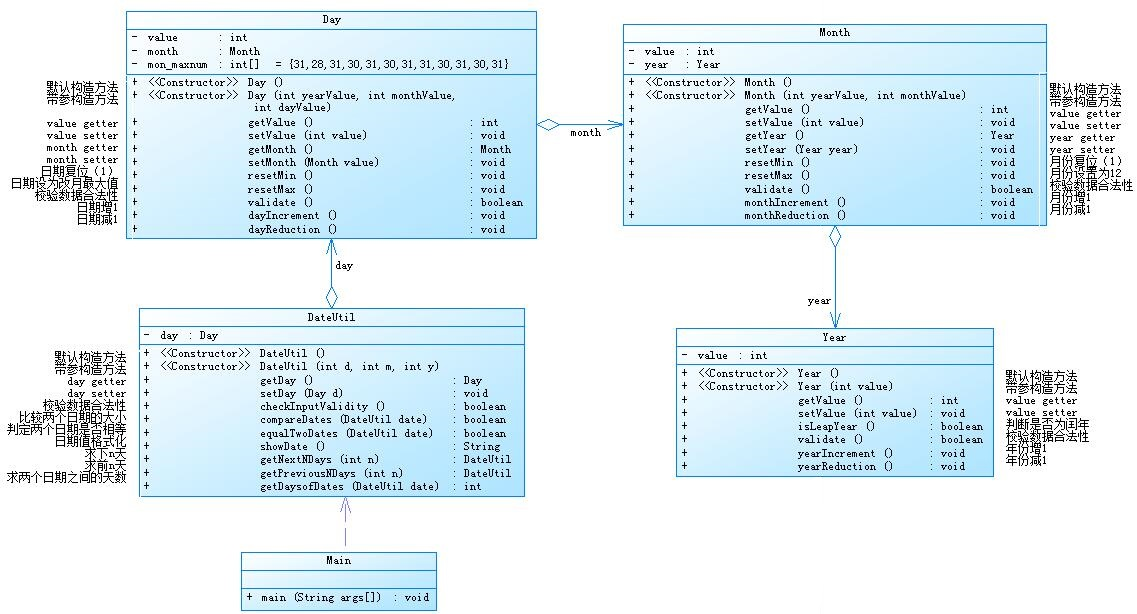
①题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-5)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
1.求下n天
2.求前n天
3.求两个日期相差的天数
以下为题目代码:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main{ 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); 5 int x=input.nextInt(); 6 switch(x) 7 { 8 case 1: 9 int y1=input.nextInt(); 10 int m1=input.nextInt(); 11 int d1=input.nextInt(); 12 int n1=input.nextInt(); 13 DateUtil date1 =new DateUtil(y1,m1,d1); 14 if(date1.validate(y1,m1,d1)==false) { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 break; 17 } 18 date1.NextNDays(n1); 19 break; 20 case 2: 21 int y2=input.nextInt(); 22 int m2=input.nextInt(); 23 int d2=input.nextInt(); 24 int n2=input.nextInt(); 25 DateUtil date2 =new DateUtil(y2,m2,d2); 26 if(date2.validate(y2,m2,d2)==false) { 27 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 28 break; 29 } 30 date2.PreviousNDays(n2); 31 break; 32 case 3: 33 int y3=input.nextInt(); 34 int m3=input.nextInt(); 35 int d3=input.nextInt(); 36 int y4=input.nextInt(); 37 int m4=input.nextInt(); 38 int d4=input.nextInt(); 39 DateUtil date3 =new DateUtil(y3,m3,d3); 40 if(date3.validate(y3,m3,d3)==false||date3.validate(y4,m4,d4)==false) { 41 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 42 break; 43 } 44 date3.DaysofDates(y4,m4,d4); 45 break; 46 default: 47 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 48 break; 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 class Year{ 53 int yearValue; 54 Year(){} 55 Year(int yearValue){ 56 this.yearValue=yearValue; 57 } 58 boolean isLeapYear(int value){ 59 if(value%4==0&&value%100!=0||value%400==0) 60 return true; 61 else 62 return false; 63 } 64 void yearIncrement() { 65 yearValue+=1; 66 } 67 void yearReduction() { 68 yearValue-=1; 69 } 70 } 71 class Month extends Year{ 72 int monthValue; 73 Month(){} 74 Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){ 75 super(yearValue); 76 this.monthValue=monthValue; 77 } 78 void monthIncrement() { 79 monthValue+=1; 80 } 81 void monthReduction() { 82 monthValue-=1; 83 } 84 } 85 class Day extends Month{ 86 int dayValue; 87 Day(){} 88 Day(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 89 super(yearValue, monthValue); 90 this.dayValue=dayValue; 91 } 92 boolean validate(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 93 94 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 95 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 96 month[1]=29; 97 if(yearValue<1900||yearValue>2050||monthValue<1||monthValue>12||dayValue<1||dayValue>31||dayValue>month[monthValue-1]) 98 return false; 99 else 100 return true; 101 } 102 void dayIncrement() { 103 dayValue+=1; 104 } 105 void dayReduction() { 106 dayValue-=1; 107 } 108 } 109 class DateUtil extends Day{ 110 DateUtil(){} 111 DateUtil(int yearValue,int monthValue,int dayValue){ 112 super(yearValue, monthValue, dayValue); 113 } 114 void NextNDays(int n){ 115 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 116 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { 117 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 118 month[1]=29; 119 else 120 month[1]=28; 121 if(dayValue==month[monthValue-1]){ 122 if(monthValue==12) { 123 yearValue+=1; 124 monthValue=1; 125 dayValue=1; 126 } 127 else{ 128 monthValue+=1; 129 dayValue=1; 130 } 131 } 132 else 133 dayValue+=1; 134 } 135 System.out.println(yearValue+"-"+monthValue+"-"+dayValue); 136 } 137 void PreviousNDays(int n){ 138 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 139 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { 140 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 141 month[1]=29; 142 else 143 month[1]=28; 144 if(dayValue==1){ 145 if(monthValue==1) { 146 yearValue-=1; 147 monthValue=12; 148 dayValue=31; 149 } 150 else{ 151 monthValue-=1; 152 dayValue=month[monthValue-1]; 153 } 154 } 155 else 156 dayValue-=1; 157 } 158 System.out.println(yearValue+"-"+monthValue+"-"+dayValue); 159 } 160 void DaysofDates(int x,int y,int z){ 161 int[] month={31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 162 int temp; 163 int i; 164 if(yearValue>x) { 165 temp=yearValue; 166 yearValue=x; 167 x=temp; 168 } 169 if(monthValue>y) { 170 temp=monthValue; 171 monthValue=y; 172 y=temp; 173 } 174 if(dayValue>z) { 175 temp=dayValue; 176 dayValue=z; 177 z=temp; 178 } 179 for(i=0;;i++) { 180 if(isLeapYear(yearValue)==true) 181 month[1]=29; 182 else 183 month[1]=28; 184 if(yearValue==x&&monthValue==y&&dayValue==z) 185 break; 186 if(dayValue==month[monthValue-1]){ 187 if(monthValue==12) { 188 yearValue+=1; 189 monthValue=1; 190 dayValue=1; 191 } 192 else{ 193 monthValue+=1; 194 dayValue=1; 195 } 196 } 197 else 198 dayValue+=1; 199 } 200 System.out.println(i); 201 } 202 }
题目集五-7-5-日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二) (40 分)
设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
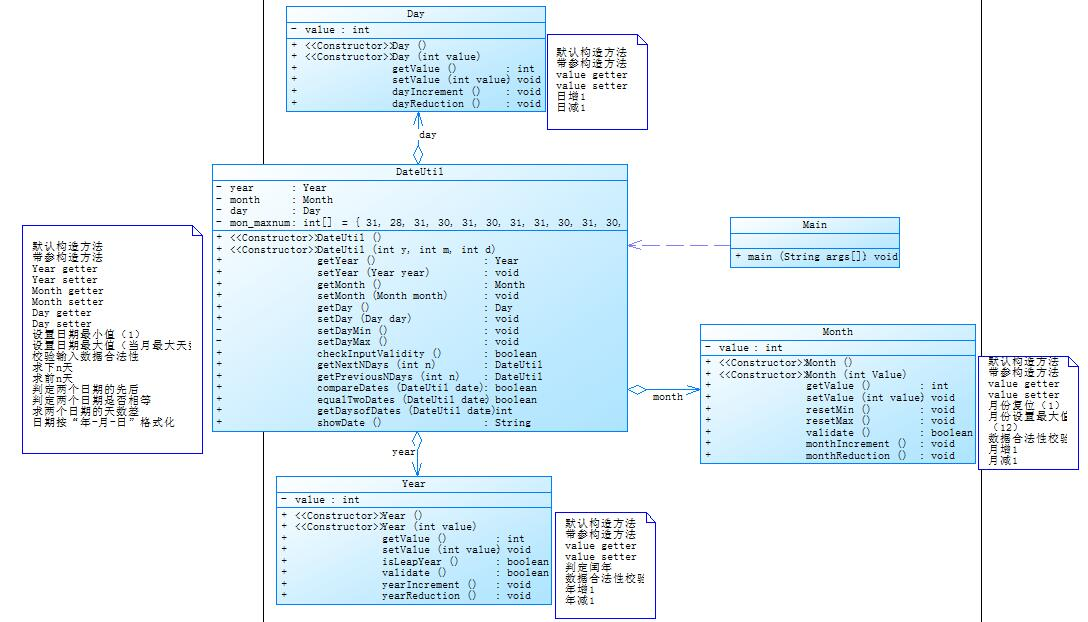
聚合是一种特殊的关联形式,它是两个类之间的关系,是一种HAS-A关系,是一种单向关联,使用聚合对类进行操作能够提高代码的复用性。
题目集四-7-2和题目集五-7-5的做法类似,都是使用聚合的方法创建类,只不过7-2中是Main类依赖DateUtil类,DateUtil类聚合Day类,Day类聚合Month类,Month类聚合Year类,而7-5中是Main类依赖DateUtil类,DateUtil类同时聚合Day类,Month类和Yea类r这三个类,类与类之间的关系不同。题目集7-2中的类较为7-5中的类更为复杂,一步一步对类进行聚合,许多个类之间进行调用,代码的复杂性大幅度提高,一旦出现错误,对代码进行修改起来将会非常的麻烦。而7-5虽然也使用了类之间相互聚合,但都是聚合在一个类中,代码的独立程度大幅度提高,更加方便对代码进行修改,代码的复用性相比于题目7-4提高了很多。
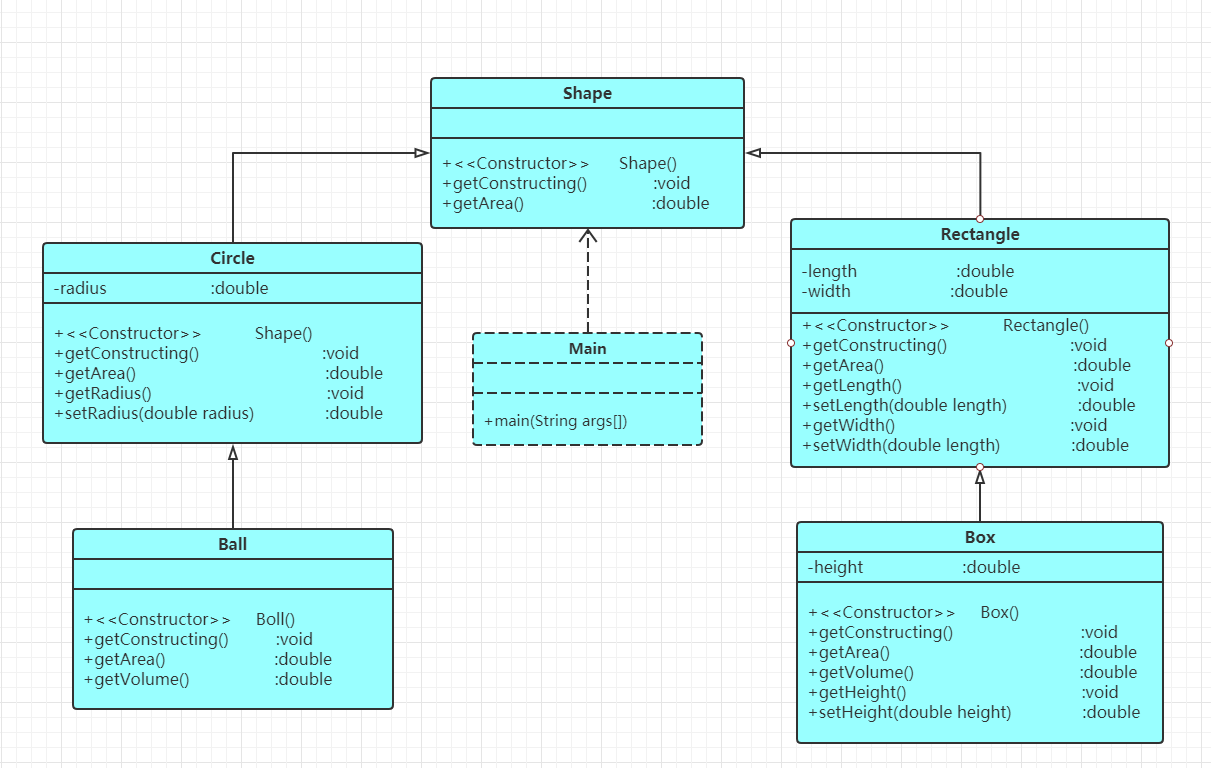
②题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用(封装、继承、多态、接口等)
public double getArea();//求图形面积 2.类Circle,继承自Shape,有一个私有实型的属性radius(半径),重写父类继承来的求面积方法,求圆的面积public double getVolume();//求球体积public double getVolume();//求立方体体积 6.注意:Constructing 类名主方法内,主要实现四个功能(1-4): 从键盘输入1,则定义圆类,从键盘输入圆的半径后,主要输出圆的面积; 从键盘输入2,则定义矩形类,从键盘输入矩形的宽和长后,主要输出矩形的面积; 从键盘输入3,则定义球类,从键盘输入球的半径后,主要输出球的表面积和体积; 从键盘输入4,则定义立方体类,从键盘输入立方体的宽、长和高度后,主要输出立方体的表面积和体积;
假如数据输入非法(包括圆、矩形、球及立方体对象的属性不大于0和输入选择值非1-4),系统输出Wrong Format
输入格式
共四种合法输入
1.圆半径矩形宽、长
2.球半径
3.立方体宽、长、高
以下为题目代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); double s; double v; // System.out.println("请输入选项:"); int n=input.nextInt(); if(n==1){ Shape shape1=new Shape(); // System.out.println("请输入半径:"); double r=input.nextDouble(); if(r<=0.000) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { shape1.getConstructing(); Circle circle=new Circle(); circle.setRadius(r); circle.getConstructing(); s=circle.getArea(); System.out.print("Circle's area:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",s); } } else if(n==2){ Shape shape2=new Shape(); // System.out.println("请输入长和宽:"); double l=input.nextDouble(); double d=input.nextDouble(); if(l<=0||d<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { shape2.getConstructing(); Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(); rectangle.setLength(l); rectangle.setWidth(d); rectangle.getConstructing(); s=rectangle.getArea(); System.out.print("Rectangle's area:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",s); } } else if(n==3){ Shape shape3=new Shape(); // System.out.println("请输入半径:"); double r=input.nextDouble(); if(r<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { shape3.getConstructing(); Ball ball=new Ball(); ball.setRadius(r); ball.getConstructing(); s=ball.getArea(); v=ball.getVolume(); System.out.print("Ball's surface area:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",s); System.out.print("Ball's volume:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",v); } } else if(n==4){ Shape shape4=new Shape(); // System.out.println("请输入长、宽和高:"); double l=input.nextDouble(); double d=input.nextDouble(); double h=input.nextDouble(); if(l<=0||d<=0||h<=0) System.out.println("Wrong Format"); else { shape4.getConstructing(); Box box=new Box(); box.setLength(l); box.setWidth(d); box.setHeight(h); box.getConstructing(); s=box.getArea(); v=box.getVolume(); System.out.print("Box's surface area:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",s); System.out.print("Box's volume:"); System.out.printf("%.2f\n",v); } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Shape{ Shape(){ } void getConstructing(){ System.out.println("Constructing Shape"); } public double getArea(){ return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape{ private double radius; void getConstructing(){ System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); } public double getArea(){ return Math.PI*getRadius()*getRadius(); } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public void setRadius(double radius) { this.radius = radius; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ private double length; private double width; void getConstructing(){ System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); } public double getArea(){ return getLength()*getWidth(); } public double getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(double length) { this.length = length; } public double getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(double width) { this.width = width; } } class Ball extends Circle{ void getConstructing(){ System.out.println("Constructing Circle"); System.out.println("Constructing Ball"); } public double getArea(){ return 4*Math.PI*getRadius()*getRadius(); } public double getVolume(){ return (double) 4/3*Math.PI*getRadius()*getRadius()*getRadius(); } } class Box extends Rectangle{ double height; public double getHeight() { return height; } public void setHeight(double height) { this.height = height; } void getConstructing(){ System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle"); System.out.println("Constructing Box"); } public double getArea(){ return (getLength()*getWidth()+getLength()*height+getWidth()*height)*2; } public double getVolume(){ return getLength()*getWidth()*height; } }
题目集六-7-5 图形继承与多态 (50 分)
掌握类的继承、多态性及其使用方法。
输入格式:
从键盘首先输入三个整型值(例如a b c),分别代表想要创建的Circle、Rectangle及Triangle对象的数量,然后根据图形数量继续输入各对象的属性值(均为实型数),数与数之间可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
1.如果图形数量非法(小于0)或图形属性值非法(数值小于0以及三角形三边关系),则输出Wrong Format。
2.如果输入合法,则正常输出,输出内容如下(输出格式见输入输出示例):
(1)各个图形的面积;
(2)所有图形的面积总和;
(3)排序后的各个图形面积;
(4)再次所有图形的面积总和。
以下为题目代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in); // System.out.println("请输入选项:"); int x=input.nextInt(); int y=input.nextInt(); int z=input.nextInt(); double[] sum = new double[x+y+z]; double num=0,temp; if(x<0||y<0||z<0) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } for(int i=0;i<x;i++) { double r=input.nextDouble(); if(r<=0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } Circle circle = new Circle(r); num=num+circle.getArea(); sum[i]=circle.getArea(); } for(int i=x;i<x+y;i++) { double l=input.nextDouble(); double d=input.nextDouble(); if(l<0||d<0){ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(l,d); num=num+rectangle.getArea(); sum[i]=rectangle.getArea(); } for(int i=x+y;i<x+y+z;i++) { double m=input.nextDouble(); double n=input.nextDouble(); double o=input.nextDouble(); if(m>=0&&n>=0&&o>=0&&m+n>o&&m+o>n&&n+o>m){ Triangle triangle = new Triangle(m,n,o); num=num+triangle.getArea(); sum[i]=triangle.getArea(); } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } } System.out.println("Original area:"); for(int i=0;i<x+y+z;i++){ System.out.printf("%.2f ",sum[i]); } System.out.printf("\n"); System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f\n",num); for(int i=0;i<x+y+z;i++) { for(int j=0;j<x+y+z-i-1;j++) { if(sum[j]>sum[j+1]) { temp = sum[j+1]; sum[j+1] = sum[j]; sum[j] = temp; } } } System.out.println("Sorted area:"); for(int i=0;i<x+y+z;i++){ System.out.printf("%.2f ",sum[i]); } System.out.printf("\n"); System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f\n",num); } } class Shape{ Shape(){ } double getArea(){ return 0.0; } } class Circle extends Shape{ double radius; Circle(){} Circle(double radius){ this.radius = radius; } public double getArea(){ double s=Math.PI*radius*radius; return s; } } class Rectangle extends Shape{ double length; double width; Rectangle(){} Rectangle(double length,double width){ this.length = length; this.width = width; } double getArea(){ double s=length*width; return s; } } class Triangle extends Shape{ double a; double b; double c; Triangle(){} Triangle(double a,double b,double c){ this.a=a; this.b=b; this.c=c; } double getArea(){ double p=(a+b+c)/2; double s=Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)); return s; } }
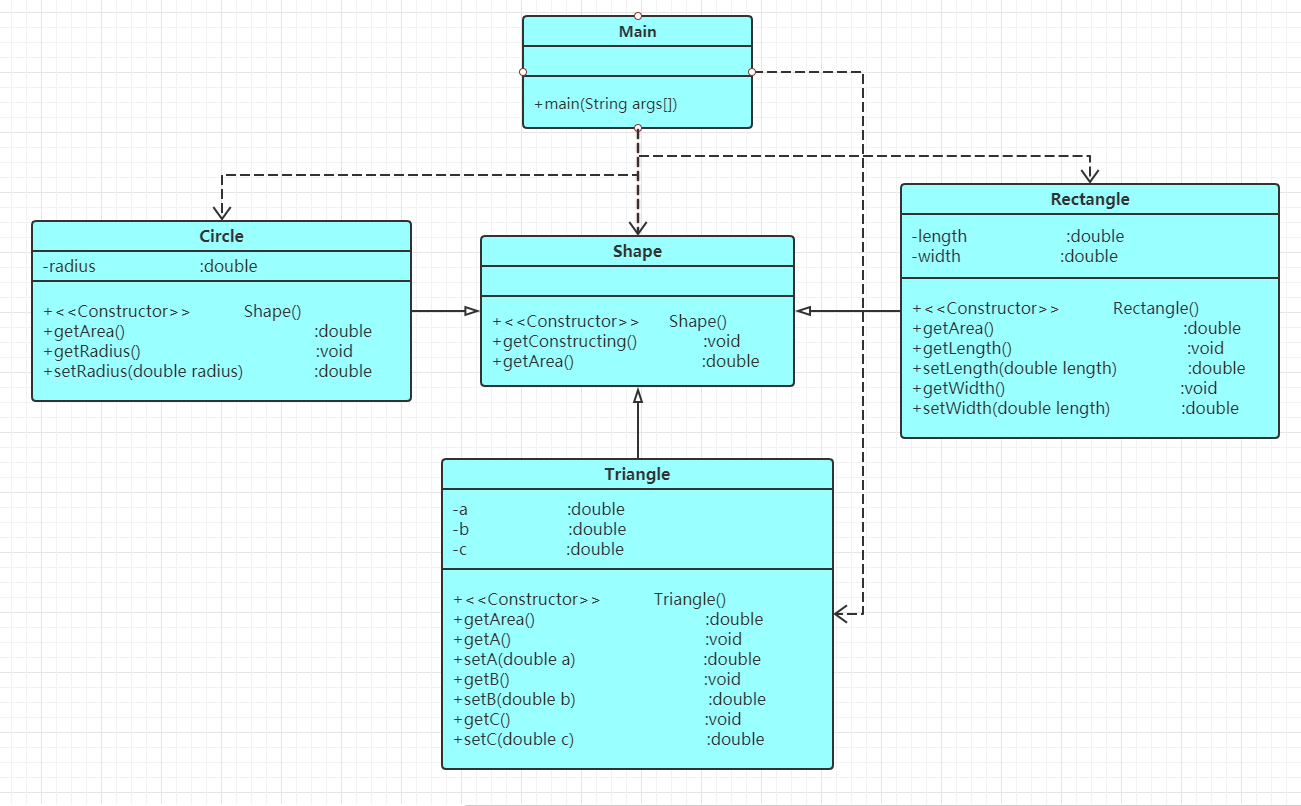
题目集六-7-6 实现图形接口及多态性 (30 分)
编写程序,使用接口及类实现多态性,类图结构如下所示:
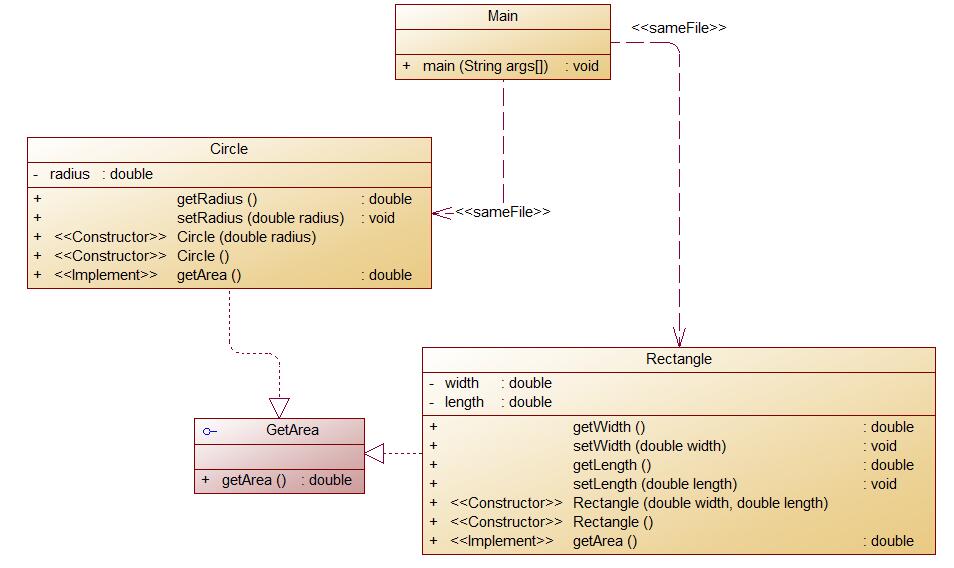
其中:
1.GetArea为一个接口,无属性,只有一个GetArea(求面积)的抽象方法;
2.Circle及Rectangle分别为圆类及矩形类,分别实现GetArea接口
3.要求:在Main类的主方法中分别定义一个圆类对象及矩形类对象(其属性值由键盘输入),使用接口的引用分别调用圆类对象及矩形类对象的求面积的方法,直接输出两个图形的面积值。(要求只保留两位小数)
题目集四中的7-3是继承类,子类Rectangle类和Circle类继承父类Shape类,然后子类Ball类继承父类Circle类,子类Box类继承父类Rectangle类,一步一步继承下去,7-3中主要运用的就是通过子类继承父类并且重写父类的方法,在方法中完成对各个图形面积等的计算,但是代码任显繁琐,多余步骤较多,并且还打破了Java三大特点的封装,虽然很容易修改和扩展已有的实现,但是无法通过子类经行改变,缺乏一定的灵活性。
题目集六7-5是子类Rectangle类、Tritangle类、Circle类直接继承Shape类,并在子类中对图形面积进行操作,在题目集六7-6则是使用了接口,在Rectangle类和Circle类中实现接口GetArea,大大降低程序的耦合性,代码简洁明了了许多,可读性大大提高。
从题目集四7-3到题目集的7-5和7-6,代码的简简洁程度越来越高,代码的使用效率也越来越高,使用的技术也是逐步地深入。
③对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
三次作业中的正则表达式中,题目集四中的 7-1的水文数据的检测题目难度最大,而题目集六中的7-1 正则表达式训练-QQ号校验和7-3 正则表达式训练-验证码校验难度都不大,都是考验正则表达式的基本运用,都不难。
主要就是通过使用字符串函数对字符串进行分割的操作,在分割过后通过正则表达式对分割出来字符串进行识别,如果识别错误,则输出Wrong Format并结束程序,反之,继续使用字符串函数对分割出的字符串进行进一步的操作。正则表达式难就是难在对字符串进行识别的正则表达式,完成识别之后,主要的都是使用字符串相关的知识进行操作。
④题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
能力水平不足,未完成。
(3)采坑心得
1.没有注意编程时符号的错误,导致很多次的编译错误,不够细心,总是忘记输入“,”或者将其输成中文符号,导致编译错误;
2.static是创建静态方法,没有注意到静态方法中不能够调用非静态方法,导致编译出错;
3.在方法中如果返回一个式子,需要对这个计算式进行强制类型转化,否则会存在一定的误差。
4.子类继承父类的参数必须使用super进行辅赋值;
(4)改进建议





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号