(v4 更新)0x10 基础
0x11 基础 Misc
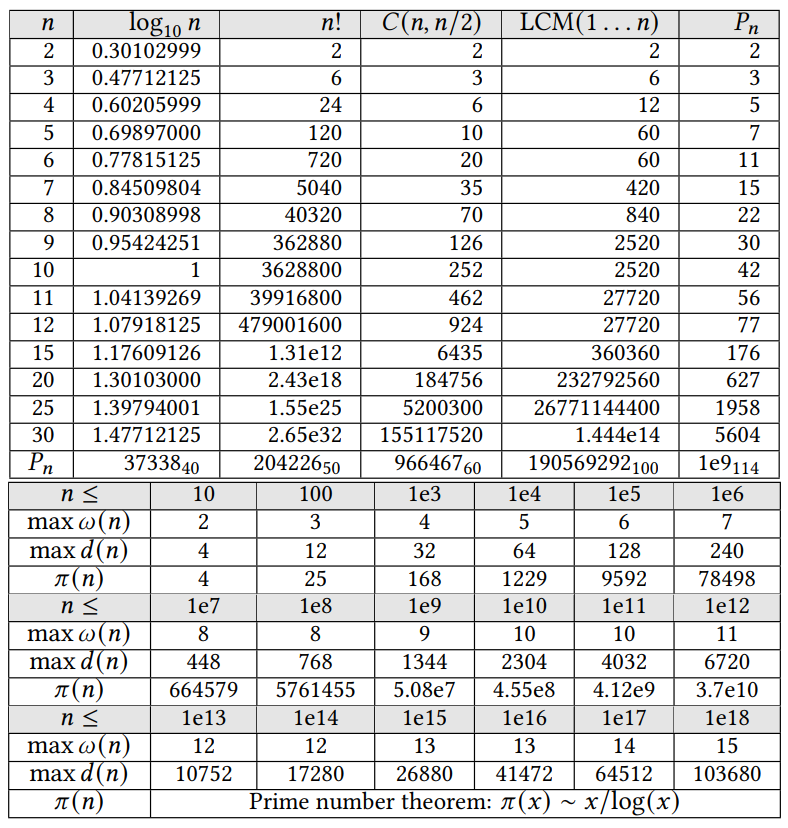
常用常数表
常用公式
日期公式
0x11 日期公式.cpp:
// 返回从 1/1/1 到 y/m/d 的天数,由于 1/1/1 是周一,所以 mod 7 可以算出是周几
int getday(int y, int m, int d) {
if (m < 3) y --, m += 12;
return (365 * y + y / 4 - y / 100 + y / 400 + (153 * (m - 3) + 2) / 5 + d - 307);
}
// 返回从 1/1/1 开始经过 n 天的日期(getday 的逆函数)
std::array<int, 3> date(int n) {
int y, m, d;
n += 429 + ((4 * n + 1227) / 146097 + 1) * 3 / 4;
y = (4 * n - 489) / 1461;
n -= y * 1461 / 4;
m = (5 * n - 1) / 153;
d = n - m * 153 / 5;
if (-- m > 12) m -= 12, y ++;
return {y, m, d};
}
xorshift
0x11 xorshift.cpp:xorshift 是一种确定、线性、可逆的变换。常用于打乱键值(key)。
u64 mask = std::mt19937_64(std::random_device{}())();
u64 xorshift(u64 x) {
x ^= mask;
x ^= x << 13, x ^= x >> 7, x ^= x << 17;
x ^= mask;
return x;
}
xorsum
0x11 xorsum.cpp:
int xorsum(int n) {
if (n % 4 == 0) {
return n;
} else if (n % 4 == 1) {
return 1;
} else if (n % 4 == 2) {
return n + 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
Sum of Powers
常用配置
makefile
CXXFLAGS = -std=c++23 -O2 -Wall -fsanitize=undefined
# -D_GLIBCXX_DEBUG : STL debug mode
# -fsanitize=address : 内存错误检查
# -fsanitize=undefined : UB 检查
对拍脚本
需要 chmod +x cmp.bash,然后再 ./cmp.bash。
while true; do
./gen >0.in
./obj <0.in >1.out
./std <0.in >2.out
if diff 1.out 2.out; then
echo ac
else
echo wa
break;
fi
done
随机数据生成
生成区间 \([l, r]\) 中的随机整数
0x11 生成区间 [l,r] 中的随机整数.cpp:
std::mt19937_64 mtrand{std::random_device{}()}; // 若使用 testlib.h,将种子替换为 rnd.next()
// 生成区间 [l, r] 中的随机整数
int rand(int l, int r) {
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> range(l, r);
return range(mtrand);
}
生成区间 \([l, r)\) 中的随机浮点数
0x11 生成区间 [l,r) 中的随机浮点数.cpp:
std::mt19937_64 mtrand{std::random_device{}()}; // 若使用 testlib.h,将种子替换为 rnd.next()
// 生成区间 [l, r) 中的随机浮点数
double rand(double l, double r) {
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> range(l, r);
return range(mtrand);
}
生成若干个互不相同的随机整数
0x11 生成若干个互不相同的随机整数.cpp:生成方式非均匀随机。
// 生成 n 个在区间 [l, r] 中的互不相同的随机整数
auto GenSequence(int n, int l, int r) {
assert(n <= r - l + 1);
std::vector<int> res(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
res[i] = rand(l, r - n + 1);
}
std::sort(res.begin(), res.end());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
res[i] += i;
}
std::shuffle(res.begin(), res.end(), mtrand);
return res;
}
生成随机区间列
0x11 生成随机区间列.cpp:生成方式非均匀随机。
// 生成 m 个端点在 [L, R] 中的随机区间列
auto GenRanges(int m, int L, int R) {
std::vector< std::pair<int, int> > res(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
int l = rand(L, R), r = rand(L, R);
if (l > r) {
std::swap(l, r);
}
res[i] = {l, r};
}
return res;
}
生成随机父向树
- 随机父向树的期望树高为 \(\mathcal{O}(\log n)\) 级别。
0x11 生成随机父向树.cpp:
// 生成 n 个点的随机父向树
auto GenTree(int n) {
std::vector< std::pair<int, int> > res;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) {
res.push_back({rand(1, i - 1), i});
}
return res;
}
生成随机树
- 随机树的期望直径为 \(\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{n})\) 级别。
0x11 生成随机树.cpp:
// 生成 n 个点的随机树
auto GenTree(int n) {
std::vector< std::pair<int, int> > res;
std::vector<int> prufer(n - 1), deg(n + 1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i ++) {
prufer[i] = rand(1, n);
deg[prufer[i]] ++;
}
int leaf = 0, p = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (deg[i] == 1) {
leaf = p = i;
break;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i ++) {
int x = prufer[i];
res.push_back({leaf, x});
if (-- deg[x] == 1 && x < p) {
leaf = x;
} else {
p ++;
while (deg[p] != 1) p ++;
leaf = p;
}
}
if (n > 1) {
res.push_back({leaf, n});
}
return res;
}
常用库函数重载
__int128
0x11 __int128.cpp:重载了 __int128 的标准输入输出流。
using i128 = __int128;
// 重载 i128 标准输入流
std::istream &operator >> (std::istream &is, i128 &x) {
std::string s;
is >> s;
int n = s.length(), f = s[0] == '-';
x = 0;
for (int i = f; i < n; i ++) {
x = x * 10 + s[i] - '0';
}
if (f) x = -x;
return is;
}
// 重载 i128 标准输出流
std::ostream &operator << (std::ostream &os, i128 x) {
if (x < 0) x = -x, os << '-';
std::string s;
do {
s += char(x % 10 + '0'), x /= 10;
} while (x);
std::reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
return os << s;
}
取最值
0x11 取最值.cpp:
// 取 min
template <class T>
inline void chmin(T &x, const T &y) {
if (x > y) {
x = y;
}
}
// 取 max
template <class T>
inline void chmax(T &x, const T &y) {
if (x < y) {
x = y;
}
}
取模
0x11 取模.cpp:
const int mod = 998244353; // 模数需要根据实际问题调整
// 模意义下 修正
template <class T>
inline int norm(T x) {
x %= mod;
return x < 0 ? x + mod : x;
}
// 模意义下 加法
inline void add(int &x, const int &y) {
x += y;
if (x >= mod) {
x -= mod;
}
}
// 模意义下 减法
inline void dec(int &x, const int &y) {
x -= y;
if (x < 0) {
x += mod;
}
}
// 模意义下 取反
inline void neg(int &x) {
if (x) {
x = mod - x;
}
}
// 模意义下 乘法
inline void mul(int &x, const int &y) {
x = 1ll * x * y % mod;
}
// 快速幂
constexpr int qpow(int a, int b, int p) {
int ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) ans = 1ll * ans * a % p;
a = 1ll * a * a % p;
}
return ans;
}
整数除法精确取整
0x11 整数除法精确取整.cpp:
// 整数除法 精确上取整
i64 ceilDiv(i64 n, i64 m) {
// assert(m);
if (m < 0) n = -n, m = -m;
if (n >= 0) {
return (n + m - 1) / m;
} else {
return n / m;
}
}
// 整数除法 精确下取整
i64 floorDiv(i64 n, i64 m) {
// assert(m);
if (m < 0) n = -n, m = -m;
if (n >= 0) {
return n / m;
} else {
return (n - m + 1) / m;
}
}
精确开根号
0x11 精确开根号.cpp:
// 精确开根号:找到最大整数 d,使得 d * d <= n
i64 isqrt(i64 n) {
i64 d = sqrt(n);
while (d * d > n) {
d --;
}
while ((d + 1) * (d + 1) <= n) {
d ++;
}
return d;
}
精确取对数
0x11 精确取对数.cpp:
// 精确取对数(下取整):找到最大整数 t,使得 a^t <= b
int ilog(i64 a, i64 b) {
int t = 0;
i64 v = 1;
while (v <= b / a) {
t ++;
v *= a;
}
return t;
}
// 精确取对数(上取整):找到最小整数 t,使得 a^t >= b
int iLog(i64 a, i64 b) {
int t = 0;
i64 v = 1;
while (v < b) {
t ++; if (v > b / a) break;
v *= a;
}
return t;
}
字符串转数字
0x11 字符串转数字.cpp:可以配合 std::string 中的 substr 来提取一段子串所表示的数字。
// 字符串转数字
int digit(const std::string &s) {
int x = 0;
for (char ch : s) {
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
}
return x;
}
快读
0x11 快读.cpp:
// 读入一个整数(无需在意类型)
template <class T>
inline void read(T &x) {
static char s;
static bool opt;
while (s = getchar(), (s < '0' || s > '9') && s != '-');
x = (opt = s == '-') ? 0 : s - '0';
while (s = getchar(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
if (opt) x = -x;
}
超级快读
0x11 超级快读.cpp:
/**
* 注意,此代码的所有输出类函数,均不带“空格”与“换行”
* 注意,虽然此代码使用了缓冲区,但不需要你手动清空,fastio 的析构函数会自动清空
* 注意,此快读快写不能与 C/C++ 风格的 IO 混用,否则会导致 IO 的顺序混乱
* 注意,如果你需要使用控制台调试,请在输入的最后使用 Ctrl+Z 手动输入 EOF 来结束读入
*/
struct fastio {
static const int N = 1 << 20;
char buf[N], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
#define gc() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, N, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1 ++)
char pbuf[N], *pp = pbuf;
void pc(const char &c) {
if (pp - pbuf == N) fwrite(pbuf, 1, N, stdout), pp = pbuf;
*pp ++ = c;
}
// 读入一个整数(无需在意类型)
template <class T>
void read(T &x) {
static char s;
static bool opt;
while (s = gc(), (s < '0' || s > '9') && s != '-');
x = (opt = s == '-') ? 0 : s - '0';
while (s = gc(), s >= '0' && s <= '9') x = x * 10 + s - '0';
if (opt) x = -x;
}
// 输出一个整数(无需在意类型)
template <class T>
void print(T x) {
int top = 0; static int stk[40];
if (x < 0) x = -x, pc('-');
do {
stk[++ top] = x % 10, x /= 10;
} while (x);
while (top) pc(stk[top --] + '0');
}
// 输出一个字符串(char 数组类型)
void puts(const char *s) {
while (*s) pc(*s), s ++;
}
// 输出一个字符串(std::string 类型)
void puts(const std::string &s) {
for (char ch : s) pc(ch);
}
~fastio() {
fwrite(pbuf, pp - pbuf, 1, stdout);
}
} io;
高精度
分数类
0x12 基础 算法
主定理
主定理:用于求解分治递归类型的渐进时间复杂度问题。
具体地,对于一个规模为 \(n\) 的问题,将其划分成 \(a\) 个规模为 \(\frac{n}{b}\) 的子问题,附带 "合并/分割" 的开销 \(f(n)\)。
以 \(n^{\log_b a}\) 为处理问题用时的基准线。
- 若 \(f(n) = O(n^{\log_b a - \epsilon})\)
直觉:总工作量由 "叶子层" 主导。
- 若 \(f(n) = \Theta(n^{\log_b a}\log^k n)\) 且满足 \(k\geq 0\)
直觉:每一层工作量相近,共 \(\log_b n\) 层。
- 若 \(f(n) = \Omega(n^{\log_b a + \epsilon})\) 且满足正则性条件 \(af(\frac{n}{b}) \leq cf(n)\)(其中 \(c < 1\))
直觉:总工作量由顶层的 合并/分割 主导。
一些例子:
- 情形 1:遍历满二叉树 \(T(n) = 2T(\frac{n}{2}) + O(1) = O(n)\)。
- 情形 2:归并排序 \(T(n) = 2T(\frac{n}{2}) + O(n) = \mathcal{O}(n \log n)\)。
- 情形 3:多项式牛顿迭代 \(T(n) = T(\frac{n}{2}) + \mathcal{O}(n \log n) = \mathcal{O}(n \log n)\)。
一个主定理处理不了的例子:\(T(n) = 2T\left(\frac{n}{2}\right) + \mathcal{O}\left(\frac{n}{\log n}\right) = \mathcal{O}(n \log \log n)\)。
快速乘
求解 \(a \times b \bmod p\),其中 \(a, b, p\) 均为 long long 范围。
正确率正道更高,效率魔道更高。
正道:__int128
0x12 快速乘(__int128).cpp:
// 快速乘(i128)
constexpr i64 qmul(i64 a, i64 b, i64 p) {
return i128(a) * b % p;
}
魔道:long double
注意到 \(a\times b \bmod p = a\times b - \lfloor \frac{a \times b}{p} \rfloor \times p\),利用 long double 来处理 \(\lfloor \frac{a \times b}{p} \rfloor\)。
模数较大时可能会出锅。
0x12 快速乘(long double).cpp:
// 快速乘(long double)
constexpr i64 qmul(i64 a, i64 b, i64 p) {
i64 c = static_cast<long double>(a) * b / p + 1e-8;
i64 ans = a * b - c * p;
if (ans < 0) ans += p;
if (ans >= p) ans -= p;
return ans;
}
光速幂
对于一个固定底数 \(a\),多次询问 \(a^i \bmod p\) 的值(其中 \(0 \leq i \leq n\))。
取阈值 \(B = \left\lceil \sqrt{n} \right\rceil\),先预处理出 \(a^1, a^2, \cdots, a^i, \cdots, a^B\),再预处理出 \(a^B, a^{2B}, \cdots, a^{iB}, \cdots, a^{\lfloor n / B \rfloor B}\)。
每次只需利用 \(a^i = a^{\lfloor i / B \rfloor B}\times a^{i \bmod B}\) 回答询问即可。
时间复杂度:预处理 \(\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{n})\),查询 \(\mathcal{O}(1)\)。
\(k\) 进制快速幂:利用 \(a^i = \left( a^k \right)^{\lfloor i / k \rfloor} \times a^{i \bmod k}\) 递归处理询问(右侧预处理,左侧递归)。
时间复杂度:预处理 \(\mathcal{O}(k \log_k n)\),查询 \(\mathcal{O}(\log_k n)\)。
0x12 光速幂.cpp:
// 光速幂
struct flashPower {
int b;
std::vector<int> w1, w2;
flashPower() {}
flashPower(int a, int n) {
init(a, n);
}
void init(int a, int n) {
b = sqrt(n) + 1;
w1.resize(b + 1), w2.resize(b + 1);
w1[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= b; i ++) {
w1[i] = 1ll * w1[i - 1] * a % mod;
}
w2[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= b; i ++) {
w2[i] = 1ll * w2[i - 1] * w1[b] % mod;
}
}
int pow(int n) {
return 1ll * w2[n / b] * w1[n % b] % mod;
}
} fp;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号