第十一届中国大学生程序设计竞赛网络预选赛(CCPC Online 2025)
Preface
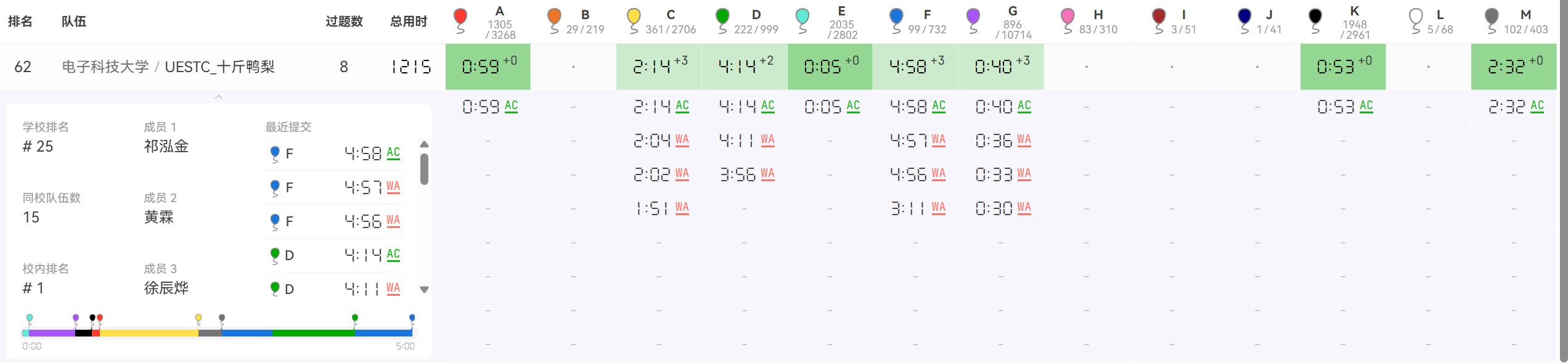
最近因为队友要准备预推免,很久没有一起训练过了;我个人也是把大部分精力都放在科研方面,算是挺久没写代码了
同时因为这场撞了本校预推免的原因,导致学校很多队伍被迫重组,但好在我们队没受影响堪堪凑齐了三个人
这场题还算符合我们队的口味吧,虽然因为大家都不会写代码了导致 dirt 很高而且写的很慢,最后压哨 8 题,没够到 9 题的及格线
但总体来说对很多题目想法都有,剩下没过的 B,H 都有思路;最后反正学校的 CCPC 名额也是打满了,只能说不粘锅了
A. 整点正方形计数2
队友开局写的,好像是个什么差分计数之类的东西,我题目都没看就过了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using llsi = long long signed int;
int n, m;
llsi _a[1000005];
inline llsi& a(int i, int j) {
return _a[i * (m + 3) + j];
}
void add(int lx, int ly, int rx, int ry, int d) {
rx += 1, ry += 1;
a(lx, ly) += d;
a(lx, ry) -= d;
a(rx, ly) -= d;
a(rx, ry) += d;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
std::cin.tie(0);
std::cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= std::min(n, m); i++) {
int x = n - i, y = m - i;
add(0, 0, x, y, 1);
add(0, i + 1, x, m + 1, -1);
add(i + 1, 0, n + 1, y, -1);
add(i + 1, i + 1, n + 1, m + 1, 1);
if(i == 1) continue;
add(1, 1, x + 1, y + 1, -1);
add(1, i, x + 1, m, 1);
add(i, 1, n, y + 1, 1);
add(i, i, n, m, -1);
}
// for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) std::cout << a(i, j) << char(j == m ? 10 : 32);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) {
if(i) a(i, j) += a(i - 1, j);
if(j) a(i, j) += a(i, j - 1);
if(i && j) a(i, j) -= a(i - 1, j - 1);
}
// for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) std::cout << a(i, j) << char(j == m ? 10 : 32);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) {
if(i) a(i, j) += a(i - 1, j);
if(j) a(i, j) += a(i, j - 1);
if(i && j) a(i, j) -= a(i - 1, j - 1);
}
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) std::cout << a(i, j) << char(j == m ? 10 : 32);
return 0;
}
C. 造桥与砍树
为什么都知道用类普利姆的做法,我只会用公式克鲁斯卡尔
将所有数模 \(k\) 后排序,很容易对每个数 \(i\) 找到它的最优匹配数 \(mt_i\);而一旦我们选择了 \((i,mt_i)\) 这条边后 \(i\) 的最优匹配数就会右移
考虑把每个数对应的匹配权值扔到堆里模拟克鲁斯卡尔的过程,并用并查集维护当前的联通关系,每次连边后把下一个最优匹配加入堆中即可
但这样做复杂度显然会爆炸,因为存在大量已经在一个集合内的匹配会导致端点的移动数量打到 \(O(n^2)\) 级别
一个显而易见的观察就是随着匹配点向右的移动,我们可以一次性跳过一段连续的位置,因此可以再用一个并查集来维护空位,即可保证总复杂度 \(O(n(\log n+\alpha(n))\)
PS:事实上这题利用类似的思路写类普利姆的做法很好写,只能说公式人是这样的
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#define RI register int
#define CI const int&
using namespace std;
typedef pair <int,int> pi;
const int N=100005;
int t,n,k,a[N],mt[N],lst[N],fa[N],rpos[N];
inline int getfa(CI x)
{
return x!=fa[x]?fa[x]=getfa(fa[x]):x;
}
inline int getrpos(CI x)
{
return x!=rpos[x]?rpos[x]=getrpos(rpos[x]):x;
}
int main()
{
for (scanf("%d",&t);t;--t)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for (RI i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]),a[i]%=k;
sort(a+1,a+n+1);
if (n==1) { puts("0"); continue; }
priority_queue <pi,vector <pi>,greater <pi>> hp;
for (RI i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
int pos=lower_bound(a+1,a+n+1,k-a[i])-a;
while (1)
{
if (pos>n) { pos=1; continue; }
if (pos==i) { ++pos; continue; }
break;
}
lst[i]=-1; mt[i]=pos; fa[i]=rpos[i]=i;
hp.push({(a[i]+a[pos])%k,i});
}
long long ans=0; int cnt=0;
while (!hp.empty())
{
auto [val,x]=hp.top(); hp.pop();
if (getfa(x)!=getfa(mt[x]))
{
// printf("val = %d, %d <-> %d\n",val,x,mt[x]);
ans+=val; ++cnt; fa[getfa(mt[x])]=getfa(x);
if (cnt==n-1) break;
}
if (lst[x]!=-1) rpos[getrpos(lst[x])]=getrpos(mt[x]);
lst[x]=mt[x];
while (getfa(mt[x])==getfa(x))
{
int nxt=getrpos(mt[x])+1;
if (nxt>n) nxt=1;
if (getfa(nxt)==getfa(x)) rpos[getrpos(mt[x])]=getrpos(nxt);
mt[x]=nxt;
}
if (mt[x]!=x) hp.push({(a[x]+a[mt[x]])%k,x});
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
D. 通配符匹配
挺套路的 DP+KMP,但实现起来细节挺多,扔给队友写了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using llsi = long long signed int;
std::string s, t;
int n, m;
int dp[500005];
std::vector<int> process(int l, int r) {
const char *ars = s.c_str() + l - 1;
static int fail[500005];
int L = r - l;
fail[0] = fail[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2, j = 0; i <= L; ++i) {
while(j && ars[i] != ars[j + 1]) j = fail[j];
if(ars[i] == ars[j + 1]) j += 1;
fail[i] = j;
}
std::vector<int> res;
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; ++i) {
while(j && t[i] != ars[j + 1]) j = fail[j];
if(t[i] == ars[j + 1]) j += 1;
if(j == L) {
j = fail[j];
res.emplace_back(i);
}
}
return res;
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin >> s >> t;
n = s.size(), m = t.size();
s = std::string("#") + s;
t = std::string("#") + t;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) dp[i] = m + 1;
int lll = 1, cur_l = -1, cur_r = -1, count = 0;
while(lll <= n) {
while(lll <= n && s[lll] == '*') lll += 1;
if(lll > n) break;
cur_l = lll;
while(lll <= n && s[lll] != '*') lll += 1;
cur_r = lll;
auto pos = process(cur_l, cur_r);
if(count > 0) {
int p = 1;
for(auto pos: pos) {
for(; p <= m; p += 1) {
if(dp[p] >= m + 1) continue;
if(pos >= dp[p] + (cur_r - cur_l))
dp[p] = pos;
else break;
}
}
// std::cerr << "p = " << p << char(10);
while(p <= m) dp[p++] = m + 1;
// for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
// auto it = std::lower_bound(pos.begin(), pos.end(), dp[i] + (cur_r - cur_l));
// if(it == pos.end()) dp[i] = m + 1;
// else dp[i] = *it;
// }
} else {
for(auto pos: pos) dp[pos - (cur_r - cur_l) + 1] = pos;
}
count += 1;
// for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) std::cerr << dp[i] << char(i == m ? 10 : 32);
}
if(count == 0) {
std::cout << m * llsi(m + 1) / 2 << char(10);
return 0;
}
bool la = (s[1] == '*'), ra = (s[n] == '*');
static int hkr[500005];
if(count == 1) {
auto pos = process(cur_l, cur_r);
int p = 0;
llsi ans = 0;
for(auto &pos: pos) pos -= cur_r - cur_l - 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
while(p < pos.size() && pos[p] < i) p += 1;
if(p >= pos.size()) break;
if(!la && i != pos[p]) continue;
if(ra) ans += m - pos[p] + 1 - (cur_r - cur_l) + 1; else
if(la) ans += (int)pos.size() - p; else
ans += 1;
}
std::cout << ans << char(10);
return 0;
}
if(la) for(int i = m - 1; i >= 1; --i) dp[i] = std::min(dp[i], dp[i + 1]);
if(ra) {
for(int i = m; i >= 1; --i) hkr[i] = m - i + 1;
} else {
auto pos = process(cur_l, cur_r);
for(auto pos: pos) hkr[pos] += 1;
for(int i = m - 1; i >= 1; --i) hkr[i] += hkr[i + 1];
}
// for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) std::cerr << hkr[i] << char(i == m ? 10 : 32);
llsi ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) ans += hkr[dp[i]];
std::cout << ans << char(10);
return 0;
}
E. 看比赛回放
签到,因为败方赢了 \(l=m-\frac{n+1}{2}\) 局,因此最坏需要看 \(2k+1\) 局才能确定
F. 连线博弈
很公式的一个题,首先看到博弈就想到打表 SG 函数
(值得一提的是刚开始犯病了以为每个子问题是独立的线段模型,后面找了反例才发现是图连通块内部的模型)
不难发现状态只和连通块内的点数有关,因此转移为 \(SG(x)=\operatorname{mex}_{y=0}^{x-2} SG(y)\oplus SG(x-y)\)
然后这个 SG 函数的规律是在几百项之后有 \(34\) 的周期,这还是给队友打了值相同的下标差分值后才找到的规律,只能说是十分神秘
剩下的问题就是怎么划分连通块了,一个经典 trick 就是用 Hash
对于一条线段,给其两侧的点集分别异或上一个不同的随机数,最后值相同的点集即属于同一个连通块内
统计个数很容易用 map 离线处理
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<random>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define RI register int
#define CI const int&
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long u64;
const int N=1005;
int t,n,m,sg[N];
mt19937_64 rng(random_device{}());
inline int SG(CI x)
{
if (sg[x]!=-1) return sg[x];
int vis[N]; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for (RI a=0;a<=x-2;++a)
{
int b=x-2-a;
vis[SG(a)^SG(b)]=1;
}
int mex=0;
while (vis[mex]) ++mex;
return sg[x]=mex;
}
inline int _SG(CI x)
{
if (x<=500) return sg[x];
return sg[(x-500)%34+500];
}
int main()
{
memset(sg,-1,sizeof(sg));
sg[0]=sg[1]=0;
for (RI x=1;x<=1000;++x) sg[x]=SG(x);
for (scanf("%d",&t);t;--t)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
if (m==0) { puts(_SG(n)!=0?"YES":"NO"); continue; }
map <int,u64> f;
vector <int> vec;
for (RI i=1;i<=m;++i)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
++x; ++y; if (x>y) swap(x,y);
vec.push_back(x); vec.push_back(y);
u64 A=rng(),B=rng();
auto insert=[&](CI l,CI r,const u64& x)
{
// printf("[%d,%d] <- %llu\n",l,r,x);
f[l]^=x; f[r+1]^=x;
};
if (x+1<=y-1) insert(x+1,y-1,A);
if (1<=x-1) insert(1,x-1,B);
if (y+1<=n) insert(y+1,n,B);
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
map <u64,int> bkt;
int lst=1; u64 res=0;
for (auto [pos,val]:f)
{
if (lst<=pos-1)
{
bkt[res]+=pos-lst-(upper_bound(vec.begin(),vec.end(),pos-1)-lower_bound(vec.begin(),vec.end(),lst));
// printf("[%d,%d] (%llu) += %d\n",lst,pos-1,res,pos-lst-(upper_bound(vec.begin(),vec.end(),pos-1)-lower_bound(vec.begin(),vec.end(),lst)));
}
res^=val;
lst=pos;
}
int ans=0;
for (auto [_,cnt]:bkt) ans^=_SG(cnt);
puts(ans!=0?"YES":"NO");
}
return 0;
}
G. 序列与整数对
很套路的根号分治,对于询问 \((x,y)\),令 \(l_x,l_y\) 分别表示 \(x,y\) 出现的次数
- \(\max(l_x,l_y)\le \sqrt n\),此时直接 two pointers 扫一遍即可得出答案;
- \(l_x>\sqrt n\),此时对应的 \(x\) 种类不超过 \(\sqrt n\),在固定 \(x\) 的情况下可以对任意 \(y\) 正向 \(O(n)\) 扫一遍原序列得到答案;
- \(l_y>\sqrt n\),此时对应的 \(y\) 种类不超过 \(\sqrt n\),在固定 \(y\) 的情况下可以对任意 \(x\) 反向 \(O(n)\) 扫一遍原序列得到答案;
总复杂度 \(O((n+q)\sqrt n)\)
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#define RI register int
#define CI const int&
using namespace std;
const int N=300005;
int n,q,S,a[N],x[N],y[N]; vector <int> rst,pos[N];
vector <pair <int,int>> qx[N],qy[N]; long long ans[N],tmp[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for (RI i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&a[i]),rst.push_back(a[i]);
for (RI i=1;i<=q;++i)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x[i],&y[i]);
rst.push_back(x[i]); rst.push_back(y[i]);
}
sort(rst.begin(),rst.end());
rst.erase(unique(rst.begin(),rst.end()),rst.end());
int all=(int)rst.size();
auto find=[&](CI x)
{
return lower_bound(rst.begin(),rst.end(),x)-rst.begin()+1;
};
for (RI i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
a[i]=find(a[i]);
pos[a[i]].push_back(i);
}
int S=(int)sqrt(n);
for (RI i=1;i<=q;++i)
{
x[i]=find(x[i]); y[i]=find(y[i]);
if ((int)pos[x[i]].size()<=S&&(int)pos[y[i]].size()<=S)
{
RI k=0;
for (RI j=0;j<(int)pos[x[i]].size();++j)
{
while (k<(int)pos[y[i]].size()&&pos[x[i]][j]>=pos[y[i]][k]) ++k;
ans[i]+=(int)pos[y[i]].size()-k;
}
continue;
}
if ((int)pos[x[i]].size()>S)
{
qx[x[i]].push_back({y[i],i});
continue;
}
if ((int)pos[y[i]].size()>S)
{
qy[y[i]].push_back({x[i],i});
continue;
}
}
for (RI x=1;x<=all;++x)
{
if (qx[x].empty()) continue;
for (RI i=1;i<=all;++i) tmp[i]=0;
int cur=0;
for (RI i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
tmp[a[i]]+=cur;
if (a[i]==x) ++cur;
}
for (auto [y,id]:qx[x]) ans[id]=tmp[y];
}
for (RI y=1;y<=all;++y)
{
if (qy[y].empty()) continue;
for (RI i=1;i<=all;++i) tmp[i]=0;
int cur=0;
for (RI i=n;i>=1;--i)
{
tmp[a[i]]+=cur;
if (a[i]==y) ++cur;
}
for (auto [x,id]:qy[y]) ans[id]=tmp[x];
}
for (RI i=1;i<=q;++i) printf("%lld\n",ans[i]);
return 0;
}
H. 教师
考虑一个 trivial 的 DP,令 \(f_{i,mask}\) 表示花费总时间为 \(i\),已经确定最大值的课程状态为 \(mask\) 的最大收益
每次考虑一个新的老师时,我们只更新当前状态的补集的子集即可,因为这样一定会把最优解给算到
但 \(O(mT\times 3^n)\) 的复杂度无法通过,考虑利用 sosdp 的思路,每次直接枚举某个课是不是当前教师作为最大值,复杂度降为 \(O(mT\times n2^n)\)
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
#define RI register int
#define CI const int&
using namespace std;
const int N=55;
int n,m,k,T,V[N][10005],f[N][1<<14],val[14];
signed main()
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&n,&m,&k,&T);
for (RI i=0;i<n;++i)
for (RI j=0;j<=k;++j)
scanf("%lld",&V[i][j]);
for (RI mask=0;mask<(1<<n);++mask)
{
int res=0;
for (RI i=0;i<n;++i)
if ((mask>>i)&1) res+=V[i][0];
for (RI i=0;i<=T;++i)
f[i][mask]=res;
}
while (m--)
{
int h,t; scanf("%lld%lld",&h,&t);
for (RI i=0;i<n;++i) val[i]=V[i][0];
while (h--)
{
int x,y; scanf("%lld%lld",&x,&y); --x;
val[x]=max(val[x],V[x][y]);
}
for (RI i=T-t;i>=0;--i)
{
static int g[1<<14];
memcpy(g,f[i],sizeof(g));
for (RI j=0;j<n;++j)
for (RI mask=0;mask<(1<<n);++mask)
if (((mask>>j)&1)==0)
g[mask|(1<<j)]=max(g[mask|(1<<j)],g[mask]+val[j]);
for (RI mask=0;mask<(1<<n);++mask)
f[i+t][mask]=max(f[i+t][mask],g[mask]);
}
}
for (RI i=1;i<=T;++i)
printf("%lld\n",f[i][(1<<n)-1]);
return 0;
}
K. 置换环
直接逆序构造 \(n,n-1,\dots,1\) 即为最优解
考虑证明,因为 \(n\) 次移动过程中每个点都会作为不动点恰好一次,而上述构造方法在每个点不是不动点时,能保证剩下的点均构成若干二元环,这一定是最优的
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("%d\n",n+n*(n-1)/2);
for (int i=n;i>=1;--i)
printf("%d%c",i," \n"[i==1]);
return 0;
}
M. 并行计算
队友都是分布式并行计算高手,我题意都没看就早早过了这个题,最躺赢的一集
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n = 188;
std::cout << n << char(10);
for(int i = 1; i < 32; ++i) {
std::cout << "add 32\n";
for(int j = 0; j < 1024; j += 32)
std::cout << j + i - 1 << char(j == 1024 - 32 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 1024; j += 32)
std::cout << j + i << char(j == 1024 - 32 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 1024; j += 32)
std::cout << j + i << char(j == 1024 - 32 ? 10 : 32);
}
for(int i = 32; i < 1024; i += 32) {
std::cout << "add 32\n";
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << i - 1 << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 1024; i += 32) {
std::cout << "mul 32\n";
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << 1024 + i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << 1024 + i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
}
for(int i = 1; i < 32; ++i) {
std::cout << "max 32\n";
for(int j = 0; j < 1024; j += 32)
std::cout << 1024 + j + i - 1 << char(j == 1024 - 32 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 1024; j += 32)
std::cout << 1024 + j + i << char(j == 1024 - 32 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 1024; j += 32)
std::cout << 1024 + j + i << char(j == 1024 - 32 ? 10 : 32);
}
for(int i = 32; i < 1024; i += 32) {
std::cout << "max 32\n";
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << 1024 + i - 1 << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << 1024 + i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << 1024 + i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 1024; i += 32) {
std::cout << "sub 32\n";
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << 1024 + i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
for(int j = 0; j < 32; ++j)
std::cout << i + j << char(j == 31 ? 10 : 32);
}
return 0;
}
Postscript
本来以为这个学期能有很多时间训练冲个好成绩,现在看来大家都很忙估计又要开始摆烂模式,比赛权当旅游了


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号