一、实验目的
- 能够使用C++语法规则正确定义、实现、测试类
- 能够使用C++语法规则正确创建对象,并基于对象编程
- 知道类的static成员用于解决什么问题场景,会正确使用c++语法规则实现和访问static成员
- 知道友元机制用于解决什么问题场景,会正确使用c++语法规则实现和使用友元函数、友元类
- 知道const限定对象、引用、类成员用于解决什么问题场景,能正确、合理使用
- 对于规模较大的程序,会用多文件方式组织代码
- 体会面向对象编程在解决问题时的思维方式
二、实验内容
实验任务1
程序代码
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
int main(){
using namespace std;
complex<double> c1{3, 4}, c2{4.5};
const complex<double> c3{c2};
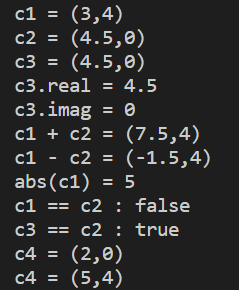
cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl;
cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl;
cout << "c3.real = " << c3.real() << endl;
cout << "c3.imag = " << c3.imag() << endl;
cout << "c1 + c2 = " << c1 + c2 << endl;
cout << "c1 - c2 = " << c1 - c2 << endl;
cout << "abs(c1) = " << abs(c1) << endl; // abs()是标准库中数学函数,对复数进行取模
cout << boolalpha; // 设置bool型值以true/false方式输出
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl;
cout << "c3 == c2 : " << (c3 == c2) << endl;
complex<double> c4 = 2;
cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl;
c4 += c1;
cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl;
}
结果截图
![]()
实验任务2
程序代码
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
// 模板函数
// 对满足特定条件的序列类型T,使用范围for输出
template<typename T>
void output1(const T &obj) {
for(auto i: obj)
std::cout << i << ", ";
std::cout << "\b\b \n";
}
// 模板函数
// 对满足特定条件的序列类型T,使用迭代器输出
template<typename T>
void output2(const T &obj) {
for(auto p = obj.cbegin(); p != obj.cend(); ++p)
std::cout << *p << ", ";
std::cout << "\b\b \n";
}
int main() {
using namespace std;
array<int, 5> x1; // 创建一个array对象,包含5个int类型元素,未初始化
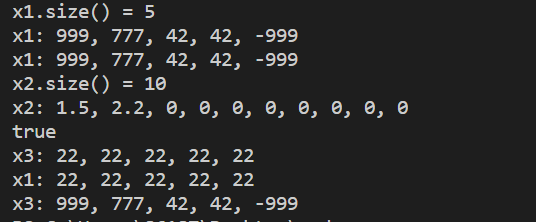
cout << "x1.size() = " << x1.size() << endl; // 输出元素个数
x1.fill(42); // 将x1的所有元素值都赋值为42
x1.at(0) = 999; // 把下标为0的元素修改为999
x1.at(4) = -999; // 把下标为4的元素修改为-999
x1[1] = 777; // 把下标为1的元素修改为777
cout << "x1: ";
output1(x1);
cout << "x1: ";
output2(x1);
array<double, 10> x2{1.5, 2.2}; // 创建要给array对象,包含10个double类型元素,初始化部分元素
cout << "x2.size() = " << x2.size() << endl;
cout << "x2: ";
output1(x2);
array<int, 5> x3{x1};
cout << boolalpha << (x1 == x3) << endl;
x3.fill(22);
cout << "x3: ";
output1(x3);
swap(x1, x3); // 交换x1和x3的数据
cout << "x1: ";
output1(x1);
cout << "x3: ";
output1(x3);
}
结果截图
![]()
实验任务3
程序代码
#pragma once
// Employee类的定义
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <iomanip>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::setfill;
using std::setw;
using std::left;
using std::right;
using std::to_string;
struct Date {
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
// Employee类的声明
class Employee
{
public:
Employee();
Employee(string name0, double salary0, int y, int m, int d = 1);
void set_info(string name0, double salary0, int y, int m, int d = 1);
// 设置雇员信息
string get_name() const; // 获取雇员姓名
double get_salary() const; // 获取雇员薪水
void display_info() const; // 显示雇员信息
void update_salary(double s); // 更新雇员薪水
void update_hire_date(int y, int m, int d); // 更新雇佣日期
void raise_salary(double by_percent); // 计算提薪加成
public:
static void display_count(); // 类方法,显示雇员总数
private:
string id; // 雇员工号
string name; // 雇员姓名
double salary; // 雇员薪水
Date hire_date; // 雇员雇佣日期
public:
static const string doc; // 类属性,用于描述类
private:
static int count; // 类属性,用于记录雇员总人数
};
const string Employee::doc {"a simple Employee class"};
int Employee::count = 0;
// 默认构造函数
Employee::Employee(): id{ to_string(count+1) } {
++count;
}
// 带参数的构造函数
Employee::Employee(string name0, double salary0, int y, int m, int d):
id{to_string(count+1)}, name{name0}, salary{salary0},
hire_date{y, m, d} {
++count;
}
// 设置员工信息
void Employee::set_info(string name0, double salary0, int y, int m, int d)
{
name = name0;
salary = salary0;
hire_date.year = y;
hire_date.month = m;
hire_date.day = d;
}
// 获取员工姓名
string Employee::get_name() const {
return name;
}
// 获取员工薪水
double Employee::get_salary() const {
return salary;
}
// 显示雇员信息
void Employee::display_info() const {
cout << left << setw(15) << "id: " << id << endl;
cout << setw(15) << "name: " << name << endl;
cout << setw(15) << "salary: " << salary << endl;
cout << setw(15) << "hire_date: " << hire_date.year << "-";
cout << right << setfill('0') << setw(2) << hire_date.month << "-" <<
setw(2) << hire_date.day;
cout << setfill(' '); // 恢复到默认空格填充
}
// 更新薪水
void Employee::update_salary(double s) {
salary = s;
}
// 更新雇佣日期
void Employee::update_hire_date(int y, int m, int d) {
hire_date.year = y;
hire_date.month = m;
hire_date.day = d;
}
// 雇员提薪加成
// by_percent是提升比例
void Employee::raise_salary(double by_percent) {
double raise = salary * by_percent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
// 类方法
// 显示雇员总数
void Employee::display_count() {
cout << "there are " << count << " employees\n";
}
#include "Employee.hpp"
#include <iostream>
void test() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
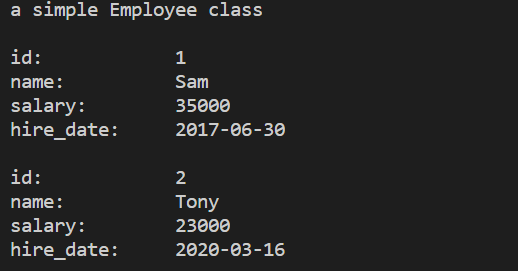
cout << Employee::doc << endl << endl;
Employee employee1;
employee1.set_info("Sam", 30000, 2015, 1, 6);
employee1.update_hire_date(2017, 6, 30);
employee1.update_salary(35000);
employee1.display_info();
cout << endl << endl;
Employee employee2{"Tony", 20000, 2020, 3, 16};
employee2.raise_salary(15); // 提成15%
employee2.display_info();
cout << endl << endl;
Employee::display_count();
}
int main() {
test();
}
结果截图
![]()
实验任务4
程序代码
"Complex.hpp"
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<math.h>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class Complex
{
private:
double x,y;
public:
Complex(double x0, double y0);
Complex(const Complex& t);
~Complex() = default;
double get_real() const;
double get_imag() const;
void show() const;
void add(Complex c1);
friend Complex add(Complex c1, Complex c2);
friend bool is_equal(Complex c1, Complex c2);
friend double abs(Complex c1);
};
Complex::Complex(double x0 = 0, double y0 = 0): x{x0}, y{y0}{}
Complex::Complex(const Complex& t):x{t.x}, y{t.y}{}
double Complex::get_real() const
{
return x;
}
double Complex::get_imag() const
{
return y;
}
void Complex::show() const
{
if(y > 0)
{
cout << x << " + " << abs(y) << "i";
}
else if (y < 0)
{
cout << x << " - " << abs(y) << "i";
}
else
cout << x;
}
void Complex::add(Complex c1)
{
x += c1.x;
y += c1.y;
}
Complex add(Complex c1, Complex c2)
{
double real = c1.x + c2.x;
double imag = c1.y + c2.y;
return Complex(real, imag);
}
bool is_equal(Complex c1, Complex c2)
{
if (c1.x == c2.x && c1.y == c2.y)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
double abs(Complex c1)
{
return sqrt(c1.x * c1.x + c1.y * c1.y);
}
task2-4.cpp
#include "Complex.hpp"
#include <iostream>
// 类测试
void test() {
using namespace std;
Complex c1(3, -4);
const Complex c2(4.5);
Complex c3(c1);
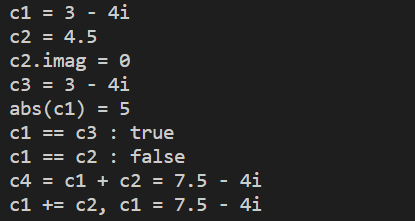
cout << "c1 = ";
c1.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = ";
c2.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "c2.imag = " << c2.get_imag() << endl;
cout << "c3 = ";
c3.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "abs(c1) = ";
cout << abs(c1) << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c3 : " << is_equal(c1, c3) << endl;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
Complex c4;
c4 = add(c1, c2);
cout << "c4 = c1 + c2 = ";
c4.show();
cout << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, " << "c1 = ";
c1.show();
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
}
结果截图
![]()
实验任务5
程序代码
User.hpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class User
{
private:
string name, passwd, email;
public:
User(string nm, string pw, string em);
~User() = default;
void set_email();
void change_passwd();
void print_info();
private:
static int n;
public:
void static print_n();
};
int User::n = 0;
User::User(string nm, string pw = "111111", string em = ""): name{nm}, passwd{pw}, email{em}
{
n++;
}
void User::set_email()
{
cout << "Enter email address: ";
cin >> email;
cout << "email is set successfully..."<< endl;
}
void User::change_passwd()
{
cout << "Enter old password: ";
string s1;
int a = 3;
while(a)
{
cin >> s1;
if(passwd == s1)
{
cout << "Enter new passwd: ";
cin >> passwd;
cout << "new passwd is set successfully..." << endl;
break;
}
else
{
cout << "password input error. ";
a--;
}
if (a)
{
cout << "Please re-enter again: ";
continue;
}
else
{
cout << "Please try after a while. " << endl;
}
}
}
void User::print_info()
{
string s2(passwd.length(), '*');
cout << setfill(' ') << setw(8) << left << "name: " << name << endl
<< setfill(' ') << setw(8) << left << "passwd: " << s2 << endl
<< setfill(' ') << setw(8) << left << "email: " << email << endl;
}
void User::print_n()
{
cout << "there are " << n << " users. ";
}
task5.cpp
#include "User.hpp"
#include <iostream>
// 测试User类
void test() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
cout << "testing 1......\n";
User user1("Jonny", "92197", "xyz@hotmail.com");
user1.print_info();
cout << endl
<< "testing 2......\n\n";
User user2("Leonard");
user2.change_passwd();
user2.set_email();
user2.print_info();
cout << endl;
User::print_n();
}
int main() {
test();
}
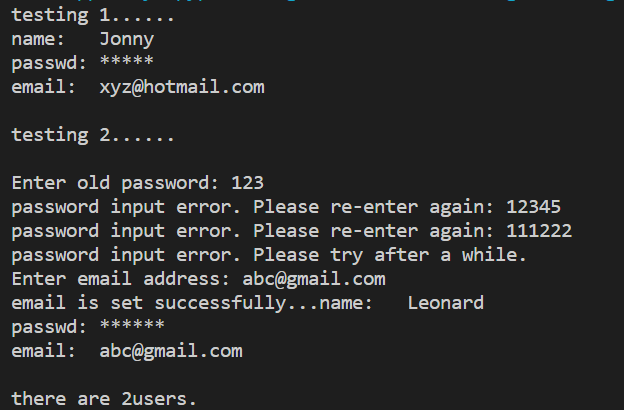
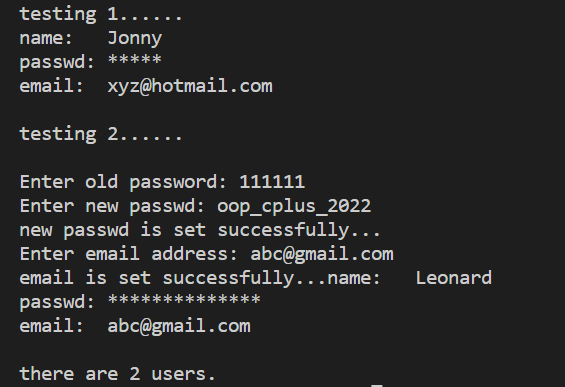
结果截图
![]()
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号