天梯赛写代码感悟
《L2-028 秀恩爱分得快》
这次给的教训是,如果说想要在数组 中
中
找到最大值,而且同时找到与最大值相同的值
要sort吗?不,更简单的方法是
用一个变量maxd来记录最大值
如何再遍历一遍dist数组,然后只要判断值是否相同即可
《其中的排序,有序问题》
《L2-039 清点代码库》

这道题首先让我没想到的是map可以以vector<>为key
并且能够区分出vector<>中的不同元素
同时这道题还要根据vector<int> 中的元素排序
在c++中可以直接用 < 来排序,默认是元素从小到大
即可以直接 vector<int>a < vector<int> b
反而是自己手写会超时和出错
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10002;
int n, m;
map<vector<int>, int> mp;
struct node
{
vector<int> t;
int cnt;
} ans[N];
int pos = 0;
bool rule(struct node x, struct node y)
{
if (x.cnt != y.cnt)
return x.cnt > y.cnt;
else
return x.t < y.t;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
vector<int> t;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
int num;
cin >> num;
t.push_back(num);
}
mp[t]++;
}
for (auto i = mp.begin(); i != mp.end(); i++)
{
ans[pos].t = i->first;
ans[pos].cnt = i->second;
pos++;
}
sort(ans, ans + pos, rule);
cout << pos << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++)
{
vector<int> t = ans[i].t;
cout << ans[i].cnt << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j++)
{
cout << t[j];
if (j != t.size() - 1)
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
《L2-038 病毒溯源》

这道题要求在dfs或bfs找最长链的时候还要求要 最小序列
这个咋办?
即在建图的时候,手动给图排个序
让在搜索的时候优先搜到最小序列
如:
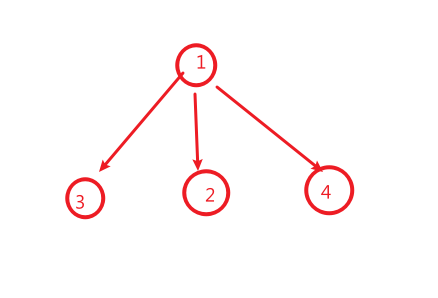
我们在搜索的时候会先搜到3
但是我们在建图的时候手动排序会:
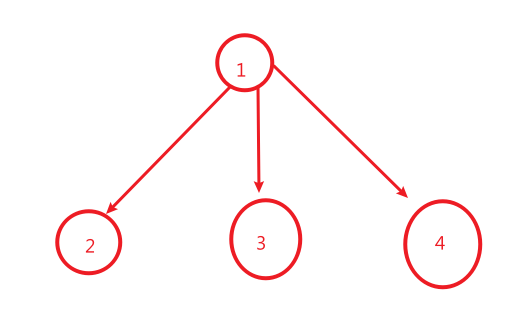
这个时候就优先搜索到2,为最小的
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10004;
int n, rd[N];
vector<int> sides[N];
int son[N];
int dfs(int root)
{
int maxd = 0;
son[root] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < sides[root].size(); i++)
{
int to = sides[root][i];
int dep = dfs(to);
if (maxd < dep)
{
maxd = dep;
son[root] = to;
}
}
return maxd + 1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int num;
cin >> num;
for (int j = 1; j <= num; j++)
{
int to;
cin >> to;
sides[i].push_back(to);
rd[to]++;
}
sort(sides[i].begin(), sides[i].end());
}
int root;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
if (rd[i] == 0)
{
root = i;
break;
}
cout << dfs(root) << endl;
cout << root;
root = son[root];
if (root != -1)
cout << " ";
while (root != -1)
{
cout << root;
root = son[root];
if (root != -1)
cout << " ";
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号