Codeforces Round #850 Div. 2
《B. Cake Assembly Line》
思维
题目大意:
给定n个蛋糕,其在x轴上占有范围[cl,cr]
还有n个巧克力喷管,其在x轴上也有范围[dl,dr]
现在就是问:
是否可以通过左右移动使得蛋糕的范围覆盖巧克力喷管的范围
解决方法:
显然:每一个蛋糕都对应于一个喷管 ,我们只要求一下每个蛋糕的最大移动范围,
然后求一下交集
如果交集不为空,则Yes
反之,No
对于移动:
1.可能是整体向左移
2.可能是整体向右移
3.可能两边都可以移
这个时候如果分类这样写代码,会写死 ,而且容易错
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 1e18;
struct node
{
ll minl, maxl, minr, maxr;
};
void solve()
{
int n, w, h;
cin >> n >> w >> h;
vector<int> a, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
a.push_back(t);
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
b.push_back(t);
}
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
vector<node> c;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ll cl = a[i] - w, cr = a[i] + w, dl = b[i] - h, dr = b[i] + h;
/* cout << "!!! " << cl << " " << cr << " " << dl << " " << dr << endl; */
// 一定要左移
if (cl > dl)
{
ll minl = cl - dl, maxl = minl + (cr - minl - dr);
c.push_back({minl, maxl, N, N});
}
// 一定要右移
else if (cr < dr)
{
ll minr = dr - cr, maxr = minr + (dl - (cl + minr));
c.push_back({N, N, minr, maxr});
}
else
{
ll minl = 0, maxl = cr - dr, minr = 0, maxr = dl - cl;
c.push_back({minl, maxl, minr, maxr});
}
/* cout << c[i].minl << " " << c[i].maxl << endl; */
}
bool flag1 = false, flag2 = false;
ll bminl = c[0].minl, bmaxl = c[0].maxl, bminr = c[0].minr, bmaxr = c[0].maxr;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (!flag1)
{
ll minl = c[i].minl, maxl = c[i].maxl;
if (bmaxl < minl || bminl > maxl)
{
flag1 = true;
}
bminl = max(bminl, minl), bmaxl = min(bmaxl, maxl);
}
if (!flag2)
{
ll minr = c[i].minr, maxr = c[i].maxr;
if (bmaxr < minr || bminr > maxr)
{
flag2 = true;
}
bminr = max(bminr, minr), bmaxr = min(bmaxr, maxr);
}
if (flag1 && flag2)
break;
}
if (flag1 && flag2)
{
cout << "No" << endl;
return;
}
if ((bminl != N && bminl <= bmaxl) || (bminr != N && bminr <= bmaxr))
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
对于只是想求一个交集是否为空
真的有必要要分的这么仔细吗?
不妨规定:
整体都向左移
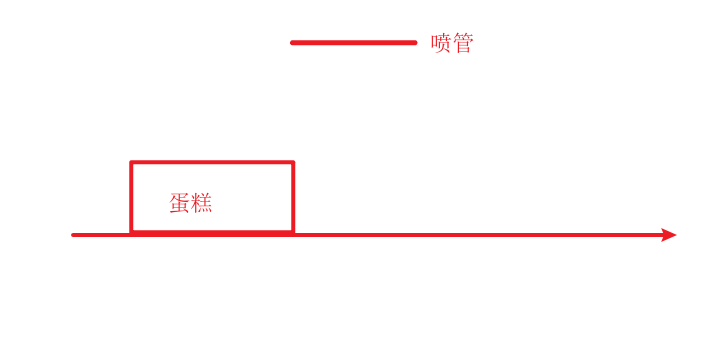
对于这样理论上必须右移的情况,
其实可以想象成,向左移动负数的距离
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 1e18;
struct node
{
ll minl, maxl, minr, maxr;
};
void solve()
{
int n, w, h;
cin >> n >> w >> h;
vector<int> a, b;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
a.push_back(t);
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
b.push_back(t);
}
sort(b.begin(), b.end());
ll l = a[0] - w - (b[0] - h), r = a[0] + w - (b[0] + h);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
// 假设全体向左移:
ll tl = a[i] - w - (b[i] - h), tr = a[i] + w - (b[i] + h);
l = max(l, tl), r = min(r, tr);
}
if (l <= r)
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
《D. Letter Exchange》
思维
题目大意:
给定n个人
每人有三个字符,每个字符只有 w,i,n中其中一个
每个人都可以与其他人交换字符
问:最小交互几次,使得每个人最后有的三个字符为:win
解决方法:
从贪心的角度:
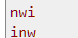
如这个案例,一次交换可以解决两个人的问题
明显应该优先处理这样的情况
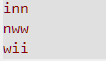
再如这个案例,
这个需要三个人之间进行多一次的交换
如果对于每个人有:可以用w来交换i
我们可以简记为:w->i
我们优先处理w->n,n->w的需求
再处理
1.w->i,i->n,n->w
2.w->n,n->i,i->w
的需求
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int get(char c)
{
if (c == 'w')
return 0;
else if (c == 'i')
return 1;
else
return 2;
}
char getI(int c)
{
if (c == 0)
return 'w';
else if (c == 1)
return 'i';
else
return 'n';
}
struct node
{
int pa, na, pb, nb;
};
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> a(3, vector<vector<int>>(3));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
string str;
cin >> str;
bool st[3] = {0, 0, 0};
int to = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++)
{
int c = get(str[j]);
if (st[c])
to = c;
else
st[c] = true;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if (!st[j])
a[to][j].push_back(i);
}
queue<node> q;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
while (a[i][j].size() && a[j][i].size())
{
q.push({a[i][j].back(), i, a[j][i].back(), j});
a[i][j].pop_back(), a[j][i].pop_back();
}
}
while (a[0][1].size() && a[1][2].size() && a[2][0].size())
{
q.push({a[0][1].back(), 0, a[1][2].back(), 1});
q.push({a[1][2].back(), 0, a[2][0].back(), 2});
a[0][1].pop_back(), a[1][2].pop_back(), a[2][0].pop_back();
}
while (a[0][2].size() && a[2][1].size() && a[1][0].size())
{
q.push({a[0][2].back(), 0, a[2][1].back(), 2});
q.push({a[2][1].back(), 0, a[1][0].back(), 1});
a[0][2].pop_back(), a[2][1].pop_back(), a[1][0].pop_back();
}
cout << q.size() << endl;
while (q.size())
{
node t = q.front();
cout << t.pa << " " << getI(t.na) << " " << t.pb << " " << getI(t.nb) << endl;
q.pop();
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号