第十三届蓝桥杯省赛C++B组
《X 进制减法》
贪心,数学推导
题目连接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/4407/
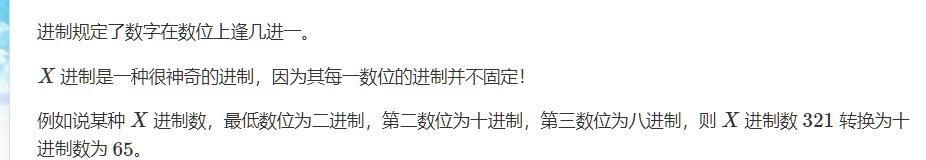
我们先来看一下这个65是如何算出来的:
321:第一位为二进制,则逢2进1,ans+=1;
第二位为十进制,其上的数为2,它是由第一位进了两次位得来:即ans+=2*2;
第三位为八进制,其上的数为3,它是由第二位进了3次位得来,而第二位进3次位需要第二位为30,而第二位为30需要第一位为30*2=60;即ans+=3*10*2;
ans=65;
可以得到:对于数A:设ai为其第i位上的数值,pi为这一位上的进制
则其十进制下为:an*积(pn-1*....*p1)+an-1*积(pn-2*...*p1)+.....+a2*p1+a1;
则对于:A-B的最小值,我们可以贪心,因为数据保证A>B,则我们可以猜想在每一位上的进制最小的情况下为A-B最小:
具体证明:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/103200/
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 using namespace std;
5 typedef long long ll;
6 const int N = 1e5 + 10;
7 const ll mod = 1000000007;
8 ll a[N], b[N];
9 int ma, mb, n;
10 int main()
11 {
12 cin >> n;
13 cin >> ma;
14 for (int i = ma; i >= 1; i--)
15 scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
16 cin >> mb;
17 for (int i = mb; i >= 1; i--)
18 scanf("%lld", &b[i]);
19 ll ans = 0;
20 ll p = 1;
21 for (int i = 1; i <= ma; i++)
22 {
23 ans = (ans + (a[i] - b[i]) * p) % mod;
24 p = (p * max(max(a[i] + 1, b[i] + 1), (ll)2)) % mod;
25 }
26 cout << ans;
27 return 0;
28 }
《统计子矩阵》
二维双指针算法,二维前缀和
题目连接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/4408/

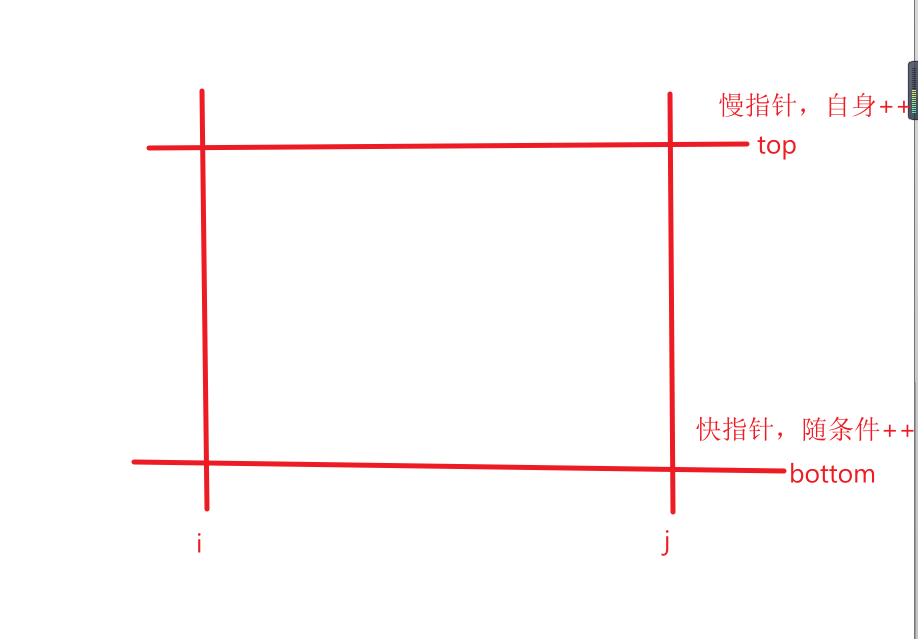
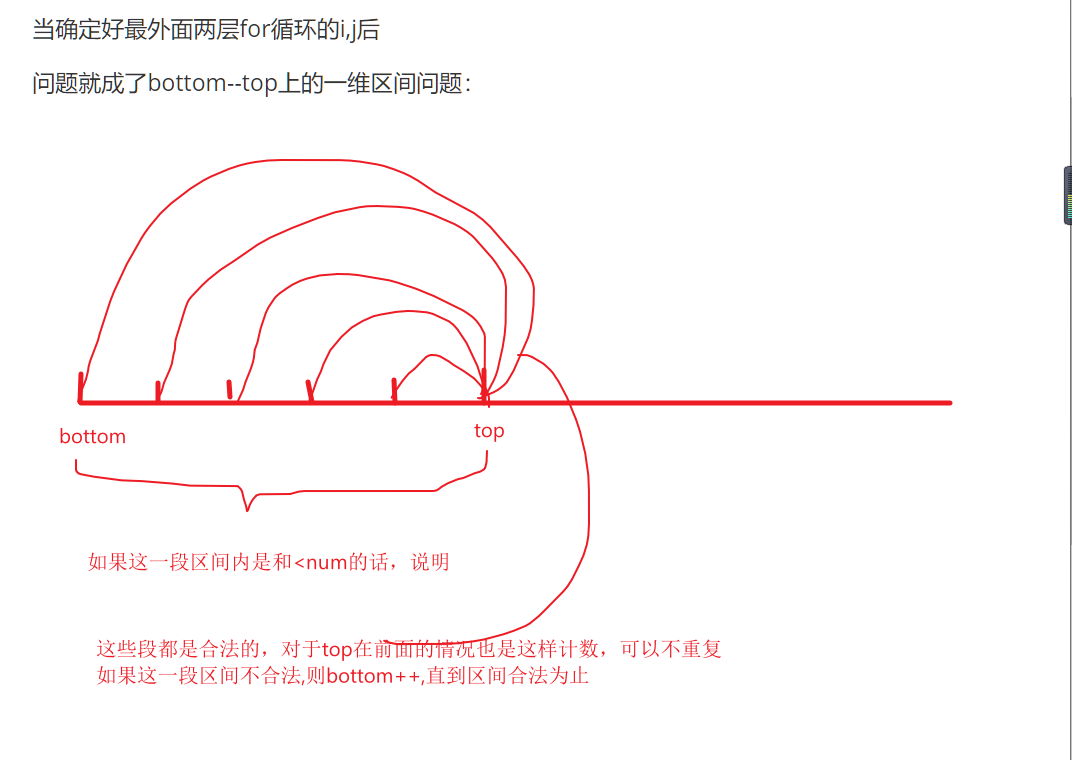
很明显的双指针与前缀和,因为这里我们要枚举子矩阵的话如果是n^4会超时(n^3都是1.25*1e8有点吃紧)
而双指针就是利用单调关系,将n^2优化为n的算法
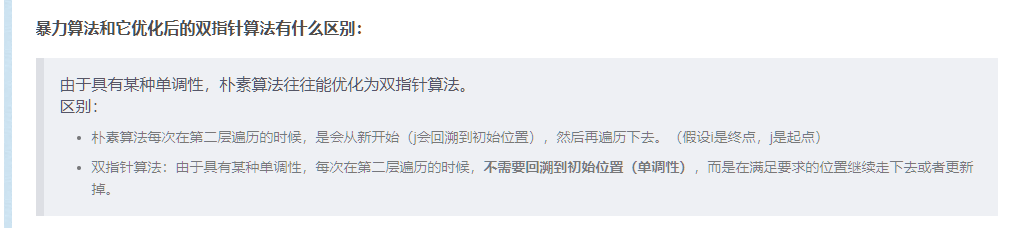
双指针算法的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54773252/article/details/122836179
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 using namespace std;
5 const int N = 501;
6 int g[N][N], pre[N][N], n, m, k;
7 int main()
8 {
9 cin >> n >> m >> k;
10 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
11 for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
12 scanf("%d", &g[i][j]);
13 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
14 for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
15 pre[i][j] = pre[i - 1][j] + pre[i][j - 1] - pre[i - 1][j - 1] + g[i][j];
16 long long ans = 0;
17 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
18 for (int j = i; j <= m; j++)
19 for (int top = 1, bottom = 1; top <= n && bottom <= n; top++)
20 {
21 int num = pre[top][j] - pre[top][i - 1] - pre[bottom - 1][j] + pre[bottom - 1][i - 1];
22 while (bottom < top && num > k)
23 {
24 bottom++;
25 num = pre[top][j] - pre[top][i - 1] - pre[bottom - 1][j] + pre[bottom - 1][i - 1];
26 }
27 if (num <= k)
28 ans += (top - bottom + 1);
29 }
30 cout << ans;
31 return 0;
32 }
《积木画》
线性dp
题目连接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/4409/

这道题唯一要注意的是:状态的转移方式
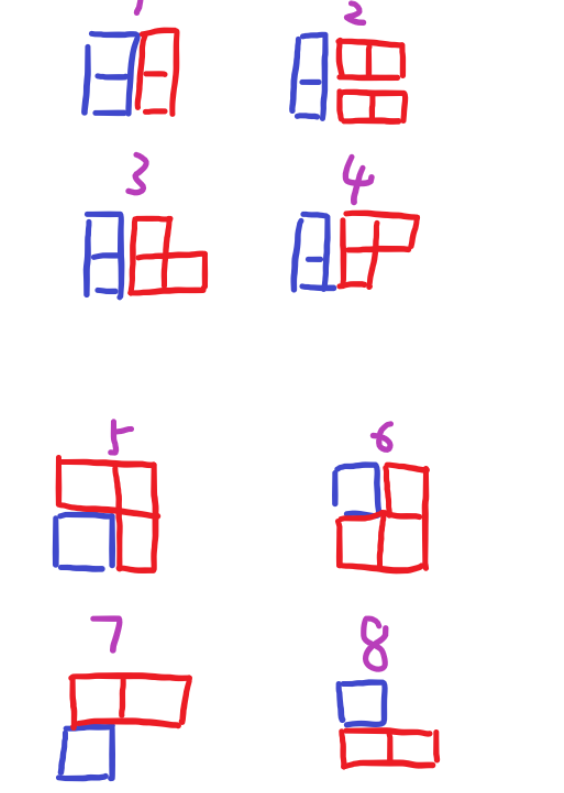
这个状态的转移方式是比较好的
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 using namespace std;
5 const int N = 1e7 + 5, mod = 1000000007;
6 //dp[i][j]:表示1—i-1的都全部装满,而且第i列的状态为j
7 //1表示这一列下面有,2表示上面有,3表示都有
8 int dp[N][3], n;
9 int main()
10 {
11 cin >> n;
12 dp[0][3] = 1;
13 dp[1][3] = 1;
14 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
15 {
16 dp[i][1] = (dp[i][1] + dp[i - 2][3] + dp[i - 1][2]) % mod;
17 dp[i][2] = (dp[i][2] + dp[i - 2][3] + dp[i - 1][1]) % mod;
18 dp[i][3] = (dp[i][3] + (dp[i - 1][2] + dp[i - 1][1]) % mod + (dp[i - 1][3] + dp[i - 2][3]) % mod) % mod;
19 }
20 cout << dp[n][3];
21 return 0;
22 }
《 扫雷》
图论,dfs,哈希

现在的我看一下确实是明显的图论(当时完全没看出来),r十分小,完全可以对于每一个导弹枚举其周围是否有可以炸到的导弹
如果有可以转移过去,然后就像普通dfs或bfs一样,有点像找连通块的个数?
虽然但是map的常数有点大,下面的这份代码会超时,但是对的:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <map>
5 #include <vector>
6 #include <cmath>
7 using namespace std;
8 typedef pair<int, int> PII;
9 int n, m;
10 struct node
11 {
12 int r = 0, times = 0;
13 bool vis = false;
14 };
15 map<PII, node> mapp;
16 vector<PII> start;
17 int ans = 0;
18 void dfs(int x, int y)
19 {
20 ans += mapp[{x, y}].times;
21 mapp[{x, y}].vis = true;
22 int r = mapp[{x, y}].r;
23 for (int i = x - r; i <= x + r; i++)
24 for (int j = y - r; j <= y + r; j++)
25 {
26 if (sqrt((i - x) * (i - x) + (j - y) * (j - y)) <= r)
27 {
28 if (!mapp[{i, j}].vis && mapp[{i, j}].times > 0)
29 dfs(i, j);
30 }
31 }
32 }
33 int main()
34 {
35 cin >> n >> m;
36 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
37 {
38 int x, y, r;
39 scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &r);
40 if (mapp[{x, y}].times > 0)
41 {
42 if (mapp[{x, y}].r < r)
43 {
44 mapp[{x, y}].r = r;
45 mapp[{x, y}].times++;
46 }
47 else
48 mapp[{x, y}].times++;
49 }
50 else
51 {
52 mapp[{x, y}].r = r;
53 mapp[{x, y}].times++;
54 }
55 }
56 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
57 {
58 int x, y, r;
59 scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &r);
60 if (mapp[{x, y}].times > 0)
61 {
62 if (mapp[{x, y}].r < r)
63 {
64 mapp[{x, y}].r = r;
65 mapp[{x, y}].times++;
66 }
67 else
68 mapp[{x, y}].times++;
69 }
70 else
71 {
72 mapp[{x, y}].r = r;
73 mapp[{x, y}].times++;
74 }
75 start.push_back({x, y});
76 }
77 for (int i = 0; i < start.size(); i++)
78 {
79 int x = start[i].first, y = start[i].second;
80 if (!mapp[{x, y}].vis)
81 dfs(x, y);
82 }
83 cout << ans - m;
84 return 0;
85 }
《李白打酒》
线性dp
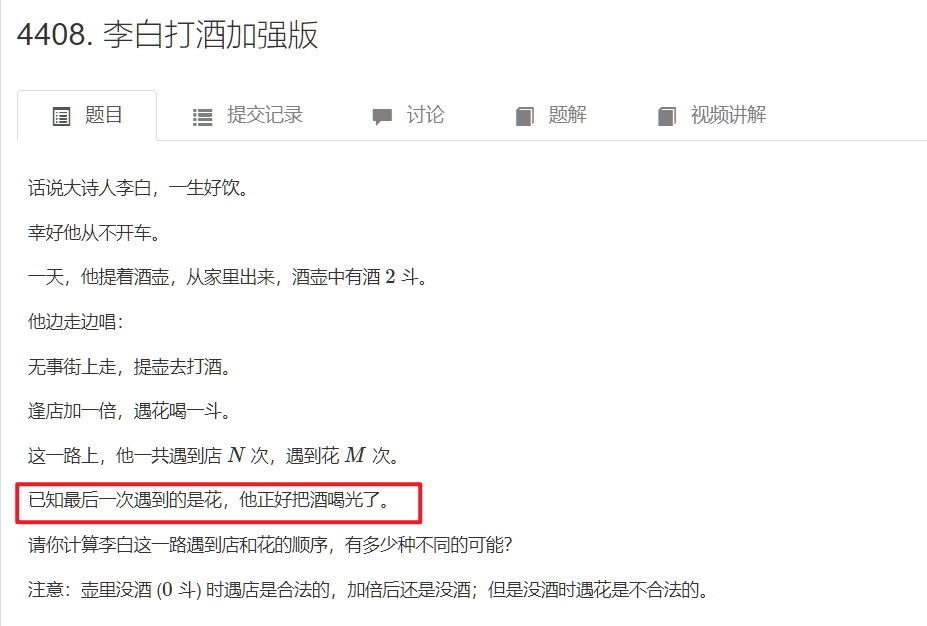
这道题我的评价是:我要看清楚最后问的状态是什么,即要输出如下
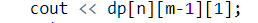
而不是输出:dp[n][m][0];
《砍竹子》
思维题
题目连接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/4412/

这道题的关键是在看清楚即使是h=1--1e18,也可以只最多经过上面6次运算后变成1后
如何对区间连续进行操作?答案是用堆先选出最高的竹子,砍去,然后再看下一个最高的竹子是否是与上一个最高的竹子连续,以此类推
这道题有个明显的想法是先去砍最高的竹子
其实这里我们就可以想到用优先队列了,优先队列的第一排序是高度,然后第二排序是竹子的位置:即在高度相等的情况下
位置越前的优先级越大,这样方便我们对连续相同高度的竹子进行处理
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstring>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <queue>
5 #include <vector>
6 #include <cmath>
7 using namespace std;
8 struct node
9 {
10 long long h;
11 int pos;
12 bool operator<(const node &b) const
13 {
14 // pos小的具有较高优先级
15 if (h == b.h)
16 return pos > b.pos;
17 // h大的具有较高优先级
18 return h < b.h;
19 }
20 };
21 priority_queue<node> heap;
22 int n, ans = 0;
23 long long get(long long h)
24 {
25 return (long long)(sqrt(h / 2 + 1));
26 }
27 int main()
28 {
29 cin >> n;
30 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
31 {
32 long long h;
33 scanf("%lld", &h);
34 heap.push(node({h, i}));
35 }
36 while (heap.size())
37 {
38 long long maxh = heap.top().h;
39 int pos = heap.top().pos;
40 heap.pop();
41 if (maxh <= 1)
42 break;
43 heap.push(node({get(maxh), pos}));
44 int neh = heap.top().h, nepos = heap.top().pos;
45 while (neh == maxh && nepos == pos + 1)
46 {
47 heap.pop();
48 heap.push(node({get(neh), nepos}));
49 pos = nepos;
50 neh = heap.top().h, nepos = heap.top().pos;
51 }
52 ans++;
53 }
54 cout << ans;
55 return 0;
56 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号