树上区间问题----树链剖分
本博客主要是对前辈们的内容我认为好的部分摘取过来了
《入门》
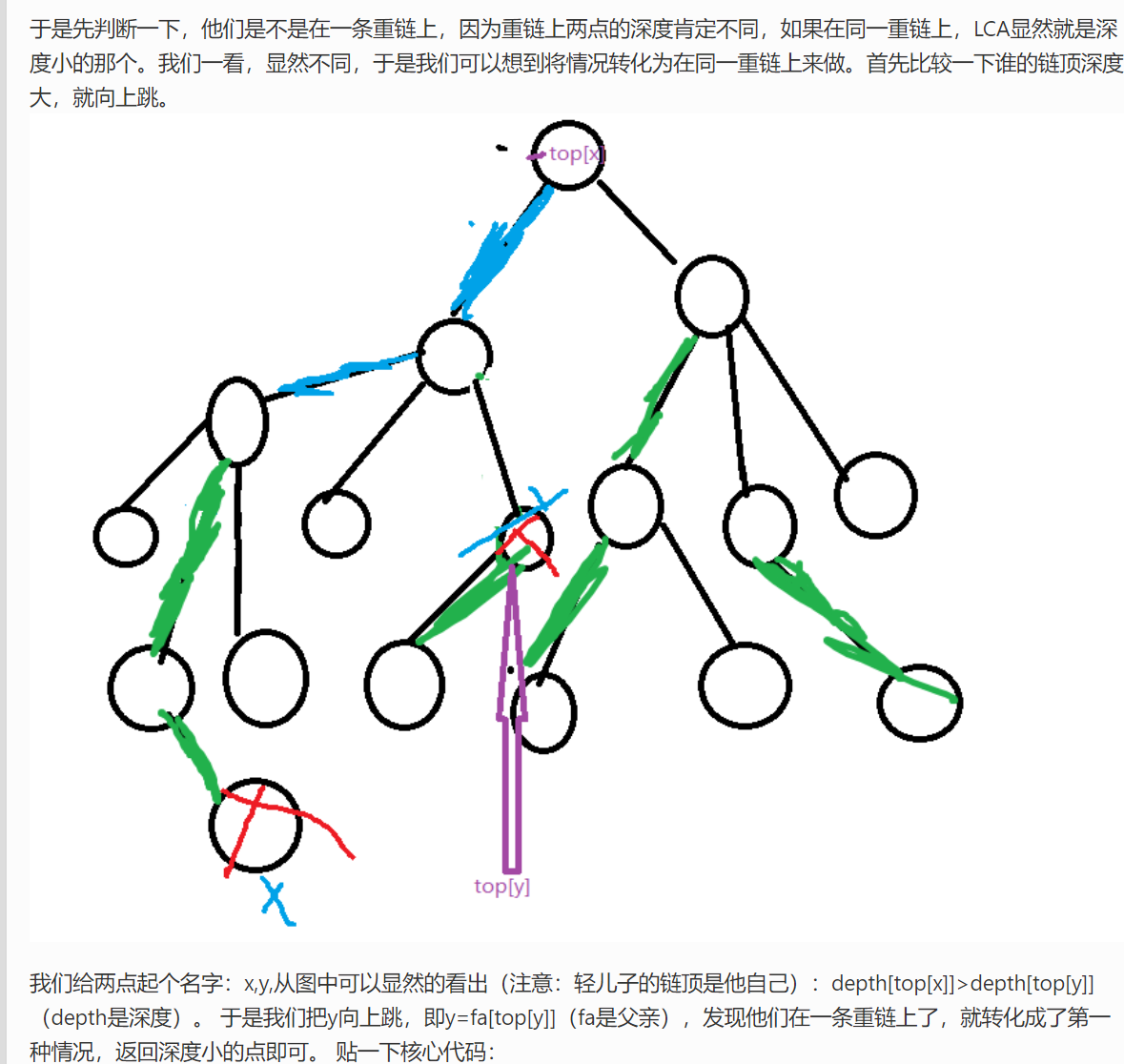
LCA用轻重链剖分解决:
好博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/ivanovcraft/p/9019090.html
https://www.luogu.com.cn/blog/by-random/solution-p3379




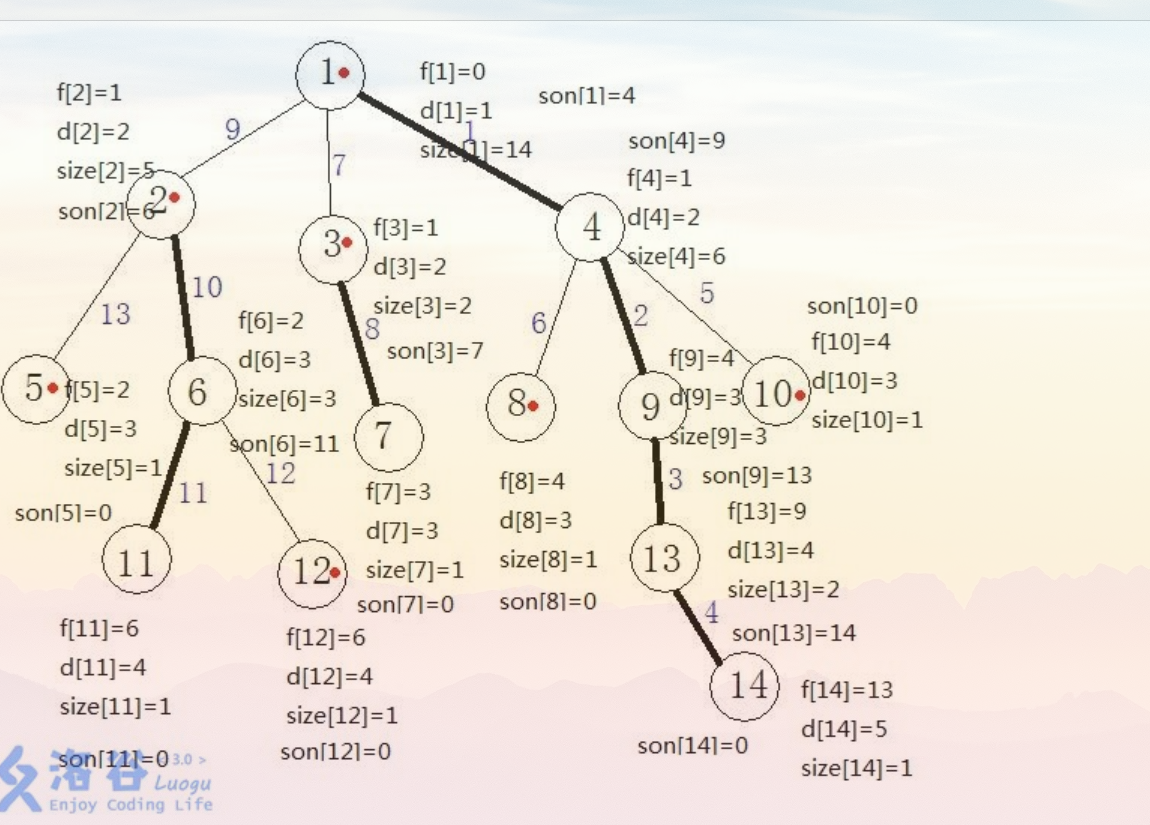

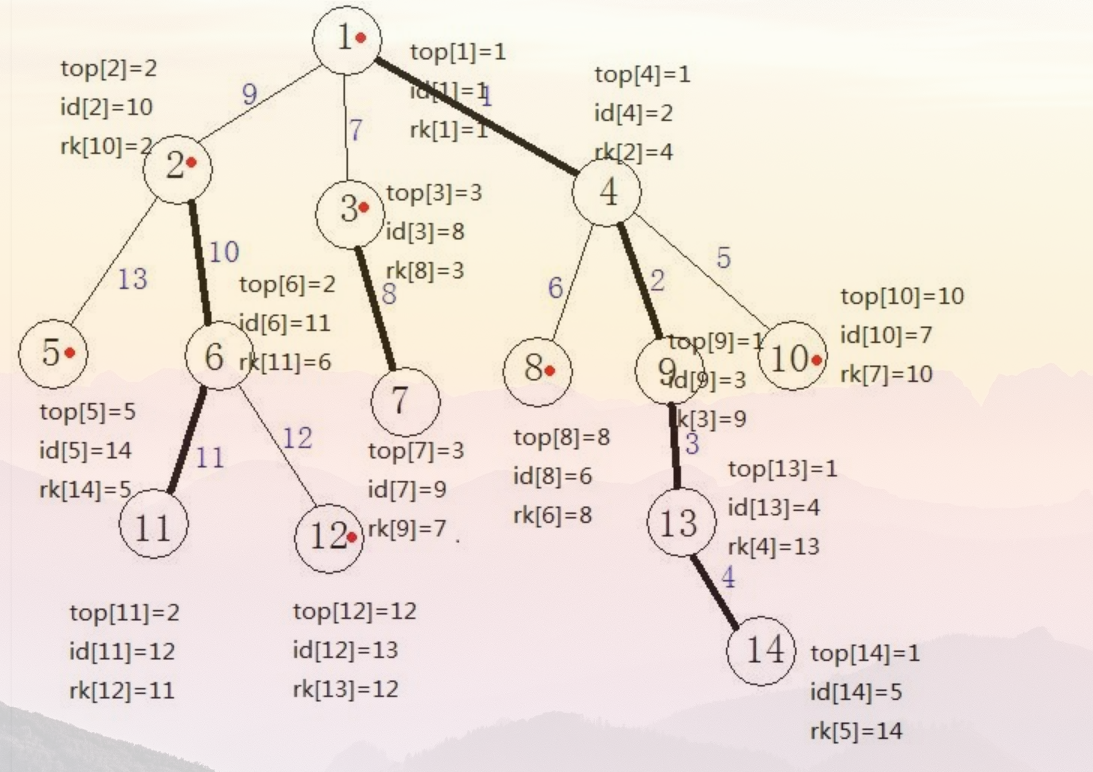
//因为这个只是入门树剖,还没有用上线段树,所以像id[],size[]等这些数组没有用上
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 500010;
vector<int> tree[N];
int n, m, s;
//节点的父节点,重子儿子,深度,子树的大小
//规定:根节点dep=1,f=0; size包含自身;
int f[N], son[N], dep[N], size[N];
bool st[N];
//求出节点的f,son,dep,size
void dfs1(int s)
{
if (!st[s])
{
st[s] = true;
size[s] += 1;
int maxv = 0, v = s;
for (int i = 0; i < tree[s].size(); i++)
{
int child = tree[s][i];
if (!st[child])
{
dep[child] = dep[s] + 1;
f[child] = s;
dfs1(child);
size[s] += size[child];
if (size[child] > maxv)
{
maxv = size[child];
v = child;
}
}
}
son[s] = v;
}
}
//规定:根节点top=自己,轻链top=自己
int top[N];
// dfs2将重链的链顶改变
void dfs2(int s)
{
if (!st[s])
{
st[s] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < tree[s].size(); i++)
{
int child = tree[s][i];
if (!st[child] && son[s] == child)
top[child] = top[s];
dfs2(child);
}
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s);
for (int i = 1; i <= n-1; i++)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
tree[a].push_back(b), tree[b].push_back(a);
}
f[s] = 0, dep[s] = 1;
dfs1(s);
memset(st, false, sizeof(st));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
top[i] = i;
dfs2(s);
while (m--)
{
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
while (top[a] != top[b])
{
//将a与b跳到同一条链上
//指定a是dep[top[a]]更大的
if (dep[top[a]] < dep[top[b]])
swap(a, b);
a = f[top[a]];
}
int res = dep[a] < dep[b] ? a : b;
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
《轻重链剖分》
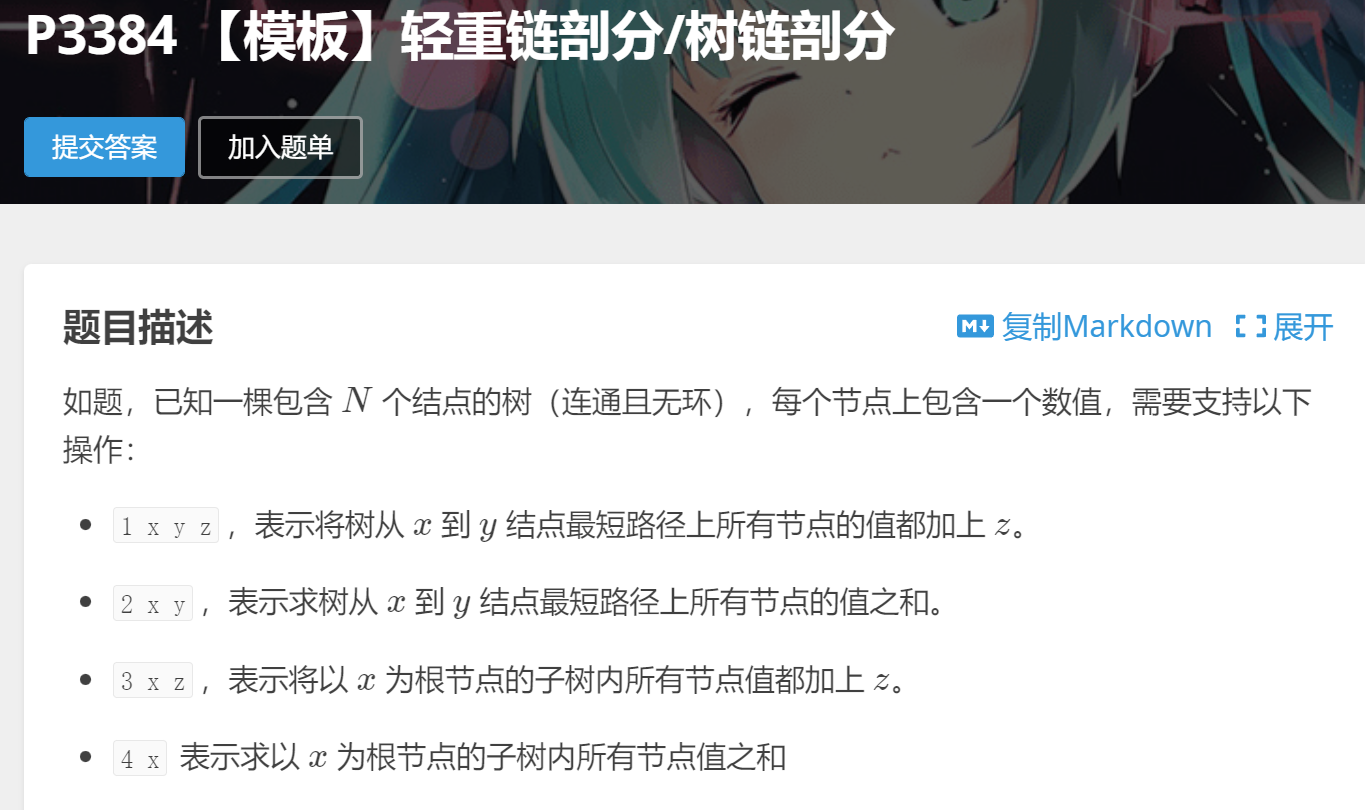
原题:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3384




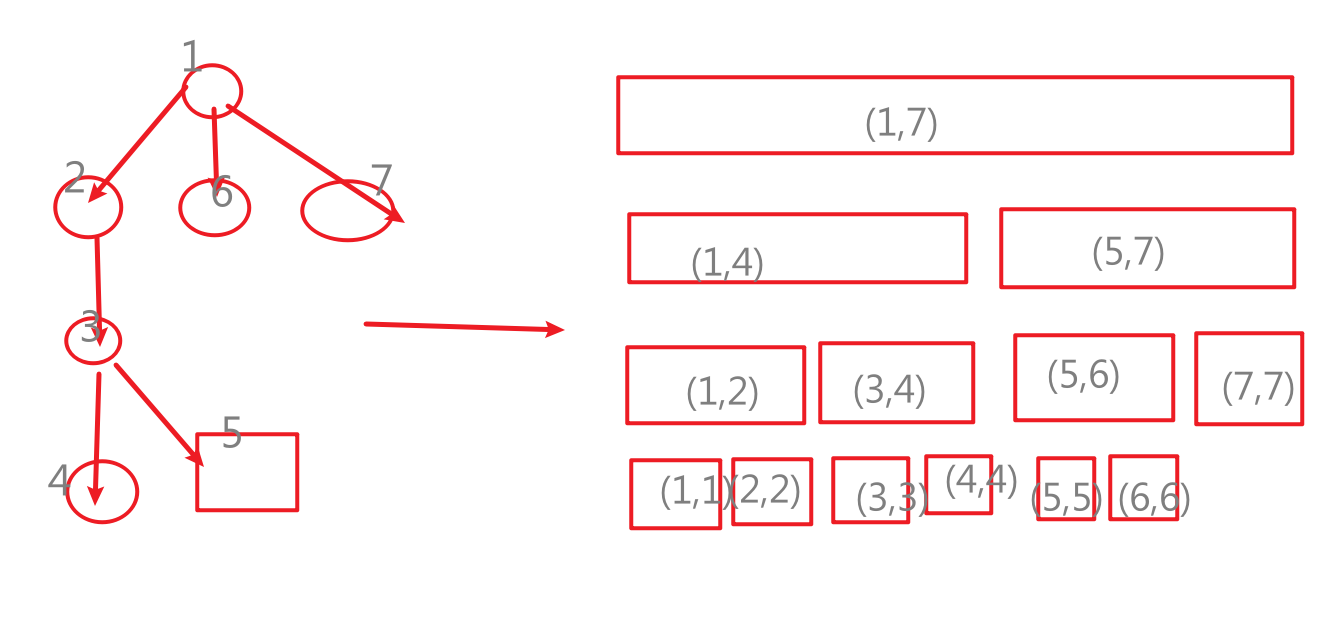
然后我们用dfs序编号去建立新的区间,用线段树管理
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <vector>
5 using namespace std;
6 typedef long long LL;
7 const int N = 1e5 + 5;
8 int n, m, r, p, a[N];
9 vector<int> tree[N];
10 int f[N], son[N], sizer[N], dep[N];
11 bool st[N];
12 void dfs1(int x)
13 {
14 if (!st[x])
15 {
16 st[x] = true;
17 sizer[x] = 1;
18 int maxv = 0, v = x;
19 for (int i = 0; i < tree[x].size(); i++)
20 {
21 int child = tree[x][i];
22 if (!st[child])
23 {
24 f[child] = x;
25 dep[child] = dep[x] + 1;
26 dfs1(child);
27 sizer[x] += sizer[child];
28 if (maxv < sizer[child])
29 {
30 //我曾经的错误点
31 maxv = sizer[child];
32 v = child;
33 }
34 }
35 }
36 son[x] = v;
37 }
38 }
39 // id[i]是原来树上的点i对应的dfs编号是id[i]
40 // rk[i]是dfs编号i对应原来树上的点是rk[i]
41 // top[i]是树上的点i的链顶为top[i]
42 int id[N], rk[N], top[N], cnt = 0;
43 //先遍历重链
44 //这个函数的意义是:节点x的链顶为t,其这一条重链上的链顶均为t
45 void dfs2(int x, int t)
46 {
47 if (!st[x])
48 {
49 st[x] = true;
50 ++cnt;
51 id[x] = cnt, rk[cnt] = x;
52 top[x] = t;
53 dfs2(son[x], t);
54 //遍历是轻链的子节点
55 for (int i = 0; i < tree[x].size(); i++)
56 {
57 int child = tree[x][i];
58 //轻链的top是自己
59 if (!st[child])
60 dfs2(child, child);
61 }
62 }
63 }
64 //以上是剖分基础
65
66 //以下是线段树的操作:
67 struct SegTree
68 {
69 int l, r, sz, sum, lazy;
70 } tr[N * 4];
71 void pushup(int u)
72 {
73 tr[u].sum = (1LL * tr[u << 1].sum + tr[u << 1 | 1].sum) % p;
74 }
75 void pushdown(int u)
76 {
77 if (tr[u].lazy)
78 {
79 int sl = u << 1, sr = u << 1 | 1;
80 //注意lazy是+=
81 tr[sl].lazy += tr[u].lazy;
82 tr[sr].lazy += tr[u].lazy;
83 tr[sl].sum = (1LL * tr[sl].sum + tr[sl].sz * tr[u].lazy) % p;
84 tr[sr].sum = (1LL * tr[sr].sum + tr[sr].sz * tr[u].lazy) % p;
85 tr[u].lazy = 0;
86 }
87 }
88 void build(int u, int l, int r)
89 {
90 tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r, tr[u].sz = r - l + 1, tr[u].lazy = 0;
91 if (l == r)
92 {
93 tr[u].sum = a[rk[l]] % p;
94 return;
95 }
96 int mid = l + r >> 1;
97 build(u << 1, l, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
98 //我的错误点:
99 pushup(u);
100 }
101 void modify(int u, int l, int r, int d)
102 {
103 if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r)
104 {
105 tr[u].sum = (1LL * tr[u].sum + tr[u].sz * d) % p;
106 tr[u].lazy += d;
107 return;
108 }
109 pushdown(u);
110 int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
111 if (l <= mid)
112 modify(u << 1, l, r, d);
113 if (r > mid)
114 modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r, d);
115 pushup(u);
116 }
117 int query(int u, int l, int r)
118 {
119 if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r)
120 return tr[u].sum;
121 pushdown(u);
122 int res = 0;
123 int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
124 /* cout << "mid: " << mid << endl; */
125 if (l <= mid)
126 res = (1LL * res + query(u << 1, l, r)) % p;
127 if (r > mid)
128 res = (1LL * res + query(u << 1 | 1, l, r)) % p;
129 /* cout << "query:" << res << endl; */
130 return res % p;
131 }
132
133 //以下是对树上的操作
134 //这个基本思路是:
135 //让链顶深度更大的节点向更小的节点的那条链跳,每一次跳都找出这个节点
136 //的链顶,然后线段树操作(假设这个节点为i):modify(1,id[i],id[top[i]],d);
137 //因为分链,每一个点到链顶的id编号是连续的,可以如上操作
138 void rangeAdd(int x, int y, int d)
139 {
140 //不在一条链上
141 while (top[x] != top[y])
142 {
143 //注意这里这样写是错误的,没有考虑两条轻链的情况
144 /* cout<<id[x]<<" "<<id[y]<<endl;
145 modify(1, id[top[x]], id[x], d);
146 x = f[top[x]]; */
147 //规定x是那个要跳的点
148 if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]])
149 swap(x, y);
150 modify(1, id[top[x]], id[x], d);
151 x = f[top[x]];
152 }
153 //到了一条链上,让x为深度更低的点
154 if (dep[x] > dep[y])
155 swap(x, y);
156 /* cout << id[x] << " " << id[y] << endl; */
157 modify(1, id[x], id[y], d);
158 }
159 //基本思路是:让链顶深度更大的节点向更小的节点的那条链跳,每一次跳都找出这个节点
160 //的链顶,然后线段树操作(假设这个节点为i):query(1,id[i],id[top[i]],d);
161 //用res变量记录答案
162 int rangeSum(int x, int y)
163 {
164 int res = 0;
165 while (top[x] != top[y])
166 {
167 if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]])
168 swap(x, y);
169 res = (1LL * res + query(1, id[top[x]], id[x])) % p;
170 x = f[top[x]];
171 }
172 if (dep[x] > dep[y])
173 swap(x, y);
174 res = (1LL * res + query(1, id[x], id[y])) % p;
175 return res % p;
176 }
177 void treeAdd(int x, int z)
178 {
179 //子树的id完全是有序的
180 /* cout <<"!!!!!!"<<id[x] << " " << id[x] + sizer[x] - 1 << endl; */
181 modify(1, id[x], id[x] + sizer[x] - 1, z);
182 }
183 int treeSum(int x)
184 {
185 /* cout << "!!!!!!" << id[x] << " " << id[x] + sizer[x] - 1 << endl; */
186 return query(1, id[x], id[x] + sizer[x] - 1) % p;
187 }
188
189 int main()
190 {
191 scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &r, &p);
192 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
193 scanf("%d", &a[i]);
194 for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
195 {
196 int a, b;
197 scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
198 tree[a].push_back(b), tree[b].push_back(a);
199 }
200 f[r] = 0, dep[r] = 1;
201 dfs1(r);
202 memset(st, false, sizeof(st));
203 dfs2(r, r);
204 /* for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
205 cout << "i: " << i << " "
206 << "f: " << f[i] << " "
207 << "son: " << son[i] << " "
208 << "sizer: " << sizer[i] << " "
209 << "dep: " << dep[i] << " "
210 << "top: " << top[i] << " "
211 << "id: " << id[i] << " "
212 << "rk: " << rk[i] << " "
213 << "a[i]:" << a[i] << endl; */
214 build(1, 1, n);
215 /* cout << "1: " << tr[8].sum << " "
216 << "2: " << tr[9].sum << " "
217 << "3: " << tr[10].sum << " "
218 << "4: " << tr[11].sum << " "
219 << "5: " << tr[12].sum << " "
220 << "6: " << tr[13].sum << " "
221 << "7: " << tr[14].sum << " "
222 << "8: " << tr[15].sum << endl; */
223 while (m--)
224 {
225
226 int op, x, y, z;
227 scanf("%d", &op);
228 if (op == 1)
229 {
230 scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z);
231 rangeAdd(x, y, z);
232 /* cout << "success" << endl; */
233 }
234 else if (op == 2)
235 {
236 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
237 printf("%d\n", rangeSum(x, y));
238 }
239 else if (op == 3)
240 {
241 scanf("%d%d", &x, &z);
242 treeAdd(x, z);
243 }
244 else if (op == 4)
245 {
246 scanf("%d", &x);
247 printf("%d\n", treeSum(x));
248 }
249 }
250 return 0;
251 }
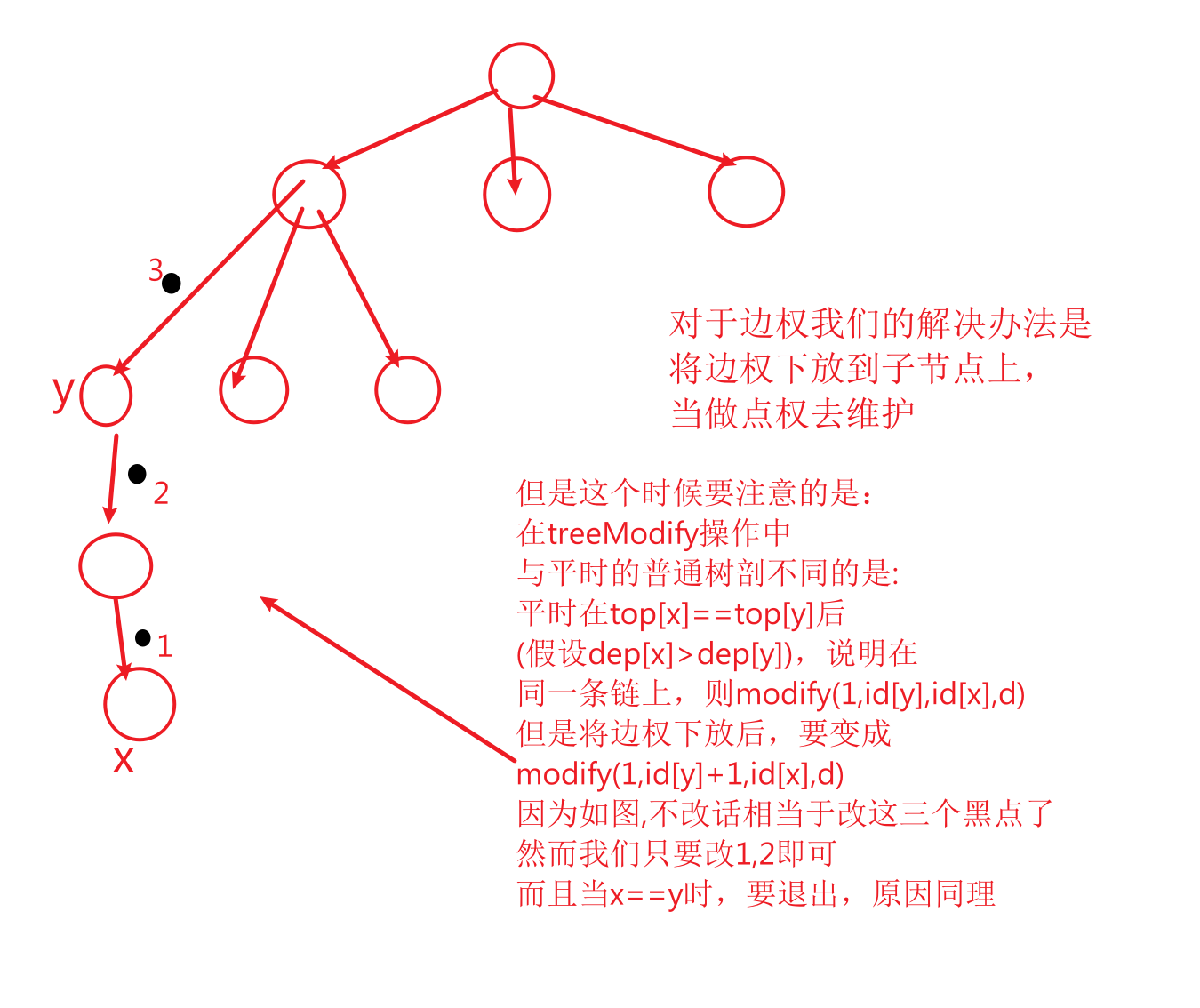
《边上操作》

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <vector>
5 using namespace std;
6 const int N = 1e5 + 5;
7 int n, m, r, p;
8 vector<int> tree[N];
9
10 int f[N], son[N], sizer[N], dep[N];
11 //根节点from为自己
12 void dfs1(int x, int from, int d)
13 {
14 f[x] = from, son[x] = -1, sizer[x] = 1, dep[x] = d;
15 for (int i = 0; i < tree[x].size(); i++)
16 {
17 int child = tree[x][i];
18 //在树上相当于不要回到父节点
19 if (child == from)
20 continue;
21 dfs1(child, x, d + 1);
22 sizer[x] += sizer[child];
23 if (son[x] == -1 || sizer[son[x]] < sizer[child])
24 son[x] = child;
25 }
26 }
27 int id[N], rk[N], top[N], cnt = 0;
28 //根节点与轻链的top为自己
29 void dfs2(int x, int t, int from)
30 {
31 cnt++;
32 id[x] = cnt, rk[cnt] = x, top[x] = t;
33 //先走重链
34 if (son[x] != -1)
35 dfs2(son[x], t, x);
36 for (int i = 0; i < tree[x].size(); i++)
37 {
38 int child = tree[x][i];
39 if (child == son[x] || child == from)
40 continue;
41 dfs2(child, child, x);
42 }
43 }
44 //以上是剖分基础
45
46 //以下是线段树的操作:
47 struct SegTree
48 {
49 int l, r, sz, sum, lazy;
50 } tr[N * 4];
51 void pushup(int u)
52 {
53 tr[u].sum = tr[u << 1 | 1].sum + tr[u << 1].sum;
54 }
55 void pushdown(int u)
56 {
57 if (tr[u].lazy)
58 {
59 int sl = u << 1, sr = u << 1 | 1;
60 tr[sl].lazy += tr[u].lazy;
61 tr[sr].lazy += tr[u].lazy;
62 tr[sl].sum += tr[sl].sz * tr[u].lazy;
63 tr[sr].sum += tr[sr].sz * tr[u].lazy;
64 tr[u].lazy = 0;
65 }
66 }
67 void build(int u, int l, int r)
68 {
69 tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r, tr[u].sz = r - l + 1, tr[u].lazy = 0;
70 if (l == r)
71 {
72 tr[u].sum = 0;
73 return;
74 }
75 int mid = l + r >> 1;
76 build(u << 1, l, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
77 pushup(u);
78 }
79 void modify(int u, int l, int r, int d)
80 {
81 if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r)
82 {
83 tr[u].sum += tr[u].sz * d;
84 tr[u].lazy += d;
85 return;
86 }
87 pushdown(u);
88 int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
89 if (r <= mid)
90 modify(u << 1, l, r, d);
91 else if (l > mid)
92 modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r, d);
93 else
94 modify(u << 1, l, r, d), modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r, d);
95 pushup(u);
96 }
97 int query(int u, int l, int r)
98 {
99 if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r)
100 return tr[u].sum;
101 pushdown(u);
102 int res = 0;
103 int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1;
104 if (r <= mid)
105 res = query(u << 1, l, r);
106 else if (l > mid)
107 res = query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
108 else
109 res = query(u << 1, l, r) + query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
110 return res;
111 }
112 void treeModify(int x, int y)
113 {
114 while (top[x] != top[y])
115 {
116 if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]])
117 swap(x, y);
118 modify(1, id[top[x]], id[x], 1);
119 x = f[top[x]];
120 }
121 if (x == y)
122 return;
123 else
124 {
125 if (dep[x] < dep[y])
126 swap(x, y);
127 modify(1, id[y] + 1, id[x], 1);
128 }
129 }
130 int main()
131 {
132 pair<int, int> side[N];
133 scanf("%d", &n);
134 for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
135 {
136 int a, b;
137 scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
138 side[i] = {a, b};
139 tree[a].push_back(b), tree[b].push_back(a);
140 }
141 dfs1(1, 1, 1);
142 dfs2(1, 1, 1);
143 build(1, 1, n);
144 scanf("%d", &m);
145 while (m--)
146 {
147 int x, y;
148 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
149 treeModify(x, y);
150 }
151 for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++)
152 {
153 int x = side[i].first, y = side[i].second;
154 if (dep[x] > dep[y])
155 swap(x, y);
156 printf("%d ", query(1, id[y], id[y]));
157 }
158 return 0;
159 }
《暴毙点》
《1.》


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <vector> 5 using namespace std; 6 const int N = 200005; 7 int n, m, r, a[N]; 8 vector<int> tree[N]; 9 int f[N], son[N], sizer[N], dep[N]; 10 bool st[N]; 11 void dfs1(int x) 12 { 13 if (!st[x]) 14 { 15 st[x] = true; 16 sizer[x] = 1; 17 int maxv = 0, v = x; 18 for (int i = 0; i < tree[x].size(); i++) 19 { 20 int child = tree[x][i]; 21 if (!st[child]) 22 { 23 f[child] = x; 24 dep[child] = dep[x] + 1; 25 dfs1(child); 26 sizer[x] += sizer[child]; 27 if (maxv < sizer[child]) 28 { 29 //我曾经的错误点 30 maxv = sizer[child]; 31 v = child; 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 son[x] = v; 36 } 37 } 38 int id[N], rk[N], top[N], cnt = 0; 39 void dfs2(int x, int t) 40 { 41 if (!st[x]) 42 { 43 st[x] = true; 44 ++cnt; 45 id[x] = cnt, rk[cnt] = x; 46 top[x] = t; 47 dfs2(son[x], t); 48 //遍历是轻链的子节点 49 for (int i = 0; i < tree[x].size(); i++) 50 { 51 int child = tree[x][i]; 52 //轻链的top是自己 53 if (!st[child]) 54 dfs2(child, child); 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 //以下是线段树的操作: 60 struct SegTree 61 { 62 // lazy 0是不要改变的意思,1是要改变的意思 63 int l, r, sz, sum, lazy; 64 } tr[N * 4]; 65 void pushup(int u) 66 { 67 tr[u].sum = tr[u << 1].sum + tr[u << 1 | 1].sum; 68 } 69 void pushdown(int u) 70 { 71 if (tr[u].lazy) 72 { 73 int sl = u << 1, sr = u << 1 | 1; 74 tr[sl].lazy ^= 1; 75 tr[sr].lazy ^= 1; 76 /* cout << "@" << sl << " " << tr[sl].sum << endl; 77 cout << "@" << sr << " " << tr[sr].sum << endl; */ 78 tr[sl].sum = tr[sl].sz - tr[sl].sum; 79 tr[sr].sum = tr[sr].sz - tr[sr].sum; 80 /* cout << "#" << sl << " " << tr[sl].sum << endl; 81 cout << "#" << sr << " " << tr[sr].sum << endl; */ 82 tr[u].lazy = 0; 83 } 84 } 85 void build(int u, int l, int r) 86 { 87 tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r, tr[u].sz = r - l + 1, tr[u].lazy = 0; 88 if (l == r) 89 { 90 if (a[rk[l]] == 1) 91 tr[u].sum = 1; 92 return; 93 } 94 int mid = l + r >> 1; 95 build(u << 1, l, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r); 96 pushup(u); 97 } 98 void modify(int u, int l, int r) 99 { 100 if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r) 101 { 102 tr[u].sum = tr[u].sz - tr[u].sum; 103 //这里当时我写成了tr[u].lazy=1,没有考虑到tr[u].lazy原本的情况 104 tr[u].lazy ^= 1; 105 return; 106 } 107 pushdown(u); 108 int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1; 109 if (r <= mid) 110 modify(u << 1, l, r); 111 else if (l > mid) 112 modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r); 113 else 114 modify(u << 1, l, r), modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r); 115 pushup(u); 116 } 117 int query(int u, int l, int r) 118 { 119 /* cout << "query:" << l << " " << r << endl; */ 120 if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r) 121 return tr[u].sum; 122 pushdown(u); 123 int res = 0; 124 int mid = tr[u].l + tr[u].r >> 1; 125 if (r <= mid) 126 { 127 /* cout << "!!!" << l << " " << mid << endl; */ 128 //这里写错了:!!!!!!!!!!! 129 res = query(u << 1, l, r); 130 } 131 else if (l > mid) 132 { 133 /* cout << "!!!" << mid + 1 << " " << r << endl; */ 134 res = query(u << 1 | 1, l, r); 135 } 136 else 137 res = query(u << 1, l, r) + query(u << 1 | 1, l, r); 138 return res; 139 } 140 141 void treeModify(int u) 142 { 143 /* cout << id[u] << " " << id[u] + sizer[u] - 1 << endl; */ 144 modify(1, id[u], id[u] + sizer[u] - 1); 145 } 146 int treeQuery(int u) 147 { 148 /* cout << id[u] << " " << id[u] + sizer[u] - 1 << endl; */ 149 return query(1, id[u], id[u] + sizer[u] - 1); 150 } 151 int main() 152 { 153 scanf("%d", &n); 154 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) 155 { 156 int a; 157 scanf("%d", &a); 158 tree[a].push_back(i); 159 tree[i].push_back(a); 160 } 161 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 162 scanf("%d", &a[i]); 163 r = 1; 164 f[r] = 0, dep[r] = 1; 165 dfs1(r); 166 memset(st, false, sizeof(st)); 167 dfs2(r, r); 168 build(1, 1, n); 169 scanf("%d", &m); 170 getchar(); 171 while (m--) 172 { 173 char op[5]; 174 int num; 175 scanf("%s %d", op, &num); 176 if (op[0] == 'g') 177 printf("%d\n", treeQuery(num)); 178 else 179 treeModify(num); 180 } 181 return 0; 182 }
一个简单题目,但是我modify和query写成如下,我就死都不知道错在哪里
if (l <= mid)
modify(u << 1, l, r);
if (r > mid)
modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
if (l <= mid)
{
res += query(u << 1, l, r);
}
else if (r > mid)
{
/* cout << "!!!" << mid + 1 << " " << r << endl; */
res += query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号