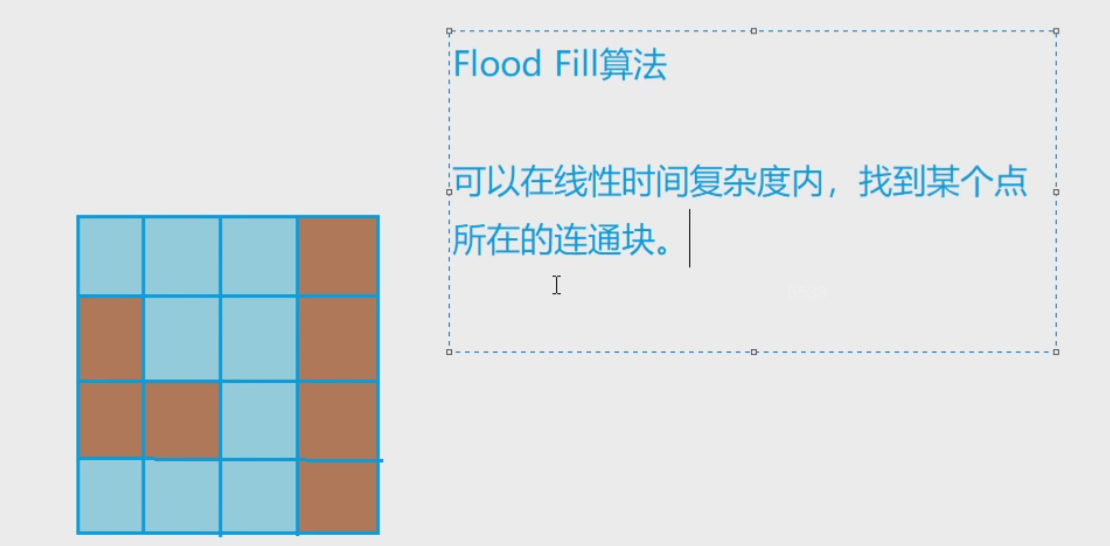
Bfs
《flood fill算法》
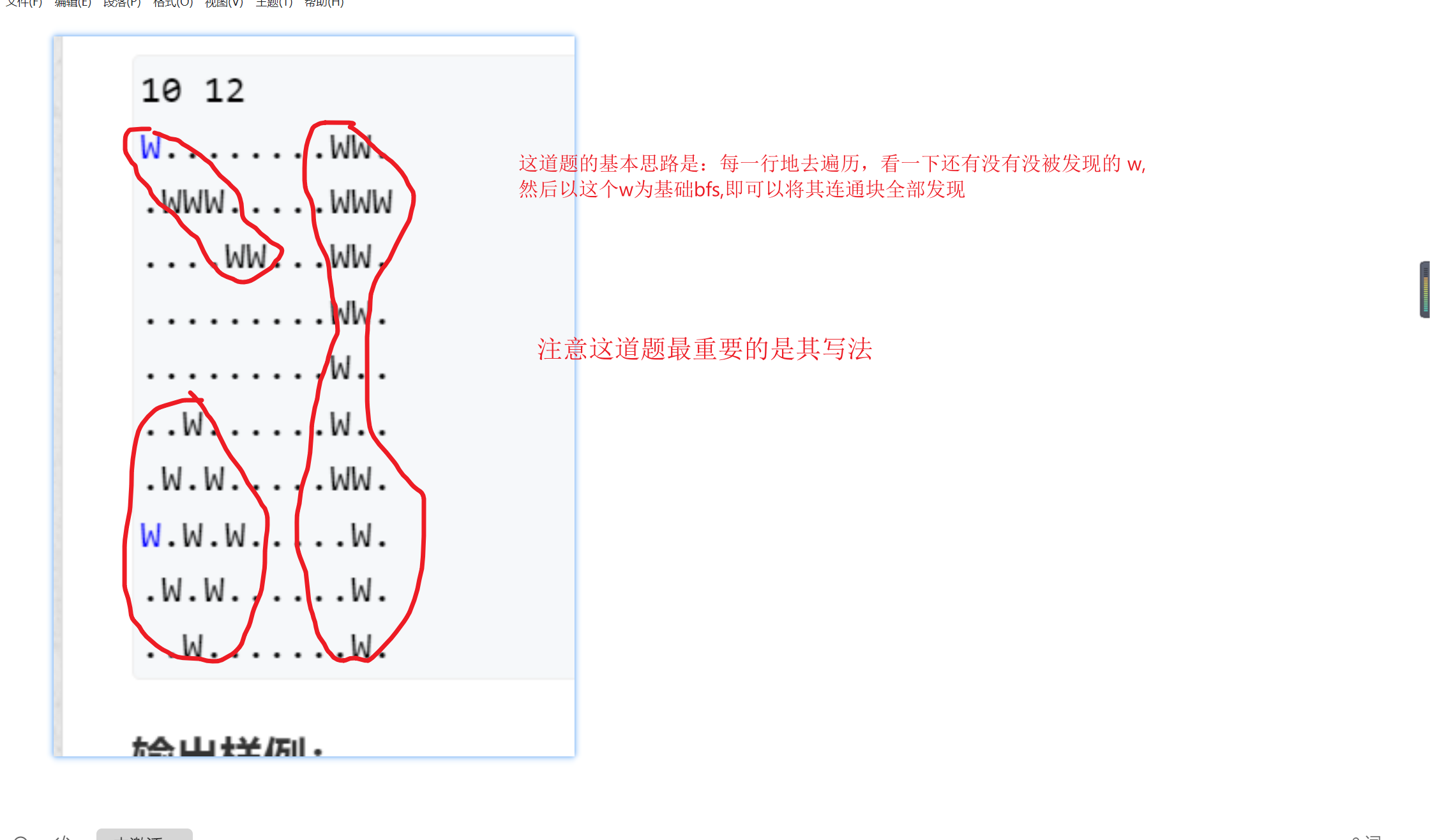
1 1097. 池塘计数
2 农夫约翰有一片 N∗M 的矩形土地。
3
4 最近,由于降雨的原因,部分土地被水淹没了。
5
6 现在用一个字符矩阵来表示他的土地。
7
8 每个单元格内,如果包含雨水,则用”W”表示,如果不含雨水,则用”.”表示。
9
10 现在,约翰想知道他的土地中形成了多少片池塘。
11
12 每组相连的积水单元格集合可以看作是一片池塘。
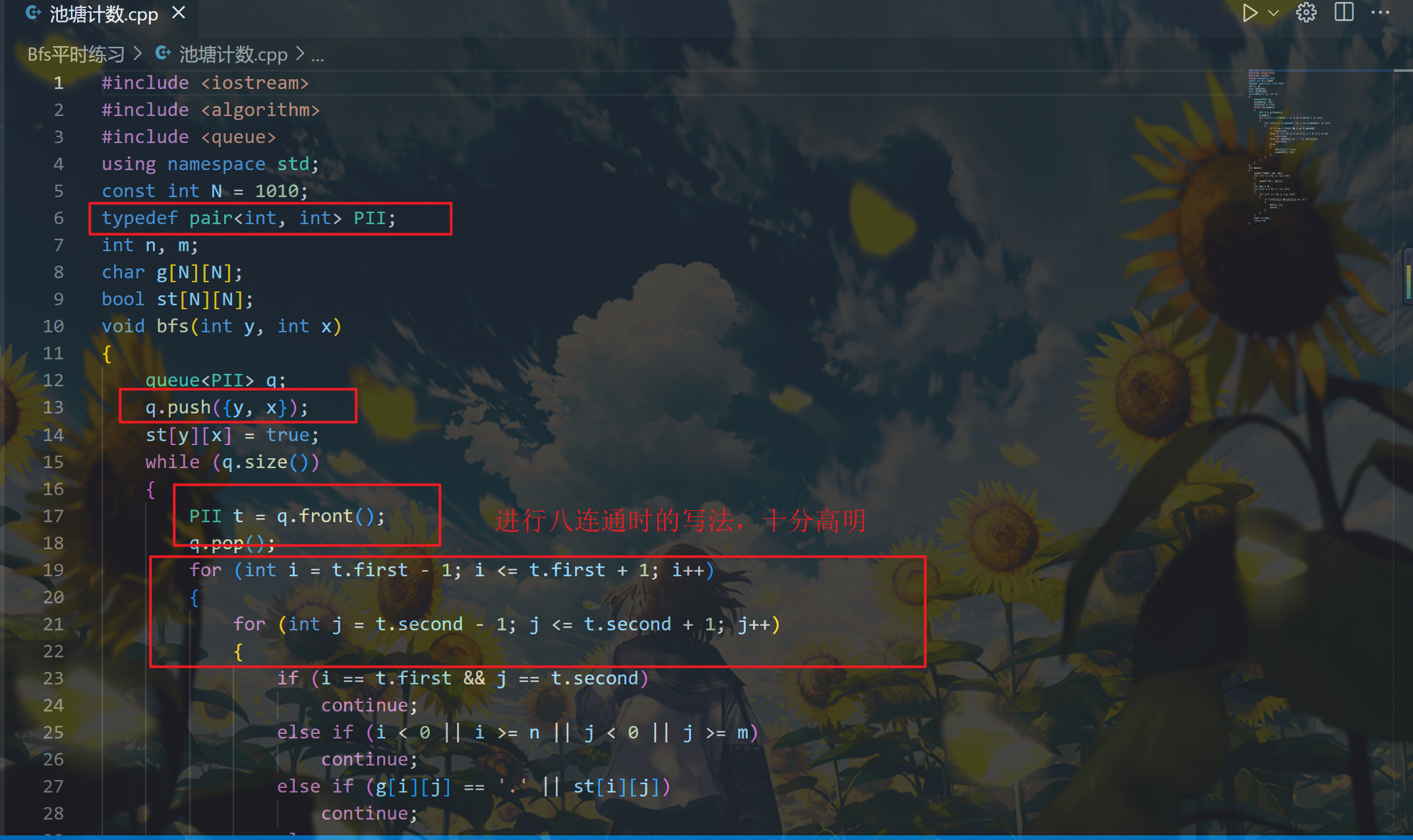
13
14 每个单元格视为与其上、下、左、右、左上、右上、左下、右下八个邻近单元格相连。
15
16 请你输出共有多少片池塘,即矩阵中共有多少片相连的”W”块。
17
18 输入格式
19 第一行包含两个整数 N 和 M。
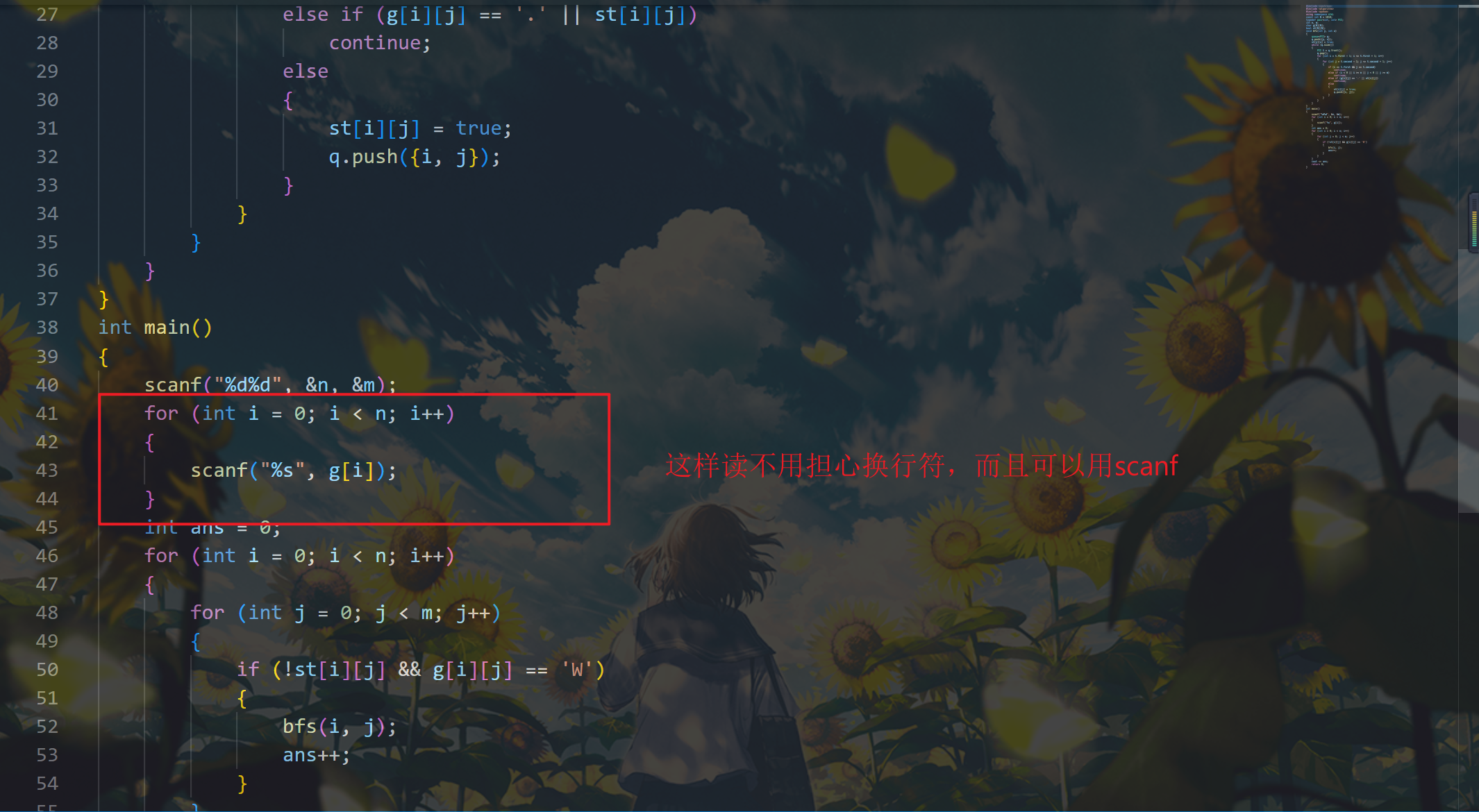
20
21 接下来 N 行,每行包含 M 个字符,字符为”W”或”.”,用以表示矩形土地的积水状况,字符之间没有空格。
22
23 输出格式
24 输出一个整数,表示池塘数目。
25
26 数据范围
27 1≤N,M≤1000
28 输入样例:
29 10 12
30 W........WW.
31 .WWW.....WWW
32 ....WW...WW.
33 .........WW.
34 .........W..
35 ..W......W..
36 .W.W.....WW.
37 W.W.W.....W.
38 .W.W......W.
39 ..W.......W.
40 输出样例:
41 3
《多源BFS》
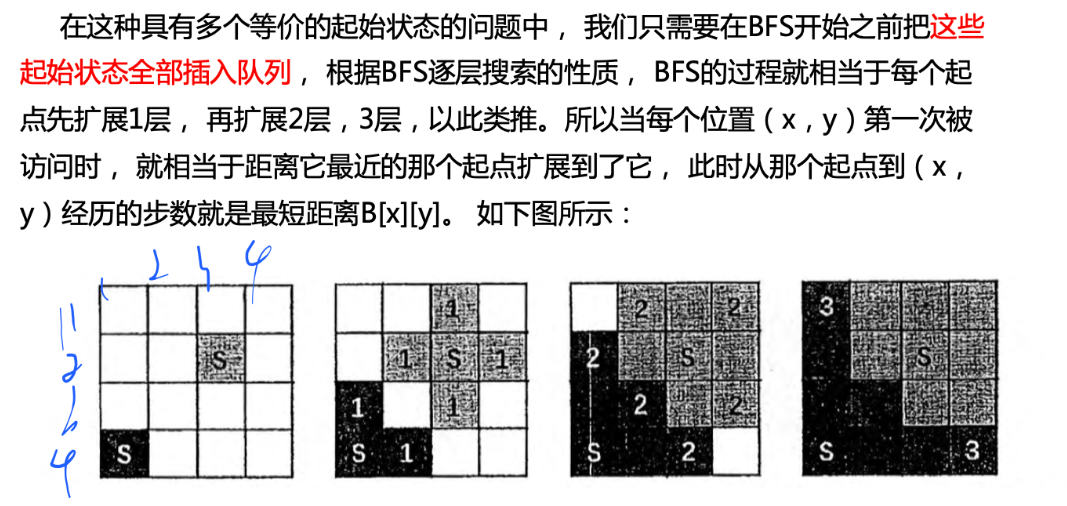
所谓多源BFS就是有多个起点:
例子如下:
1 173. 矩阵距离
2
3 给定一个 N 行 M 列的 01 矩阵 A,A[i][j] 与 A[k][l] 之间的曼哈顿距离定义为:
4
5 dist(A[i][j],A[k][l])=|i−k|+|j−l|
6 输出一个 N 行 M 列的整数矩阵 B,其中:
7
8 B[i][j]=min1≤x≤N,1≤y≤M,A[x][y]=1dist(A[i][j],A[x][y])
9 输入格式
10 第一行两个整数 N,M。
11
12 接下来一个 N 行 M 列的 01 矩阵,数字之间没有空格。
13
14 输出格式
15 一个 N 行 M 列的矩阵 B,相邻两个整数之间用一个空格隔开。
16
17 数据范围
18 1≤N,M≤1000
19 输入样例:
20 3 4
21 0001
22 0011
23 0110
24 输出样例:
25 3 2 1 0
26 2 1 0 0
27 1 0 0 1
这道题很容易看出:当A【i】[j]矩阵的数为1则B[i][j]==0;
否则开始BFS找到距离(i,j)最近的数是1的位置,而且查找的深度就是B【i】[j]的数值
但是这样查找,很容易出问题,比如当1数值十分少时,而且我好不容易找到了1数值,当进行下一次查找时又要从新找过
有没有解决办法?
我们可以反向来看:从数值时1的点开始BFS,找到众多数值时1的点到(i,j)这个点的最短路
因为是有多个数值1的点,即为有多个起点,同时BFS();
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
char g[N][N];
int ans[N][N];
int dy[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int n, m;
void BFS()
{
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
memset(ans, -1, sizeof(ans));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (g[i][j] == '1')
{
ans[i][j] = 0;
q.push({i, j});
}
}
}
while (q.size())
{
pair<int, int> t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int nx = t.first + dx[i], ny = t.second + dy[i];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m)
continue;
if (ans[nx][ny] != -1)
continue;
if (g[nx][ny] == '0')
{
q.push({nx, ny});
ans[nx][ny] = ans[t.first][t.second] + 1;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%s", g[i]);
BFS();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
cout << ans[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
《状态的最短步数》
这个问题主要是求将图的一种状态转化成目标的另一种状态的最小操作次数:
比如:
1 1107. 魔板
8 Rubik 先生在发明了风靡全球的魔方之后,又发明了它的二维版本——魔板。
9
10 这是一张有 8 个大小相同的格子的魔板:
11
12 1 2 3 4
13 8 7 6 5
14 我们知道魔板的每一个方格都有一种颜色。
15
16 这 8 种颜色用前 8 个正整数来表示。
17
18 可以用颜色的序列来表示一种魔板状态,规定从魔板的左上角开始,沿顺时针方向依次取出整数,构成一个颜色序列。
19
20 对于上图的魔板状态,我们用序列 (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8) 来表示,这是基本状态。
21
22 这里提供三种基本操作,分别用大写字母 A,B,C 来表示(可以通过这些操作改变魔板的状态):
23
24 A:交换上下两行;
25 B:将最右边的一列插入到最左边;
26 C:魔板中央对的4个数作顺时针旋转。
27
28 下面是对基本状态进行操作的示范:
29
30 A:
31
32 8 7 6 5
33 1 2 3 4
34 B:
35
36 4 1 2 3
37 5 8 7 6
38 C:
39
40 1 7 2 4
41 8 6 3 5
42 对于每种可能的状态,这三种基本操作都可以使用。
43
44 你要编程计算用最少的基本操作完成基本状态到特殊状态的转换,输出基本操作序列。
45
46 注意:数据保证一定有解。
47
48 输入格式
49 输入仅一行,包括 8 个整数,用空格分开,表示目标状态。
50
51 输出格式
52 输出文件的第一行包括一个整数,表示最短操作序列的长度。
53
54 如果操作序列的长度大于0,则在第二行输出字典序最小的操作序列。
55
56 数据范围
57 输入数据中的所有数字均为 1 到 8 之间的整数。
58
59 输入样例:
60 2 6 8 4 5 7 3 1
61 输出样例:
62 7
63 BCABCCB
68 来源:《信息学奥赛一本通》 , usaco training 3.2

unordered_map的具体用法:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40838478/article/details/114664223;
可以看做键值对来用:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <unordered_map>
5 #include <queue>
6 using namespace std;
7 string start = "", finall = "";
8 //表示变成状态state要经历dist[state]步操作
9 unordered_map<string, int> dist;//第一个是键,第二个是值;
10 //表示变成状态state要通过状态pre[state].second通过操作pre[state].first由来
11 unordered_map<string, pair<char, string>> pre;
12
13 string moveA(string t)
14 {
15 reverse(t.begin(), t.end());
16 return t;
17 }
18 string moveB(string t)
19 {
20 for (int i = 2; i >= 0; i--)
21 {
22 swap(t[i + 1], t[i]);
23 }
24 for (int i = 4; i <= 6; i++)
25 {
26 swap(t[i + 1], t[i]);
27 }
28 return t;
29 }
30 string moveC(string t)
31 {
32 swap(t[1], t[2]);
33 swap(t[5], t[6]);
34 swap(t[1], t[5]);
35 return t;
36 }
37 int BFS(string start, string finall)
38 {
39 if (start == finall)
40 return 0;
41 queue<string> q;
42 q.push(start);
43 dist[start] = 0;
44 while (q.size())
45 {
46 auto t = q.front();
47 q.pop();
48 string m[3];
49 m[0] = moveA(t);
50 m[1] = moveB(t);
51 m[2] = moveC(t);
52 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
53 {
54 if (!dist.count(m[i]))
55 //这个dist.count()方法
56 unordered_map::count()是C++中的内置方法,用于通过给定 key 对unordered_map中存在的元素数量进行计数。
57
58 注意:由于unordered_map不允许存储具有重复键的元素,因此count()函数本质上检查unordered_map中是否存在具有给定键的元素。
59
60 {
61 dist[m[i]] = dist[t] + 1;
62 pre[m[i]] = {i + 'A', t};
63 q.push(m[i]);
64 if (finall == m[i])
65 return dist[m[i]];
66 }
67 }
68 }
69 }
70 int main()
71 {
72 int num;
73 for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++)
74 {
75 cin >> num;
76 finall += char(num);//最后状态
77 start += char(i);//初始状态
78 }
79 int step = BFS(start, finall);
80 cout << step<<endl;
81 if (step != 0)
82 {
83 string ans = "";
84 string state = finall;
85 while (state != start)
86 {
87 ans += pre[state].first;
88 state = pre[state].second;
89 }
90 reverse(ans.begin(), ans.end());
91 cout << ans;
92 }
93 return 0;
94 }
《双向BFS对最小步数的状态转移的优化》
双向BFS一般用在最小步数中的状态很多的情况下, 如果只单单从起始状态开始搜索会超时或爆栈
原因如下图:
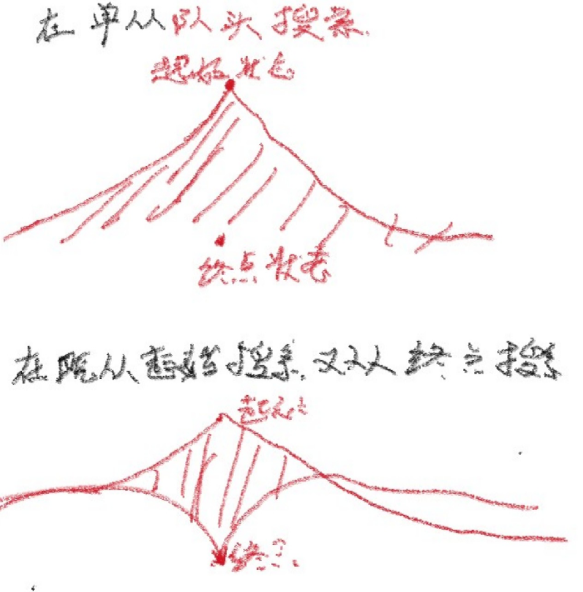
能够明显看出双向BFS搜索的范围更小
以下来自一个大佬:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/43817/

题目:
1 190. 字串变换
2
3 已知有两个字串 A, B 及一组字串变换的规则(至多 6 个规则):
4
5 A1→B1
6 A2→B2
7 …
8
9 规则的含义为:在 A 中的子串 A1 可以变换为 B1、A2 可以变换为 B2…。
10
11 例如:A=abcd B=xyz
12
13 变换规则为:
14
15 abc → xu ud → y y → yz
16
17 则此时,A 可以经过一系列的变换变为 B,其变换的过程为:
18
19 abcd → xud → xy → xyz
20
21 共进行了三次变换,使得 A 变换为 B。
22
23 输入格式
24 输入格式如下:
25
26 A B
27 A1 B1
28 A2 B2
29 … …
30
31 第一行是两个给定的字符串 A 和 B。
32
33 接下来若干行,每行描述一组字串变换的规则。
34
35 所有字符串长度的上限为 20。
36
37 输出格式
38 若在 10 步(包含 10 步)以内能将 A 变换为 B ,则输出最少的变换步数;否则输出 NO ANSWER!。
39
40 输入样例:
41 abcd xyz
42 abc xu
43 ud y
44 y yz
45 输出样例:
46 3
字符串状态多样一般用双向BFS
使用了unordered_map的判重方式是unorderedMap(名字)[key].count(value);
其出现过返回1,没有返回0;
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <queue>
5 #include <unordered_map>
6 using namespace std;
7 string start, finall;
8 string fromS[7], toS[7];
9 int step = 0, counter = 0;
10 int tochange(queue<string> &q, string nfrom[], string nto[], unordered_map<string, int> &smap, unordered_map<string, int> &fmap)
11 {
12 int d = smap[q.front()]; //这里的层是指到达目标字符串的操作次数
13 while (q.size() && smap[q.front()] == d)
14 { //为了要扩展一层,当smap[q.front()] != d说明层数改变了
15 string t = q.front();
16 q.pop();
17 for (int i = 0; i < counter; i++) //枚举变化方法
18 {
19 for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j++) //枚举出能够替换的地方
20 {
21 if (t.substr(j, nfrom[i].size()) == nfrom[i])
22 {
23 string newt = t.substr(0, j) + nto[i] + t.substr(j+nfrom[i].size());
24 if (fmap.count(newt))
25 //能够保证最先出的是最小的,如果这个不行,以后更不行,所以这里不要将newt保存
26 return fmap[newt] + smap[t] + 1;
27 if (smap.count(newt))
28 continue;
29 smap[newt] = smap[t] + 1;
30 q.push(newt);
31 }
32 }
33 }
34 }
35 return 11;
36 }
37 int BFS()
38 {
39 if (start == finall)
40 return 0;
41 int ans;
42 queue<string> sq, fq;
43 unordered_map<string, int> smap, fmap; //记录状态
44 sq.push(start), fq.push(finall);
45 smap[start] = 0, fmap[finall] = 0;
46 while (sq.size() && fq.size())
47 {
48 //选择层数小的开始扩展,这样可以在枚举最小的情况下找到答案,算是个优化,不是必须
49 if (sq.size() < fq.size())
50 ans = tochange(sq, fromS, toS, smap, fmap);
51 else
52 ans = tochange(fq, toS, fromS, fmap, smap);
53 if (ans <= 10)
54 return ans;
55 if (++step >= 10)
56 return -1;
57 }
58 return -1;
59 }
60 int main()
61 {
62 cin >> start >> finall;
63 while (cin >> fromS[counter] >> toS[counter])
64 counter++;
65
66 int ans = BFS();
67 if (ans == -1)
68 cout << "NO ANSWER!";
69 else
70 cout << ans;
71 return 0;
72 }
《双向bfs+最小步数问题的记录路径的问题》
八数码
在一个 3×3 的网格中,1∼8 这 8 个数字和一个 X 恰好不重不漏地分布在这 3×3 的网格中。
例如:
1 2 3
X 4 6
7 5 8
在游戏过程中,可以把 X 与其上、下、左、右四个方向之一的数字交换(如果存在)。
我们的目的是通过交换,使得网格变为如下排列(称为正确排列):
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 X
例如,示例中图形就可以通过让 X 先后与右、下、右三个方向的数字交换成功得到正确排列。
交换过程如下:
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
X 4 6 4 X 6 4 5 6 4 5 6
7 5 8 7 5 8 7 X 8 7 8 X
把 X 与上下左右方向数字交换的行动记录为 u、d、l、r。
现在,给你一个初始网格,请你通过最少的移动次数,得到正确排列。
输入格式
输入占一行,将 3×3 的初始网格描绘出来。
例如,如果初始网格如下所示:
1 2 3
x 4 6
7 5 8
则输入为:1 2 3 x 4 6 7 5 8
输出格式
输出占一行,包含一个字符串,表示得到正确排列的完整行动记录。
如果答案不唯一,输出任意一种合法方案即可。
如果不存在解决方案,则输出 unsolvable。
输入样例:
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
输出样例
ullddrurdllurdruldr
这道题目我有两种写法:
1.单向bfs():
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <unordered_map> #include <queue> using namespace std; unordered_map<string, pair<string, char>> pre; //表示变成state1这个状态是由state2通过char的操作而来的 string start, finall = "12345678x"; string arr[4]; char moves[] = {'u', 'r', 'd', 'l'}; string getmove(string state, char move) { int p; for (int i = 0; i <= 8; i++) { if (state[i] == 'x') { p = i; break; } } if (move == 'u') { if (p >= 3) swap(state[p], state[p - 3]); } else if (move == 'r') { if ((p + 1) % 3 != 0) swap(state[p], state[p + 1]); } else if (move == 'd') { if (p <= 5) swap(state[p], state[p + 3]); } else if (move == 'l') { if (p % 3 != 0) swap(state[p], state[p - 1]); } return state; } bool BFS() { if (start == finall) return true; queue<string> q; q.push(start); while (q.size()) { string t = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { arr[i] = getmove(t, moves[i]); if (!pre.count(arr[i])) { pre[arr[i]] = {t, moves[i]}; q.push(arr[i]); if (arr[i]==finall) return true; } } } return false; } int main() { char x; while (cin >> x) start += x; bool ans = BFS(); if (ans) { string t = finall; string res; while (t != start) { res += pre[t].second; t = pre[t].first; } reverse(res.begin(), res.end()); cout << res; } else cout << "unsolvable"; return 0; }
2.双向bfs,但是双向bfs在没有答案的情况下可能会超时:
这是因为当我们在没有答案的情况下,如果没有特判,那么两边都会一直搜索没有交集,最后都快搜索到底才停止
相当于普通单向bfs的双倍,所以在这种情况下可以特判:
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <unordered_map> #include <queue> using namespace std; string start, finall = "12345678x"; unordered_map<string, pair<string, char>> prel, prer; char moves[] = {'u', 'r', 'd', 'l'}; string arr[4]; string getmove(string state, char move) { int p; for (int i = 0; i <= 8; i++) { if (state[i] == 'x') { p = i; break; } } if (move == 'u') { if (p >= 3) swap(state[p], state[p - 3]); } else if (move == 'r') { if ((p + 1) % 3 != 0) swap(state[p], state[p + 1]); } else if (move == 'd') { if (p <= 5) swap(state[p], state[p + 3]); } else if (move == 'l') { if (p % 3 != 0) swap(state[p], state[p - 1]); } return state; } string extend(queue<string> &q, unordered_map<string, pair<string, char>> &prep, unordered_map<string, pair<string, char>> &prea) { string t = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { arr[i] = getmove(t, moves[i]); if (prep.count(arr[i])) continue; prep[arr[i]] = {t, moves[i]}; q.push(arr[i]); if (prea.count(arr[i])) return arr[i]; } return ""; } string bfs() { int num = 0; queue<string> ql, qr; ql.push(start), qr.push(finall); prel[start] = {" ", ' '}, prer[finall] = {" ", ' '}; string t = ""; while (ql.size() && qr.size()) { if (num>=1e9) return "";//特判,num相当于至今搜索到的状态,当num大于某个数还没有搜索到时默认不存在 if (ql.size() < qr.size()) { t = extend(ql, prel, prer); num += ql.size(); } else { t = extend(qr, prer, prel); num += qr.size(); } if (t != "") return t; } return ""; } int main() { char x; while (cin >> x) { start += x; } if (start == finall) cout << ""; else { string ans = bfs(); if (ans != "") { string resl, resr; string tl = ans, tr = ans; while (tl != start) { resl += prel[tl].second; tl = prel[tl].first; } reverse(resl.begin(), resl.end()); while (tr != finall) { char reword = prer[tr].second; if (reword == 'u') reword = 'd'; else if (reword == 'r') reword = 'l'; else if (reword == 'd') reword = 'u'; else if (reword == 'l') reword = 'r';
//注意我上面的写法,这个写的太麻烦了,主要是当时我没注意到
我从最终状态反过来搜索时,记录的是:状态state是由状态midstate通过操作word来实现的,
记录的是midstate->state的操作,而当我输出路径时是要state->midstate的操作,即跟记录的操作相反
resr += reword;
tr = prer[tr].first;
}
string res = resl + resr;
cout << res;
}
else
cout << "unsolvable";
}
return 0;
}
《双端队列在BFS中的应用》
双端队列deque,主要应用在BFS中只有0或1的边权图中,当边权是0则加入到队列的首部,当边权是1时,加入到队列的尾部
c++中提供了deque
#include<deque>
deque<类型>队列名字


具体网址:
https://blog.csdn.net/sevenjoin/article/details/88530962?spm=1001.2101.3001.6661.1&utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7Edefault-1-88530962-blog-108089691.pc_relevant_multi_platform_whitelistv2&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_t0.none-task-blog-2%7Edefault%7ECTRLIST%7Edefault-1-88530962-blog-108089691.pc_relevant_multi_platform_whitelistv2&utm_relevant_index=1
题目:
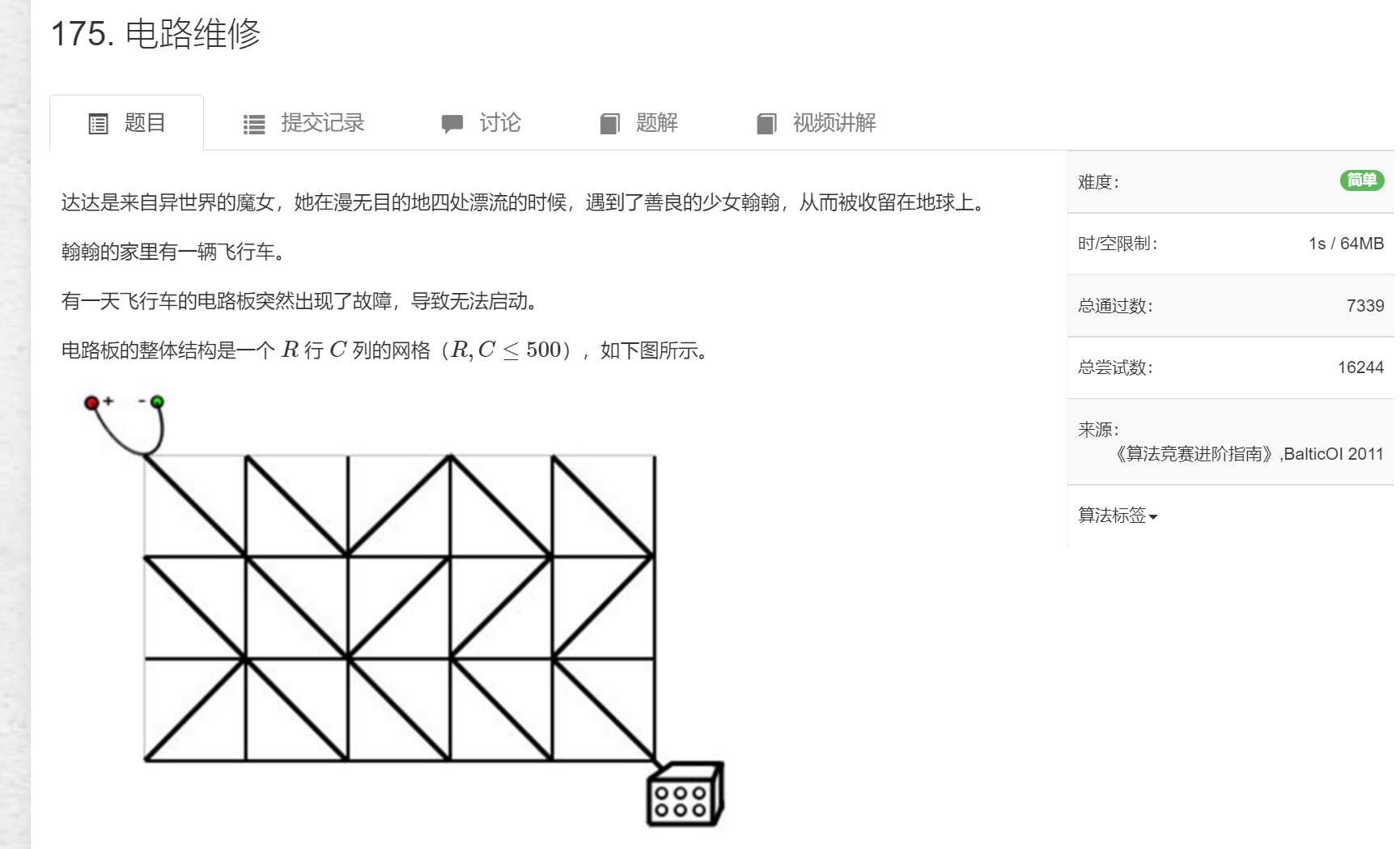

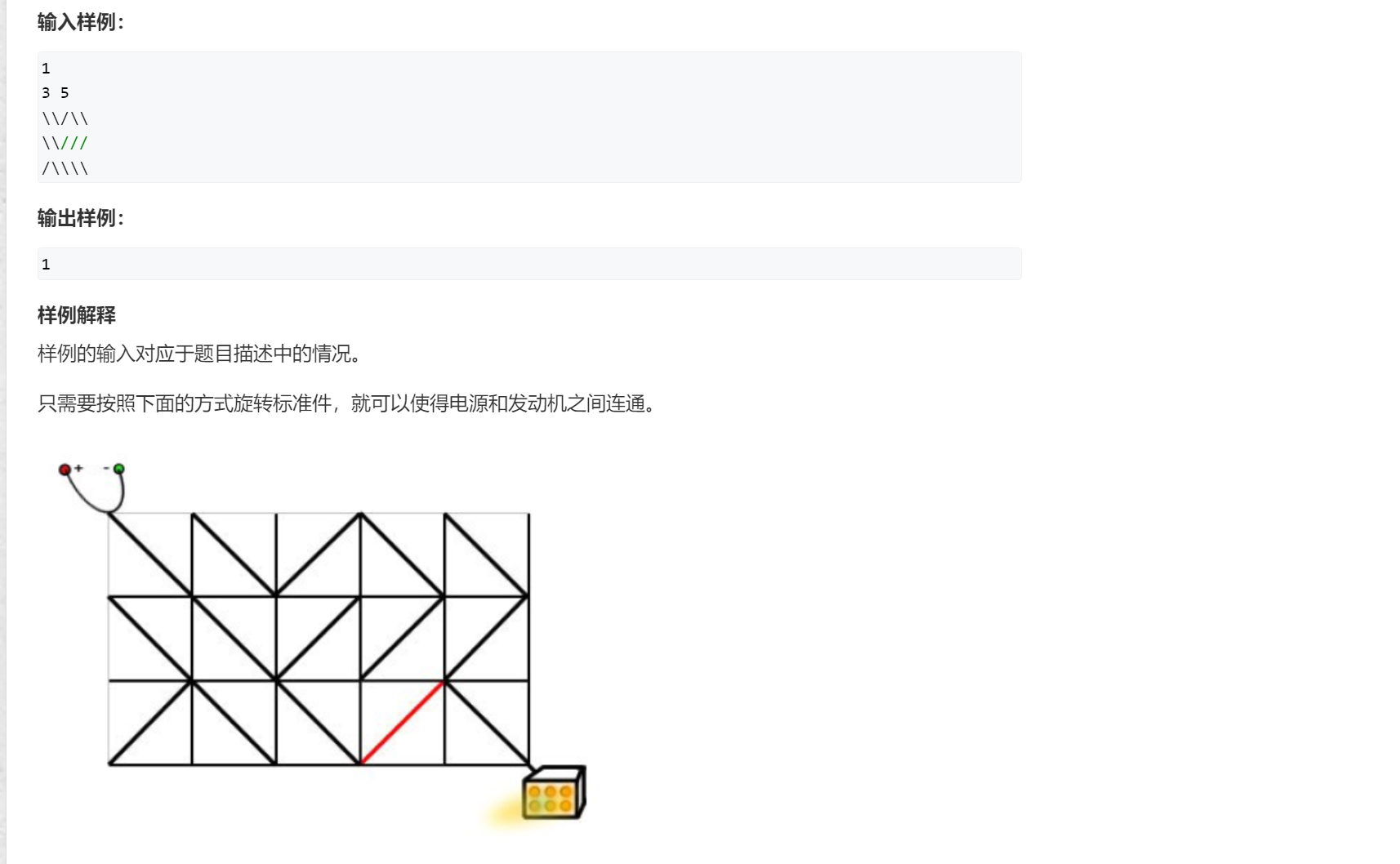
思路:

双端队列可以看作Dijkstra的特殊版本,十分适合处理权重只有0和1的求最短路问题的图;
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <algorithm>
3 #include <cstring>
4 #include <deque>
5 using namespace std;
6 typedef pair<int, int> PII;
7 const int N = 510;
8 int n, m, w;
9 char g[N][N];
10 char state[] = "\\/\\/";//主要”/”要进行转意,写成“//”,按照的是左上,右上,右下,左下的顺序
11 bool st[N][N];//用于记录点i到点j是否看过
12 int dist[N][N];//用来记录点i到点j的距离
13 int dx[] = {-1, 1, 1, -1}, dy[] = {-1, -1, 1, 1};//到达顶点的变化
14 int jx[] = {-1, 0, 0, -1}, jy[] = {-1, -1, 0, 0};//获取g中信息时用的点的变化
15 int BFS()
16 {
17 memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
18 memset(st, false, sizeof(st));
19 deque<PII> dq;
20 dq.push_front({0, 0});
21 st[0][0] = true;
22 dist[0][0] = 0;
23 while (dq.size())
24 {
25 auto t = dq.front();
26 dq.pop_front();
27 st[t.first][t.second] = true;
28
29 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
30 {
31 int ny = t.first + dy[i], nx = t.second + dx[i];
32 if (ny < 0 || ny > n || nx < 0 || nx > m)
33 continue;
34 if (st[ny][nx])//因为st是在当点被拿出的时候标记为true的,所以一定是最短的
35 continue;
36 int jny = t.first + jy[i], jnx = t.second + jx[i];
37 if (state[i] == g[jny][jnx])
38 w = 0;
39 else
40 w = 1;
41 if (dist[ny][nx] > dist[t.first][t.second] + w)//只有在有更优的情况下才加入点,可以保证双端队列求解是O(m)的时间复杂度,m为边数
42 {
43 dist[ny][nx] = dist[t.first][t.second] + w;
44
45 if (w)
46 dq.push_back({ny, nx});
47 else
48 dq.push_front({ny, nx});
49 }
50 }
51 }
52 if (dist[n][m] >= 0x3f3f3f3f)
53 return -1;
54 else
55 return dist[n][m];
56 }
57 int main()
58 {
59 int t;
60 cin >> t;
61 while (t--)
62 {
63 cin >> n >> m;
64 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
65 scanf("%s", g[i]);
66 int ans = BFS();
67 if (ans == -1)
68 cout << "NO SOLUTION" << endl;
69 else
70 cout << ans << endl;
71 }
72 return 0;
73 }
《我再一次写双端队列BFS的感想以及错误纠正》
疑惑点一:为什么明明是BFS,应该是越先出来的点其路径越短,为什么还要: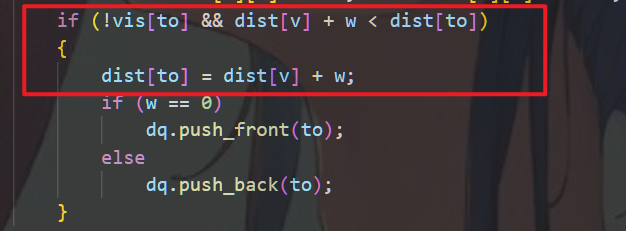
作像这样的判断?
这是因为双端队列BFS的特殊性,在一般的BFS中其路径长度都为1,所以有最先出来的点到目标点为最短路径,但是
双端队列BFS的路径有0,1这两条,即使我们将路径为0的路径往队列前面放,但是有时就是先BFS不是0的那条路,然后再BFS是0的那条路
如:
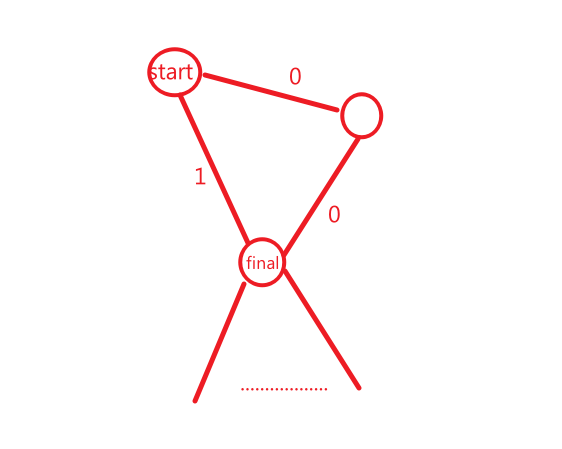
如果先从1那条开始,然后到了final,但是后面才BFS 0的道路,所以每次就像更新最短距离一样要判断一下
《BFS时间复杂度分析》

以走迷宫这个经典例题为例:
这里我想与dfs对比来讲:
1、当使用dfs时,明显,这里我们不用回溯,所以dfs跑顶多把整个网格跑满,O(n*n)
2、问题来了:如果跑网格问题时,可以上下左右移动,我们用dfs而且为了解决问题(如在网格中到某个点的最小路程),不得不使用
回溯,这个时候的时间复杂度是多少?
根据搜索树,对于第i层,这层的节点数为4*3^(i-1),因为要回溯,必须要跑满这些点,则时间复杂度为O(4*3^(n-1))
十分恐怖,即用dfs求网格上的最值问题并不是一个好主意
3.当使用bfs时,如果就专门针对这个问题,也是顶多把把整个网格跑满,O(n*n)
但是如果题目变化一下:
在原来的题目基础上加上这句话:
即现在我们用BFS求有条件了,面对这种情况如果要解决用暴力dfs十分好解决,但是要回溯,时间复杂度是指数型的
如果用BFS来解决这个问题其实我们给每个格子都在附上一种状态即可:
即如果没有加上这个条件的原题目,我们是用bool st[N][N]来看那些点我们走过,以免再走,解决的时间复杂度为O(n*n)
这里我们可以设置bool st[N][N][3],st[i][j][k]:表示当我们从源点走到点(i,j)的时候,我们还可以拆除k堵墙
即使是st[1][1][3]和st[1][1][1],也是天差地别的状态
因为最多把全部的状态都跑完,则时间复杂度最大也就为O(n*n*3)
《例题》
根据上面的分析也是时候来写道题了:
题目意思很简单:
给我们一个n*m的网格(1<=n,m<=100),每个格子上有数num(1<=num<=10),如果想要到达这个格子,就必须要有
这个格子上的数,给我们出发点和终点,问从出发点到终点,最小需要多少个数
回到上面的分析,如果这里我们用dfs,超时无疑
如果用BFS,因为num<=10,十分小,我们可以用bool st【N】【N】【1<<10】
1<<10是状态压缩的表示,比如st[i][j][state]:从源点到(i,j)时,已经有数为state二进制下1的个数
时间复杂度O(n*n*(1<<10))
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 102;
int st[N][N][1 << 10], a[N][N];
int n, m, sx, sy, fx, fy;
int dy[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
struct node
{
int y, x, state;
};
int ans = 11;
int get(int x)
{
int cnt = 0;
while (x)
{
if (x & 1)
cnt++;
x = x >> 1;
}
return cnt;
}
void BFS(int y, int x)
{
queue<node> q;
q.push({y, x, 1 << a[y][x]});
while (q.size())
{
node t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (st[t.y][t.x][t.state])
continue;
st[t.y][t.x][t.state] = true;
if (t.y == fy && t.x == fx)
{
ans = min(ans, get(t.state));
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int ny = t.y + dy[i], nx = t.x + dx[i];
if (ny < 1 || ny > n || nx < 1 || nx > m)
continue;
int state = t.state | (1 << a[ny][nx]);
q.push({ny, nx, state});
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
cin >> sy >> sx >> fy >> fx;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
a[i][j]--;
}
BFS(sy, sx);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号