DDD 架构划分领域实战操作
针对自动配置大模型脚本的DDD架构的设计与搭建
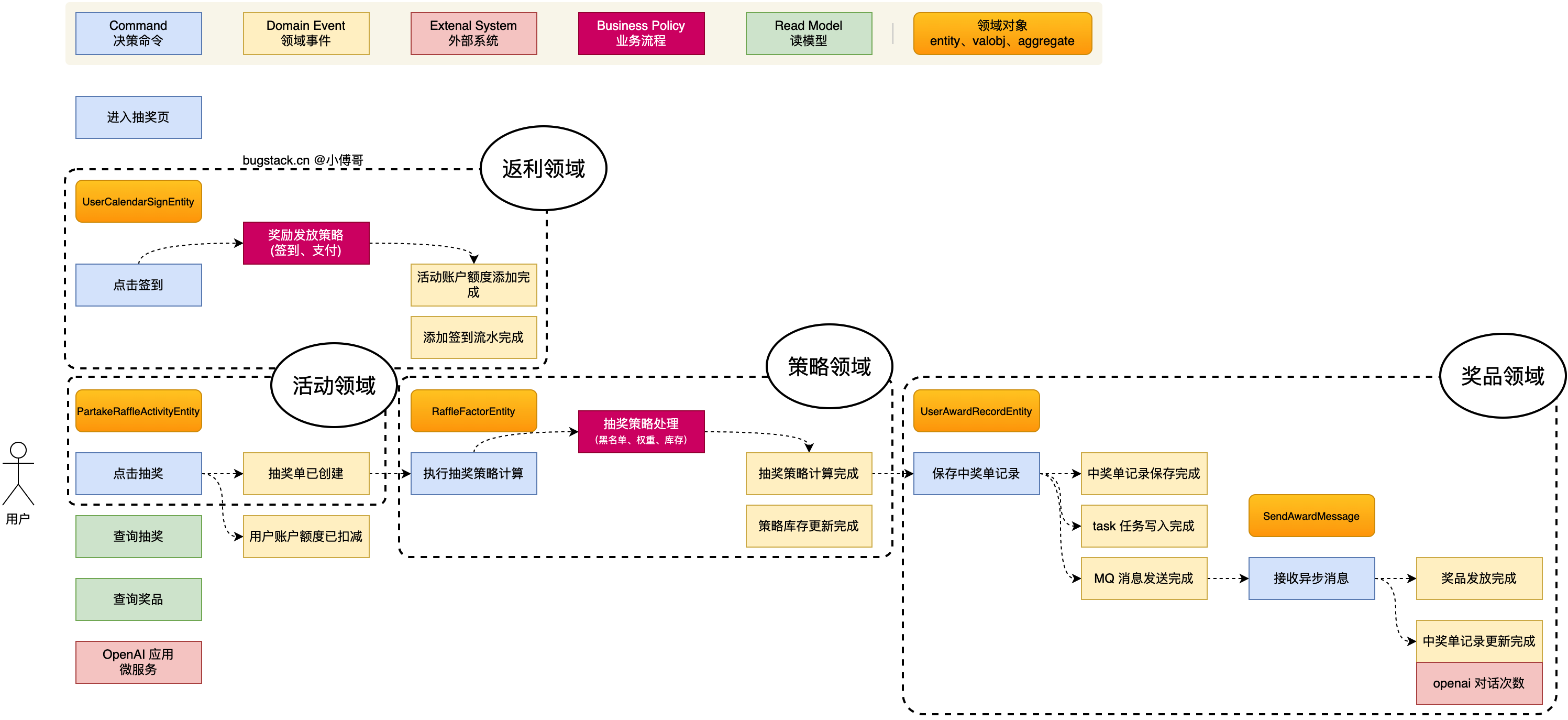
✅ 第一步:领域划分(Domain Partitioning)
严格按照DDD(领域驱动设计)的思想,划分为三个核心领域,每个领域都包含:
- 实体(Entity)
- 值对象(Value Object)
- 聚合(Aggregate)
- 聚合根(Aggregate Root)
- 领域服务(Domain Service)
- 领域事件(Domain Event)
- 仓储接口(Repository Interface)
📌 领域1:脚本管理域(Script Management)
| 概念 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 实体 | Script | 每个脚本是一个实体,包含语言类型、内容、ID |
| 值对象 | ScriptType | C++、Lua、Python |
| 聚合根 | ScriptAggregate | 脚本的聚合根,管理脚本的生命周期 |
| 聚合 | ScriptCollection | 一个项目下的多个脚本 |
| 领域服务 | ScriptExecutionService | 执行脚本 |
| 领域事件 | ScriptExecutedEvent | 脚本执行完成后触发 |
| 仓储接口 | ScriptRepository | 保存/查询脚本 |
📌 领域2:依赖管理域(Dependency Management)
| 概念 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 实体 | DependencyLibrary | 每个依赖库是一个实体 |
| 值对象 | LibraryVersion | 版本号、语言类型 |
| 聚合根 | DependencyGraph | 依赖图(DAG) |
| 聚合 | LibraryChain | 某个库的所有依赖链 |
| 领域服务 | DependencyResolverService | 解析依赖链 |
| 领域事件 | DependencyResolvedEvent | 依赖解析完成 |
| 仓储接口 | DependencyRepository | 保存/查询依赖关系 |
📌 领域3:环境管理域(Environment Management)
| 概念 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 实体 | VirtualEnvironment | 每个Conda环境 |
| 值对象 | EnvironmentConfig | Python版本、依赖列表 |
| 聚合根 | EnvironmentAggregate | 某个项目的环境 |
| 聚合 | EnvironmentCollection | 多个环境 |
| 领域服务 | EnvironmentCreationService | 创建Conda环境 |
| 领域事件 | EnvironmentCreatedEvent | 环境创建完成 |
| 仓储接口 | EnvironmentRepository | 保存/查询环境 |
✅ 第二步:UML建模(UML Modeling)
我们将为每个领域绘制类图和领域事件图。
📊 领域1:脚本管理域 UML
+------------------+
| Script |
+------------------+
| - scriptId: Long |
| - type: ScriptType |
| - content: String |
| - projectId: Long |
+------------------+
| + execute(): void|
+------------------+
+------------------+
| ScriptType |
|------------------|
| CPP, LUA, PYTHON |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| ScriptAggregate |
+------------------+
| - script: Script |
+------------------+
| + addScript() |
| + removeScript() |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| ScriptRepository |
+------------------+
| + save() |
| + findById() |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| ScriptExecutedEvent |
+------------------+
| - scriptId: Long |
| - timestamp |
+------------------+
📊 领域2:依赖管理域 UML
+------------------+
| DependencyLibrary |
+------------------+
| - id: Long |
| - name: String |
| - version: String|
| - language: String|
+------------------+
+------------------+
| DependencyEdge |
+------------------+
| - from: Long |
| - to: Long |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| DependencyGraph |
+------------------+
| - rootId: Long |
| - edges: List<Edge> |
+------------------+
| + resolve() |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| DependencyRepository |
+------------------+
| + saveGraph() |
| + findById() |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| DependencyResolvedEvent |
+------------------+
| - rootId: Long |
+------------------+
📊 领域3:环境管理域 UML
+------------------+
| VirtualEnvironment |
+------------------+
| - id: Long |
| - name: String |
| - interpreter: String |
| - config: EnvironmentConfig |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| EnvironmentConfig |
+------------------+
| - pythonVersion |
| - dependencies |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| EnvironmentAggregate |
+------------------+
| - env: VirtualEnvironment |
+------------------+
| + createEnv() |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| EnvironmentRepository |
+------------------+
| + save() |
| + findById() |
+------------------+
+------------------+
| EnvironmentCreatedEvent |
+------------------+
| - envId: Long |
+------------------+
✅ 第三步:Java代码实现(Code Implementation)
我们使用Spring Boot + JPA + PostgreSQL + RocketMQ实现。
📁 项目结构(Maven)
src/main/java/com/example/scriptplatform/
├── domain/
│ ├── script/
│ ├── dependency/
│ └── environment/
├── application/
├── infrastructure/
比较难顶的一点:聚合和聚合根的具体区别
`// 领域包结构
package com.example.domain;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
// 聚合根:订单
public class Order {
private Long id;
private List
private OrderStatus status;
// 私有构造函数,防止外部直接创建实例
private Order(Long id) {
this.id = id;
this.status = OrderStatus.CREATED;
}
// 工厂方法:创建订单
public static Order createOrder(Long id) {
return new Order(id);
}
// 添加订单项必须通过聚合根进行
public void addItem(Product product, int quantity) {
// 验证库存(业务规则)
if (product.getStock() < quantity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Insufficient product stock");
}
// 创建订单项并添加到列表
OrderItem item = new OrderItem(product, quantity);
items.add(item);
// 更新订单状态
updateStatus();
}
// 获取订单项列表的只读视图
public List<OrderItem> getItems() {
return new ArrayList<>(items); // 返回副本,防止外部修改
}
// 获取订单状态
public OrderStatus getStatus() {
return status;
}
// 更新订单状态
private void updateStatus() {
// 根据业务规则更新订单状态
this.status = OrderStatus.PENDING_REVIEW;
}
// 其他业务逻辑方法...
}
// 聚合内部对象:订单项
class OrderItem {
private Product product;
private int quantity;
public OrderItem(Product product, int quantity) {
this.product = product;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
// Getter 和 Setter 省略
}
// 枚举:订单状态
enum OrderStatus {
CREATED, PENDING_REVIEW, APPROVED, SHIPPED, CANCELLED
}
// 实体:产品(这个可能是其他聚合的根或普通实体)
class Product {
private Long id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal price;
private int stock;
public Product(Long id, String name, BigDecimal price, int stock) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.stock = stock;
}
// Getter 和 Setter 省略
public int getStock() {
return stock;
}
}
// 应用服务层:订单应用服务
package com.example.application;
import com.example.domain.Order;
public class OrderApplicationService {
private final OrderRepository orderRepository;
public OrderApplicationService(OrderRepository orderRepository) {
this.orderRepository = orderRepository;
}
public OrderDto createOrder(Long orderId) {
// 调用领域对象的工厂方法创建订单
Order order = Order.createOrder(orderId);
orderRepository.save(order);
return convertToDto(order);
}
public OrderDto getOrder(Long orderId) {
Optional<Order> orderOpt = orderRepository.findById(orderId);
if (orderOpt.isPresent()) {
return convertToDto(orderOpt.get());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Order not found");
}
}
private OrderDto convertToDto(Order order) {
// 转换为DTO对象
return new OrderDto(order.getId(), order.getStatus());
}
}
// 基础设施层:订单仓储接口
package com.example.infrastructure;
import com.example.domain.Order;
public interface OrderRepository {
void save(Order order);
java.util.Optional
}
// 基础设施层:订单仓储实现(内存实现)
class InMemoryOrderRepository implements OrderRepository {
private final java.util.Map<Long, Order> orders = new java.util.HashMap<>();
@Override
public void save(Order order) {
orders.put(order.getId(), order);
}
@Override
public java.util.Optional<Order> findById(Long id) {
return java.util.Optional.ofNullable(orders.get(id));
}
}
// 接入接口层:订单控制器
package com.example.interfaces;
import com.example.application.OrderApplicationService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/orders")
public class OrderController {
private final OrderApplicationService orderApplicationService;
public OrderController(OrderApplicationService orderApplicationService) {
this.orderApplicationService = orderApplicationService;
}
@PostMapping
public OrderDto createOrder(@RequestParam Long orderId) {
return orderApplicationService.createOrder(orderId);
}
@GetMapping("/{orderId}")
public OrderDto getOrder(@PathVariable Long orderId) {
return orderApplicationService.getOrder(orderId);
}
}
// DTO:订单数据传输对象
class OrderDto {
private Long id;
private String status;
public OrderDto(Long id, com.example.domain.OrderStatus status) {
this.id = id;
this.status = status.name();
}
// Getter 和 Setter 省略
}`
最重要的是关于DDD架构中的领域划分


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号