Java基础知识_HashMap
一、HashMap剖析
首先看看HashMap的顶部注释说了些什么:
/** * Hash table based implementation of the <tt>Map</tt> interface. This * implementation provides all of the optional map operations, and permits * <tt>null</tt> values and the <tt>null</tt> key. (The <tt>HashMap</tt> 允许为null,不保证有序
* class is roughly equivalent to <tt>Hashtable</tt>, except that it is * unsynchronized and permits nulls.) This class makes no guarantees as to * the order of the map; in particular, it does not guarantee that the order 初始容量太高和装载因子太低对遍历都不好 * will remain constant over time. * * <p>This implementation provides constant-time performance for the basic * operations (<tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>), assuming the hash function * disperses the elements properly among the buckets. Iteration over * collection views requires time proportional to the "capacity" of the * <tt>HashMap</tt> instance (the number of buckets) plus its size (the number * of key-value mappings). Thus, it's very important not to set the initial * capacity too high (or the load factor too low) if iteration performance is * important. * * <p>An instance of <tt>HashMap</tt> has two parameters that affect its * performance: <i>initial capacity</i> and <i>load factor</i>. The * <i>capacity</i> is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial * capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The * <i>load factor</i> is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to * get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of * entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the * current capacity, the hash table is <i>rehashed</i> (that is, internal data * structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the 当初始容量*装载因子小于哈希表的容量时,哈希表 * number of buckets. 会再散列,桶数会*2 * * <p>As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good * tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the 装载因子默认是0.75,设置高会减少空间,但是会增加 * space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of 遍历开销 * the operations of the <tt>HashMap</tt> class, including * <tt>get</tt> and <tt>put</tt>). The expected number of entries in * the map and its load factor should be taken into account when * setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of * rehash operations. If the initial capacity is greater than the * maximum number of entries divided by the load factor, no rehash * operations will ever occur. * * <p>If many mappings are to be stored in a <tt>HashMap</tt> 如果知道有足够多的数据存到HashMap,最好设置初始容量,比自然散列 * instance, creating it with a sufficiently large capacity will allow 要好很多。 * the mappings to be stored more efficiently than letting it perform * automatic rehashing as needed to grow the table. Note that using * many keys with the same {@code hashCode()} is a sure way to slow * down performance of any hash table. To ameliorate impact, when keys * are {@link Comparable}, this class may use comparison order among * keys to help break ties. * * <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong> 不同步但可以用Collection工具类; * If multiple threads access a hash map concurrently, and at least one of * the threads modifies the map structurally, it <i>must</i> be * synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation * that adds or deletes one or more mappings; merely changing the value * associated with a key that an instance already contains is not a * structural modification.) This is typically accomplished by * synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map. * * If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the * {@link Collections#synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedMap} * method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental * unsynchronized access to the map:<pre> * Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));</pre> * * <p>The iterators returned by all of this class's "collection view methods" 迭代器相关 * are <i>fail-fast</i>: if the map is structurally modified at any time after * the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own * <tt>remove</tt> method, the iterator will throw a * {@link ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent * modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking * arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the * future. * * <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed * as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the * presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators * throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis. * Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this * exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators * should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
再来看看HashMap的类继承图:
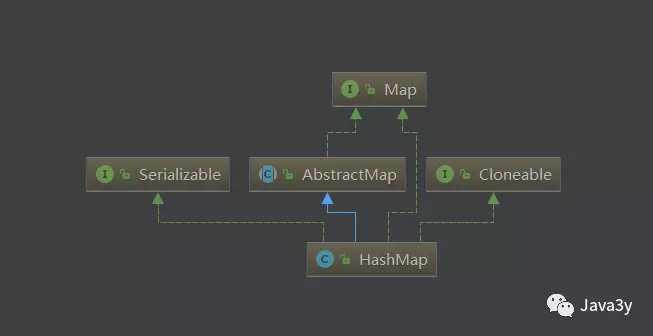
下面我们来看一下HashMap的属性
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 初始容量是16
/**
* The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified
* by either of the constructors with arguments.
* MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30.
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; 最大容量是2的31次方
/**
* The load factor used when none specified in constructor.
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 默认装载因子
/**
* The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a
* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a
* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater
* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in
* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon
* shrinkage.
*/
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; 桶超过8个节点,转化成树形结构
/**
* The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a
* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at
* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.
*/
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; 同上,不过是把树形转换成链表
/**
* The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.
* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)
* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts
* between resizing and treeification thresholds.
*/
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; 桶可能转化成树形结构的最小容量
成员属性有这么几个
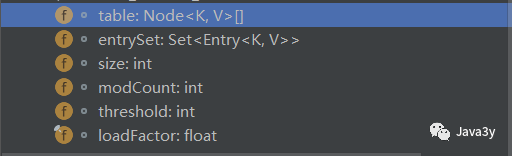
再来看一下,hashmap的一个内部类Node
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next; 链表结构,存储下一个元素
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
我们知道Hash的底层是散列表,而在Java中散列表的实现是通过数组+链表的
再来简单看看put方法就可以印证我们的说法了:数组+链表=散列表
我们可以简单总结出HashMap
无序,允许为null,非同步
底层由散列表实现
初始容量和装在因子对HashMap影响挺大的,设置小了不好,设置大了也不好
1.1 HashMap构造方法
HashMap的构造方法有4个
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
判断初始化大小是否合理,如果超过就赋值最大值,初始化装载因子
在上面的构造方法的最后一行,我们会发现调用tableSizeFor(),我们进去看看
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
返回的是一个大于输入参数且最近的2的整数次幂的数
为什么是2的整数次幂呢?hash%length=hash&(length-1),但前提是length是2的n次方,并且采用&运算比%运算效率高
这里是一个初始化,在创建哈希表的时候,它会重新赋值(capacity*loadfactor)
其他的构造方法就不多说了。
1.2 put方法
put方法可以说是HashMap的核心,我们来看看
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); 3 }
调用了putVal方法,以key计算哈希值,传入key和value,还有两个参数
我们来看看是怎么计算哈希值的
1 static final int hash(Object key) { 2 int h; 3 return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); 4 }
得到key的HashCode,与KeyHashCode的高16位做异或运算
为什么要这么干呢??我们一般来说直接将key作为哈希值不就好了,做异或运算是干嘛用的??
我们看下来
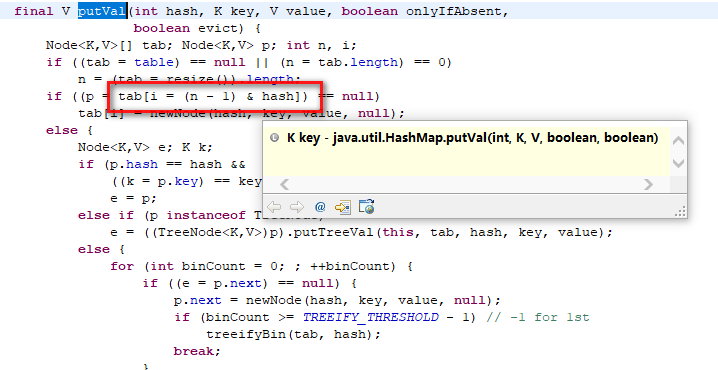
我们是根据key的哈希值来保存在散列表中的,我们表默认的初始容量是16,要放到散列表中也就是0-15的位置
也就是tab[n-1&hash],我们可以发现的是仅仅后四位有效,那如果我们key的哈希值高位变化很大,地位变化很小。直接拿过去&运算,这就会导致计算出来的Hash值相同的很多。
而设计者将key的哈希值的高位做了运算(与高16位做异或运算,使得在做&的时候,此时的低位实际上是高位和地位的结合),这就增加了随机性,减少了碰撞冲突的可能性。
下面我们再来看看流程是怎么样的
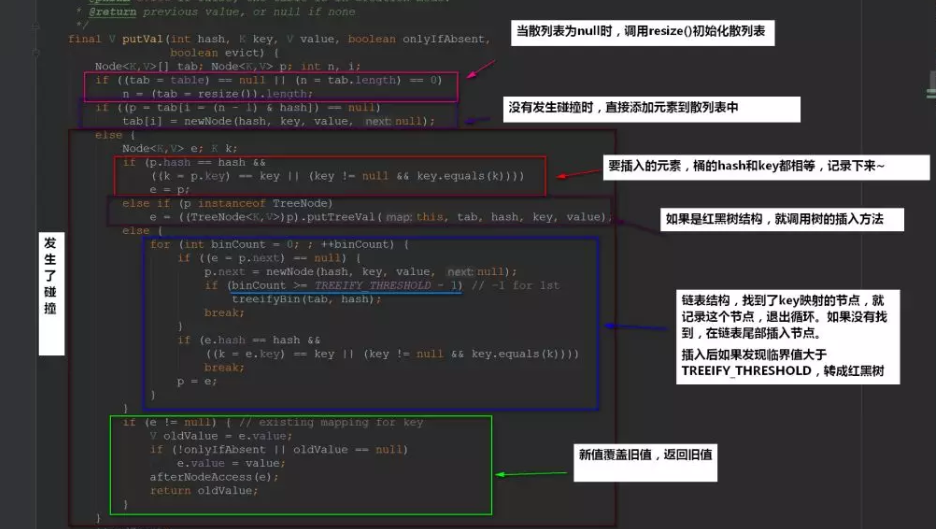
1.3 get方法
1 public V get(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value; 4 }
计算key的哈希值,调用getNode获取相对应的value
接下来我们看看getNode()是怎么实现的:
1 final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { 2 Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; 3 if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && 4 (first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { 5 if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node 6 ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 7 return first; 8 if ((e = first.next) != null) { 9 if (first instanceof TreeNode) 10 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); 11 do { 12 if (e.hash == hash && 13 ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) 14 return e; 15 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 16 } 17 } 18 return null; 19 }
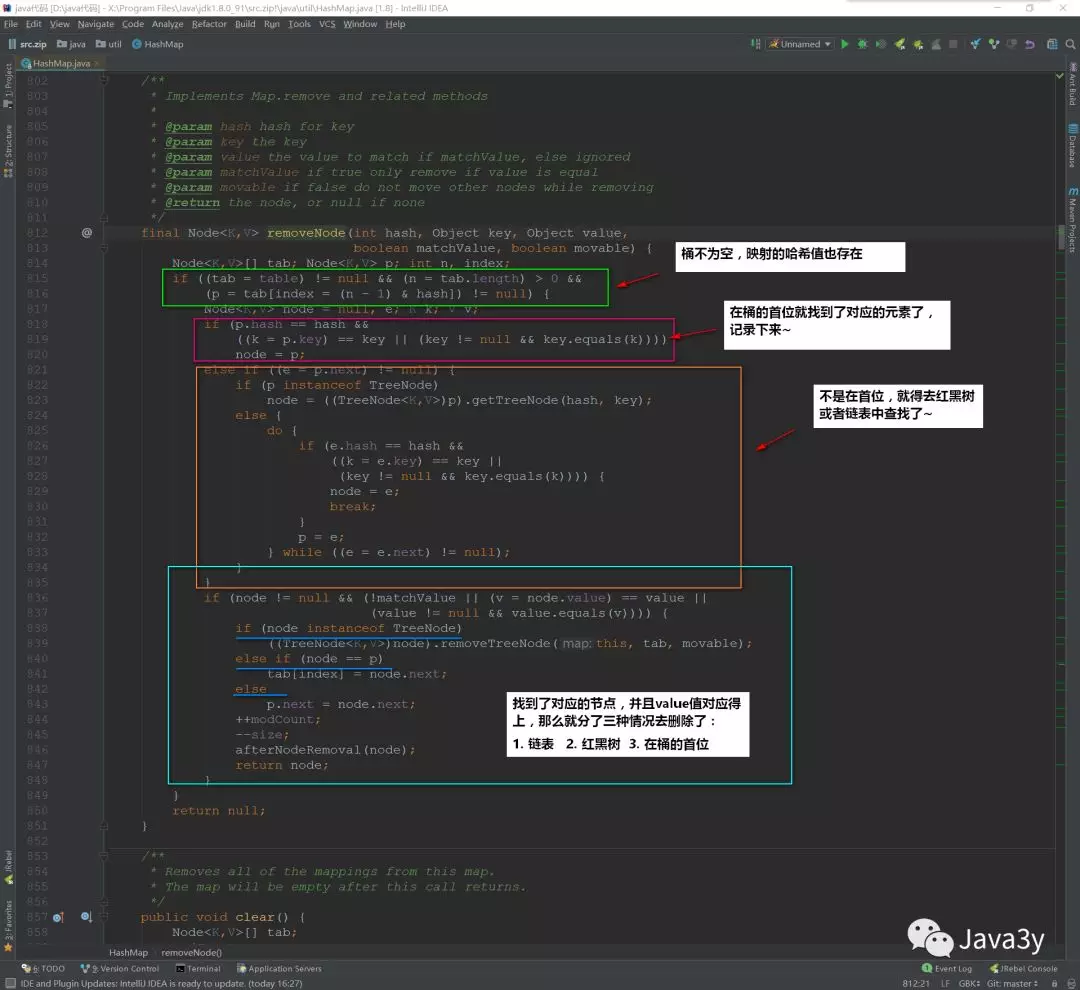
计算出来的哈希值是在哈希表上的,如果在桶的首位上就可以找到,那么就直接返回,否则就在红黑树或者链表中寻找。
1.4 remove方法
1 public V remove(Object key) { 2 Node<K,V> e; 3 return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ? 4 null : e.value; 5 }
也是计算key的哈希值来计算来删除value
再来看看removeNode()的实现:
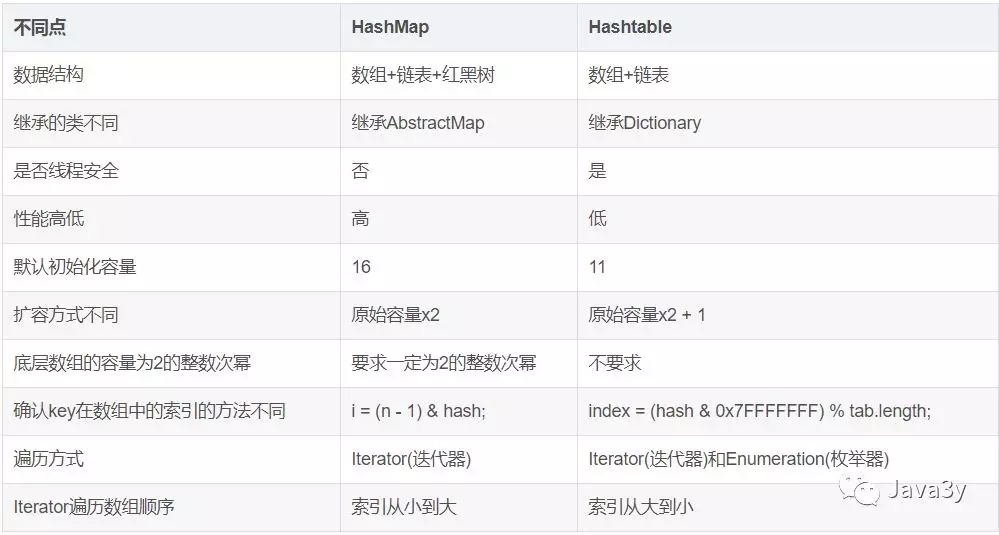
二、HashMap和HashTable对比
从存储结构和实现来讲基本上都是相同的。它和HashMap的最大的不同是它是线程安全的,另外它不允许key和value为null。Hashtable是个过时的集合类,不建议在新代码中使用,不需要线程安全的场合可以用HashMap替换,需要线程安全的场合可以用ConcurrentHashMap替换
四、总结
在JDK8中HashMap的底层是数组+链表(散列表)+红黑树
在散列表中有装载因子这么一个属性,当装载因子*初始容量小于散列表元素时,该散列表会再扩散,扩容2倍
装载因子的默认值是0.75,无论初始大了还是初始小了,都对Hash Map的性能都不好
装载因子初始值大了,可以减少散列表的扩容次数,但同时会导致散列冲突的可能性变大(散列冲突也是耗性能的一个操作,要得操作链表红黑树)
装载因子初始值小了,可以减少冲突得可能性,但同时扩容得次数会变多
初始容量默认值是16,也一样,无论是大了还说小了,对我们得HashMap都是有影响的:
初始容量过大,那么我们遍历的速度就会受到影响
初始容量过小,那么再散列(扩容的次数)可能就变得多了,扩容也是一件非常耗性能的事情
从源码上我们可以发现:HashMap并不是直接拿Key的哈希值来用的,它会将key的哈希值的最高位16位进行异或操作,使得我们将元素放入哈希表的时候增加了一定的随机性。
还要值得注意的是:并不是桶子上有8位元素的时候它就能变成红黑树的,得同时满足散列表得容量大于64才行的


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号