Figure 5-1. Data structures associated with processes and threads
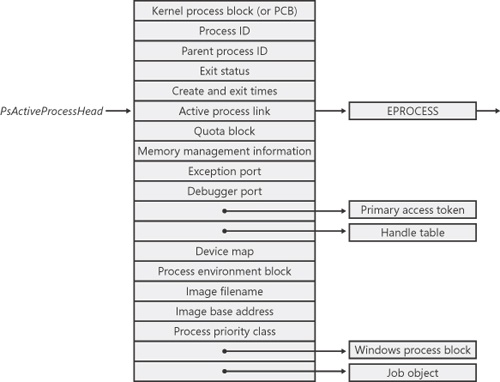
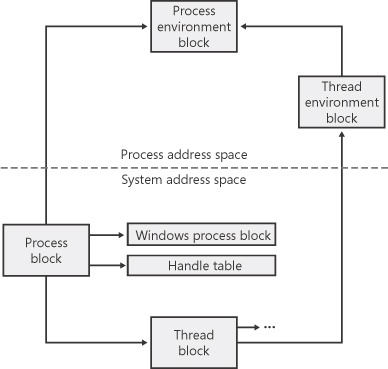
Figure 5-2. Structure of an executive process block
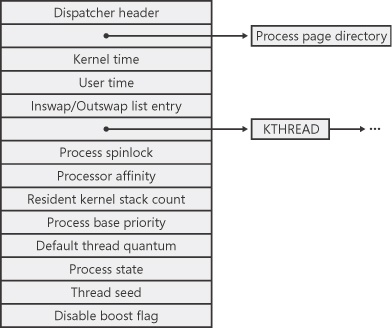
Figure 5-3. Structure of the executive process block
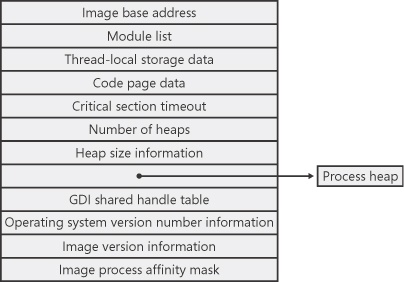
Figure 5-4. Fields of the process environment block
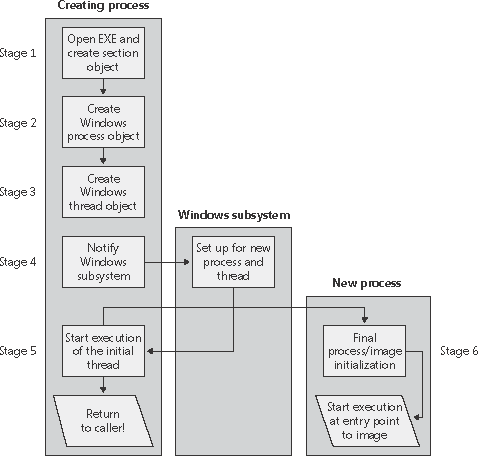
Figure 6-5. The main stages of process creation
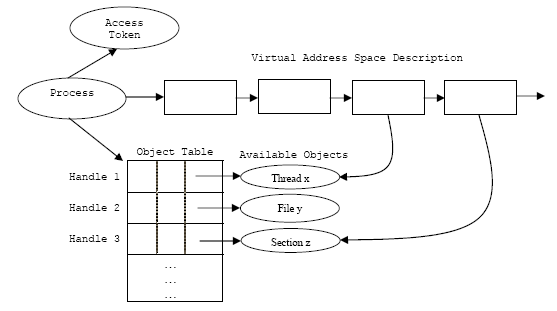
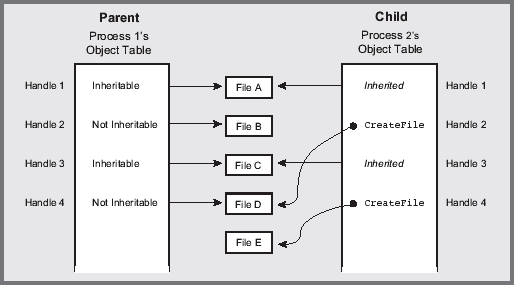
Figure 3: Windows NT process and its resources
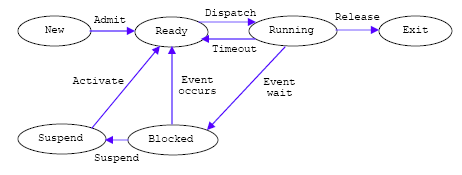
Figure 4: An example of a process state transition diagram
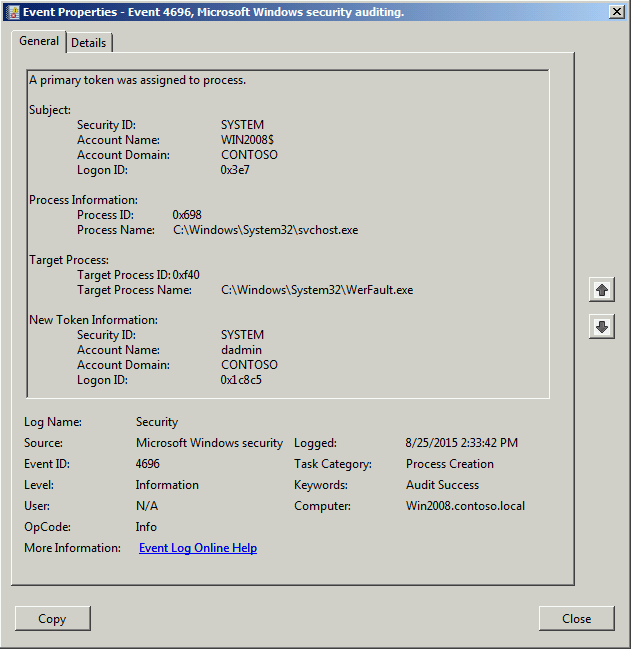
A primary token was assigned to process
BOOL ok = CreateProcess(
NULL, cmd, NULL, NULL, FALSE, 0, NULL, NULL, &si, &pi);
ExitProcess(0);
CloseHandle(process);
if (*tmp == L'-' &&
(! SbieApi_QueryProcessInfo(
(HANDLE)(ULONG_PTR)GetCurrentProcessId(), 0))) {}
return OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_ALL_ACCESS, phToken);
status = NtQueryInformationProcess(
NtCurrentProcess(), ProcessBasicInformation,
&info, sizeof(PROCESS_BASIC_INFORMATION), &len);
hParentProcess = OpenProcess(
SYNCHRONIZE, FALSE, (ULONG)info.InheritedFromUniqueProcessId);
GetWindowThreadProcessId(hwnd, &pid);
BOOL ok = GetProcessTimes(hProcess, &time, &time1, &time2, &time3);
if (EnumProcesses(pids, 16384, &len))
len /= sizeof(ULONG);
if (! ProcessIdToSessionId(GetCurrentProcessId(), &session_id))
session_id = 0;
status = WaitForSingleObject(hParentProcess, INFINITE);
if (status == WAIT_OBJECT_0)
ExitProcess(0);
if (RegisterWaitForSingleObject(
&WaitHandles[0], hProcess,
ConsoleCallbackSlave, (void *)WaitHandles,
INFINITE, WT_EXECUTEONLYONCE)) {}