2025年12月09日 模拟赛总结
Treasure Hunt
前面 \(k(x+y)\) 米都不用管,只有判断最后不到 \(x+y\) 米就可以了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int x, y, a;
void solve() {
cin >> x >> y >> a;
int lst = a % (x + y);
if (lst < x) cout << "NO\n";
else cout << "YES\n";
}
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) solve();
return 0;
}
Pushing Balls
如果一个球的左边与上边都没有全部填满,那么就绝对不可能成功,因此用二维前缀和维护就可以了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
int a[55][55];
int pre[55][55];
bool flag;
char c;
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
flag = false;
cin >> n >> m;
// 读取矩阵数据(处理输入中的空白字符)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (c != '0' && c != '1') c = getchar();
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
a[i][j] = c - '0';
c = getchar();
}
}
// 计算二维前缀和
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
pre[i][j] = pre[i - 1][j] + pre[i][j - 1] - pre[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j];
}
}
// 检查每个1的位置是否符合条件
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (a[i][j] == 1) {
if (pre[i][j] - pre[i][j - 1] != i && pre[i][j] - pre[i - 1][j] != j) {
cout << "NO\n";
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag) break;
}
if (flag) continue;
cout << "YES\n";
}
return 0;
}
Dining Hall
下图表示到达大厅中的所有桌子(灰色部分)所需的最小步数:
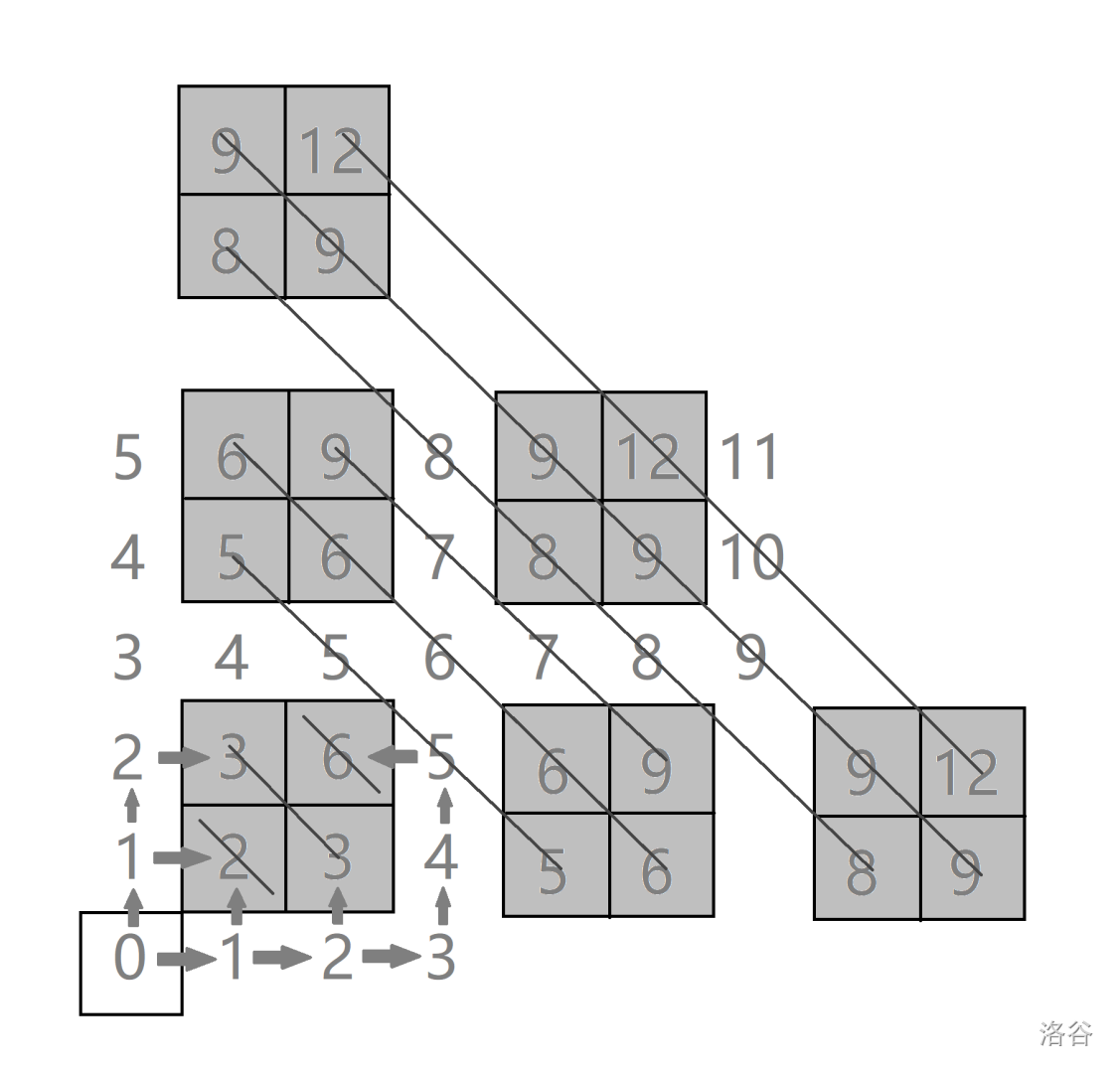
由此可以发现相同步数的位置呈斜向排列,我们可以得到:到达一个桌子上的位置 \((x,y)\) 的步数,等同于到达另一张桌子上的位置 \((x+3,y-3)\) 的步数。
为了找到当前距离最小的点,可以用优先队列维护。为了防止堆空情况,我们还有维护一个目前可能的最优位置,这个位置所在的桌子没有人。
具体如下:
- 如果当前客人需要空位置,我们就去优先队列里找(前提是堆不为空,并且要求队顶距离要小于目前已知并且可以提供的最小距离),那么就把优先队列队顶的元素给予这位客人,并且弹出。
- 如果上述条件没有满足,则把目前可能的最优位置所在桌子的另外三个位置塞入队列,并把目前可能的最优位置给予这位客人,然后更新可能的最优位置。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct node {
int dis, x, y;
bool operator<(const node t) const {
if (dis != t.dis) return dis > t.dis;
if (x != t.x) return x > t.x;
if (y != t.y) return y > t.y;
}
};
ll T, n;
int main() {
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
priority_queue<node> pq;
ll x = 1, y = 1, now = 2;
cin >> n;
vector<pair<ll, ll>> ans(n + 1);
for (ll i = 1, xx; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> xx;
if (xx && !pq.empty() && pq.top().dis < now) {
auto p = pq.top();
pq.pop();
ans[i] = { p.x, p.y };
} else {
ans[i] = { x, y };
pq.push({x + y + 1, x + 1, y});
pq.push({x + y + 1, x, y + 1});
pq.push({x + y + 4, x + 1, y + 1});
if (y - 1) x += 3, y -= 3;
else swap(x, y), y += 3;
now = x + y;
}
}
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << ans[i].first << " " << ans[i].second << endl;
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号