工作流中的数据持久化详解!Activiti框架中JPA的使用分析

Activiti中JPA简介
- 可以使用JPA实体作为流程变量, 并进行操作:
- 基于流程变量更新已有的JPA实体,可以在用户任务的表单中填写或者由服务任务生成
- 重用已有的领域模型,不需要编写显示的服务获取实体或者更新实体的值
- 根据已有实体的属性做出判断(网关即分支聚合)
JPA实体要求
- Activiti中JPA只支持符合以下要求的实体:
- 实体应该使用JPA注解进行配置, 支持字段和属性访问两种方式.@MappedSuperclass也要能够被使用
- 实体中应该有一个使用@Id注解的主键,不支持复合主键@EmbeddedId 和 @IdClass:
- Id字段或者属性能够使用JPA规范支持的任意类型:
- 原生态数据类型和他们的包装类型(Boolean除外)
- String
- BigInteger
- BigDecimal
- java.util.Date
- java.sql.Date
- Id字段或者属性能够使用JPA规范支持的任意类型:
JPA配置
- 引擎必须有一个对EntityManagerFactory的引用才能够使用JPA的实体,这样可以通过配置引用或者提供一个持久化单元名称
- 作为变量的JPA实体将会被自动检测并进行相应的处理
- 使用jpaPersistenceUnitName配置:
<bean id="processEngineConfiguration" class="org.activiti.engine.impl.cfg.StandaloneInMemProcessEngineConfiguration">
<!-- 数据库的配置 -->
<property name="databaseSchemaUpdate" value="true" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:h2:mem:JpaVariableTest;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=1000" />
<property name="jpaPersistenceUnitName" value="activiti-jpa-pu" />
<property name="jpaHandleTransaction" value="true" />
<property name="jpaCloseEntityManager" value="true" />
<!-- job executor configurations -->
<property name="jobExecutorActivate" value="false" />
<!-- mail server configurations -->
<property name="mailServerPort" value="5025" />
</bean>
- 配置一个自定义的EntityManagerFactory,
- 这里使用了OpenJPA实体管理器
- 该代码片段仅仅包含与例子相关的beans,去掉了其他beans.
- OpenJPA实体管理的完整并可以使用的例子可以在activiti-spring-examples(/activiti-spring/src/test/java/org/activiti/spring/test/jpa/JPASpringTest.java) 中找到
<bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean">
<property name="persistenceUnitManager" ref="pum"/>
<property name="jpaVendorAdapter">
<bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.OpenJpaVendorAdapter">
<property name="databasePlatform" value="org.apache.openjpa.jdbc.sql.H2Dictionary" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="processEngineConfiguration" class="org.activiti.spring.SpringProcessEngineConfiguration">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
<property name="databaseSchemaUpdate" value="true" />
<property name="jpaEntityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory" />
<property name="jpaHandleTransaction" value="true" />
<property name="jpaCloseEntityManager" value="true" />
<property name="jobExecutorActivate" value="false" />
</bean>
- 也可以在编程式创建一个引擎时完成配置:
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngineConfiguration
.createProcessEngineConfigurationFromResourceDefault()
.setJpaPersistenceUnitName("activiti-pu")
.buildProcessEngine();
配置的属性有:
- jpaPersistenceUnitName: 使用持久化单元的名称:
- 要确保该持久化单元在类路径下是可用的,默认的路径是 /META-INF/persistence.xml
- 要么使用jpaEntityManagerFactory要么或者是jpaPersistenceUnitName
- jpaEntityManagerFactory: 一个实现了javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory的bean的引用:
- 将被用来加载实体并且刷新更新
- 要么使用jpaEntityManagerFactory要么或者是jpaPersistenceUnitName
- jpaHandleTransaction: 在被使用的EntityManager实例上,该标记表示流程引擎是否需要开始和提交或者回滚事务:
- 当使用Java事务API(JTA) 时,设置为false
- jpaCloseEntityManager: 该标记表示流程引擎是否应该关闭从 EntityManagerFactory获取的EntityManager的实例:
- 当EntityManager是由容器管理的时候需要设置为false: 当使用并不是单一事务作用域的扩展持久化上下文的时候
JPA用法
简单示例
- 首先,需要创建一个基于META-INF/persistence.xml的EntityManagerFactory作为持久化单元:包含持久化单元中所有的类和一些供应商特定的配置
- 使用一个简单的实体作为测试,其中包含有一个id和String类型的value属性,也将会被持久化
- 在测试之前,创建一个实体并且保存:
@Entity(name = "JPA_ENTITY_FIELD")
public class FieldAccessJPAEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "ID_")
private Long id;
private String value;
public FieldAccessJPAEntity() {
// Empty constructor needed for JPA
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
- 启动一个新的流程实例,添加一个实体作为变量. 其他的变量,将会被存储在流程引擎的持久化数据库中.下一次获取该变量的时候,将会根据该类和存储Id从EntityManager中加载:
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>();
variables.put("entityToUpdate", entityToUpdate);
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("UpdateJPAValuesProcess", variables);
- 流程定义中的第一个节点是一个服务任务,将会调用entityToUpdate上的setValue方法,其实就是之前在启动流程实例时候设置的JPA变量并且将会从当前流程引擎的上下文关联的EntityManager中加载:
<serviceTask id='theTask' name='updateJPAEntityTask' activiti:expression="${entityToUpdate.setValue('updatedValue')}" />
- 当完成服务任务时,流程实例将会停留在流程定义中定义的用户任务环节上:
- 可以查看该流程实例
- EntityManager已经被刷新了并且改变的实体已经被保存进数据库中
- 获取entityToUpdate的变量value时,该实体将会被再次加载并且获取该实体属性的值将会是updatedValue
// Servicetask in process 'UpdateJPAValuesProcess' should have set value on entityToUpdate.
Object updatedEntity = runtimeService.getVariable(processInstance.getId(), "entityToUpdate");
assertTrue(updatedEntity instanceof FieldAccessJPAEntity);
assertEquals("updatedValue", ((FieldAccessJPAEntity)updatedEntity).getValue())
查询JPA流程变量
- 以查询某一JPA实体作为变量的ProcessInstances和Executions
- 在ProcessInstanceQuery和ExecutionQuery查询中仅仅variableValueEquals(name, entity) 支持JPA实体变量:
- [variableValueNotEquals],[variableValueGreaterThan],[variableValueGreaterThanOrEqual],[variableValueLessThan],[variableValueLessThanOrEqual]不被支持并且传递JPA实体值的时候会抛出一个ActivitiException
ProcessInstance result = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().variableValueEquals("entityToQuery", entityToQuery).singleResult();
使用Spring beans和JPA结合
- JPASpringTest, 在activiti-spring-examples中:
- 已经存在了一个使用JPA实体的Spring-bean, 用来存储贷款申请
- 使用Activiti,可以通过已经存在的bean获取已经使用的实体,并使用它作为变量用于流程中
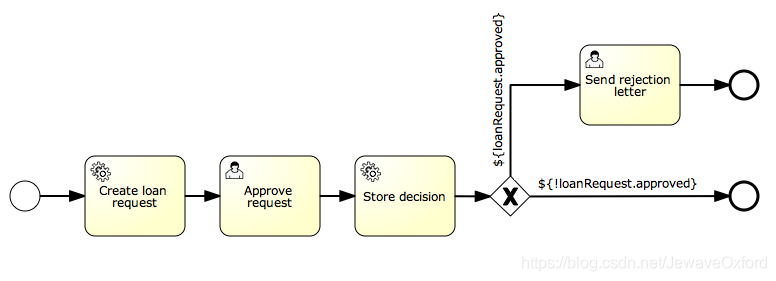
- 流程定义步骤:
- 服务任务:
- 创建一个新的贷款申请,使用已经存在的LoanRequestBean接受启动流程时候的变量(来自流程启动时候的表单)
- 使用activiti:resultVariable(作为一个变量对表达式返回的结果进行存储)将创建出来的实体作为变量进行存储
- 用户任务:
- 允许经理查看贷款申请,并填入审批意见(同意/不同意)
- 审批意见将作为一个boolean变量approvedByManager进行存储
- 服务任务:
- 更新贷款申请实体,因此该实体与流程保持同步
- 根据贷款申请实体变量approved的值,将利用唯一网关自动决定下一步该选择那一条路径:
- 当申请批准,流程结束
- 否则,一个额外的任务将会使用(发送拒绝信),这样就可以发送拒绝信手动通知客户
![在这里插入图片描述]()
- 服务任务:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions id="taskAssigneeExample"
xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:activiti="http://activiti.org/bpmn"
targetNamespace="org.activiti.examples">
<process id="LoanRequestProcess" name="Process creating and handling loan request">
<startEvent id='theStart' />
<sequenceFlow id='flow1' sourceRef='theStart' targetRef='createLoanRequest' />
<serviceTask id='createLoanRequest' name='Create loan request'
activiti:expression="${loanRequestBean.newLoanRequest(customerName, amount)}"
activiti:resultVariable="loanRequest"/>
<sequenceFlow id='flow2' sourceRef='createLoanRequest' targetRef='approveTask' />
<userTask id="approveTask" name="Approve request" />
<sequenceFlow id='flow3' sourceRef='approveTask' targetRef='approveOrDissaprove' />
<serviceTask id='approveOrDissaprove' name='Store decision'
activiti:expression="${loanRequest.setApproved(approvedByManager)}" />
<sequenceFlow id='flow4' sourceRef='approveOrDissaprove' targetRef='exclusiveGw' />
<exclusiveGateway id="exclusiveGw" name="Exclusive Gateway approval" />
<sequenceFlow id="endFlow1" sourceRef="exclusiveGw" targetRef="theEnd">
<conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression">${loanRequest.approved}</conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
<sequenceFlow id="endFlow2" sourceRef="exclusiveGw" targetRef="sendRejectionLetter">
<conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression">${!loanRequest.approved}</conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
<userTask id="sendRejectionLetter" name="Send rejection letter" />
<sequenceFlow id='flow5' sourceRef='sendRejectionLetter' targetRef='theOtherEnd' />
<endEvent id='theEnd' />
<endEvent id='theOtherEnd' />
</process>
</definitions>
上面的例子展示了JPA结合Spring和参数化方法表达式的强大优势 :所有的流程就不需要自定义java代码(Spring bean除外),大幅度的加快了流程部署




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号