20242216 实验二《Python程序设计》实验报告
学号 2024-2025-2 《Python程序设计》实验二报告
课程:《Python程序设计》
班级: 2422
姓名: 王乐天
学号:20242216
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2025年3月26日
必修/选修: 公选课
1.实验内容
-
设计并完成一个完整的应用程序,完成加减乘除模等运算,功能包括普通模式的加减乘除乘方对数取模(支持小数)、二进制模式的与或非异或、复数模式的加减乘除;
-
考核基本语法、判定语句、循环语句、逻辑运算等知识点;
2. 实验过程及结果
-
设计计算器模式,找到需要用户输入的参数并填写提示词
-
实现计算器功能,注意二进制非运算只需要一个参数
-
试运行程序,确保程序可以应对各种数据
import math
def calculate(a, b, o):
if o == "+":
return a + b
elif o == "-":
return a - b
elif o == "*":
return a * b
elif o == "/":
if b == 0:
return "Division by zero is not allowed"
return a / b
elif o == "~":
return ~a
elif o == "&":
return a & b
elif o == "|":
return a | b
elif o == "^":
return a ^ b
elif o == "%":
return a % b
elif o == "log":
if a <= 0:
return "Input must be > 0 for log"
if b <= 0 or b == 1:
return "Invalid base. Must be > 0 and != 1"
return math.log(a, b)
else:
return "Invalid operator"
print("Welcome to the calculator!")
print("This calculator supports normal, binary mode and complex mode.")
print("Pay attention: the number you enter must be integer in normal mode!")
while True:
print("Choose the mode of calculator (or enter 'q' to quit):")
print("1. normal")
print("2. binary")
print("3. complex")
mode_input = input()
if mode_input == "q":
print("Exiting the calculator. Goodbye!")
break
mode = int(mode_input)
operator = input("Enter operator:")
if mode == 2 and operator == "~":
a = int(input("Enter the number:"))
print("The result is: ", calculate(a, 0, operator))
else:
if operator == "log" and mode == 1:
a = float(input("Enter the number: "))
b = float(input("Enter the base: "))
print("The result is: ", calculate(a, b, operator))
continue
if mode == 3:
a = complex(input("Enter the first complex number: "))
b = complex(input("Enter the second complex number: "))
if operator in ["+", "-", "*", "/"]:
print("The result is: ", calculate(a, b, operator))
else:
print("Invalid operator for complex mode")
else:
a = int(input("Enter the first number: ")) if mode == 2 else float(input("Enter the first number: "))
b = int(input("Enter the second number: ")) if mode == 2 else float(input("Enter the second number: "))
if mode == 1:
if operator in ["+", "-", "*", "/", "%","^"]:
print("The result is: ", calculate(a, b, operator))
else:
print("Invalid operator")
elif mode == 2:
if operator in ["&", "|", "^"]:
print("The result is: ", calculate(a, b, operator))
else:
print("Invalid operator")
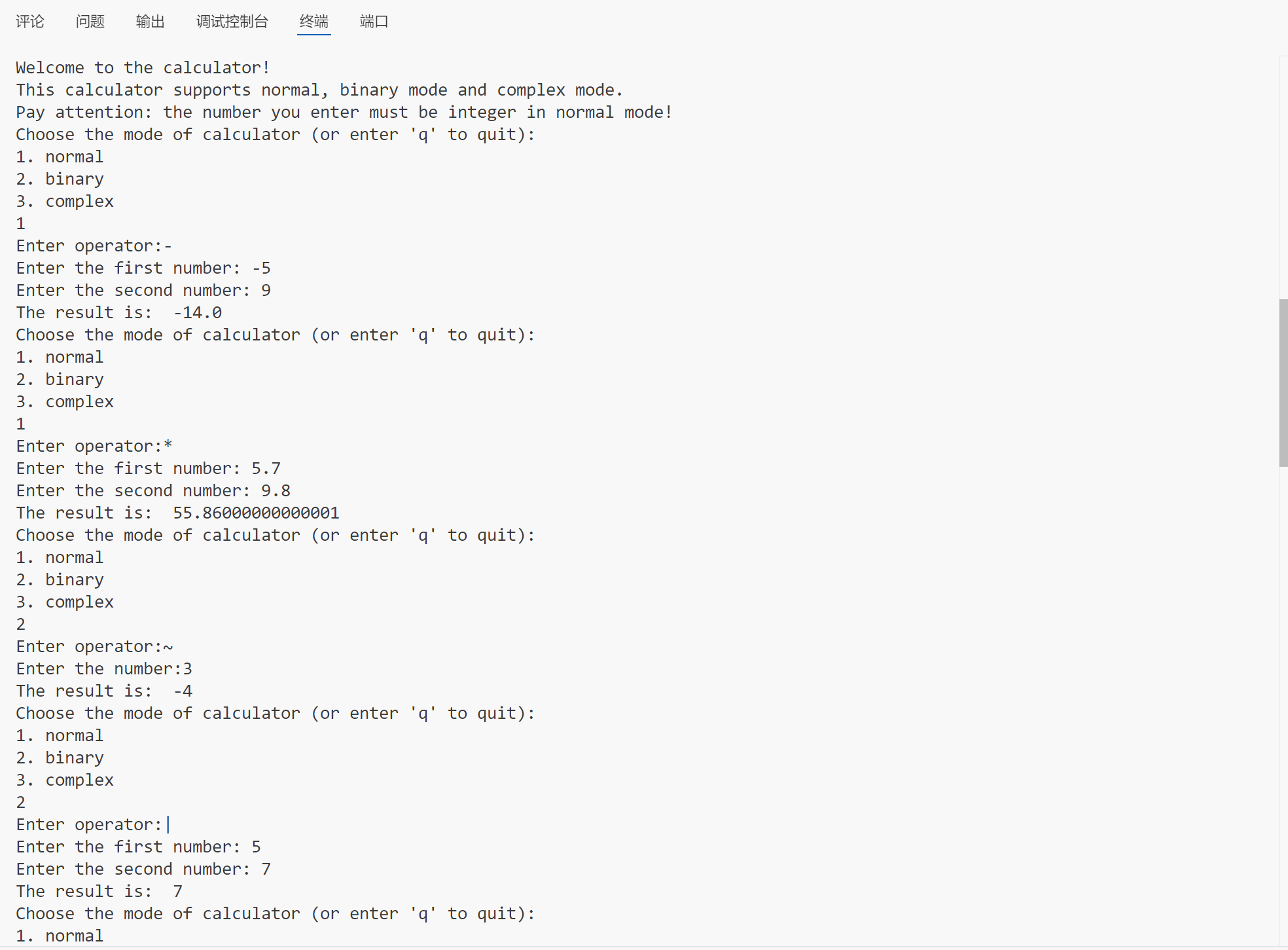
4. 利用随机数生成一个随机出题软件
import random
n = int(input("The number of the problem: "))
point = 0
for _ in range(n):
a = random.randint(0, 9)
b = random.randint(0, 9)
operate = random.randint(0, 3)
if operate == 0:
user_answer = int(input("{a}+{b}=? "))
result = a + b
elif operate == 1:
if a < b:
a, b = b, a
user_answer = int(input("{a}-{b}=? "))
result = a - b
elif operate == 2:
user_answer = int(input("{a}*{b}=? "))
result = a * b
else:
while b == 0:
b = random.randint(1, 9)
user_answer = float(input("{a}/{b}=? "))
result = a / b
if user_answer == result:
print("Correct!")
point += 10
else:
print("Wrong!")
print("Your total score is {point}")
5. 托管代码到gitee
gitee
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:复数输入无法识别;
- 问题1解决方案:查询后发现,在python中,虚部的单位为j而不是i;
其他(感悟、思考等)
函数可以极大的提高代码复用性,降低程序编写的复杂度。而且在这一次的函数使用中,我更清晰的认识到了python的动态特点,对它和先前所使用的语言区分更加明了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号