区域生长算法
区域生长(Region Growing)是指将成组的像素或区域发展成更大区域的过程。从种子点的集合开始,从这些点的区域增长是通过将与每个种子点有相似属性像强度、灰度级、纹理颜色等的相邻像素合并到此区域。在二维图像中实现区域生长可以采用之前的文章中所介绍的种子点生长算法,但在实际应用中,可以有不同的生长准则可以选择,这依赖于用户的需求,本文简要的介绍几种在ITK库(Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit)中提到的几种生长准则。
几种生长准则
本文主要介绍下面四种区域生长准则,对每一种准则都有相应的实现和实验测试。这些准则如下表所示:
|
方法 |
原理描述 | 输入参数 |
| 连续阈值法 | 基于用户提供的灰度区间。用户提供区间的最小值Lower和最大值Upper。如果邻近像素的像素值落在区间内,区域生长算法会将像素包含人生长区域。 |
Lower Bound Upper Bound |
| 邻接连续阈值法 | 基于用户提供的灰度区间。用户提供区间的最小值Lower和最大值Upper。如果邻近像素的像素值落在区间内,区域生长算法会将像素包含人生长区域。 |
Lower Bound Upper Bound Radius |
| 梯度法 | 以一个像素的邻近像素的值是否与之差别在指定的值之内为准则,差别小于一定值,则将其纳入区域。 | MaxiumnDelta |
| 置信连接阈值法 |
以当前区域的统计特性为准则,判定像素是否包 含在生长区域内。算法将当前像素的邻近区域内像素值落在一定区间内的像素包含人生长区域。这个区间的确定方法是先计算当前生长区域所有像素灰度值的均值和标准方差, 再将用户提供的因子乘 以标准方差,定义一个均值附近的区间。如公式:
如果邻近区域中再没有满足这一准则的像素,算 法将完成第一次迭代。这时,重新计算当前生长区域 内所有像素的均值与标准方差。它们定义了一个新的区间,判定新邻域的所有像素值是否落在这一区间。如此迭代,直到没有更多的像素包含人生长 区域或到达迭代最大次数。 |
Confidence Fator Max Iteration Time Initializing Radius |
这几种方法具有的特点罗列如下:
| 方法 | 特点描述 |
| 连续阈值法 | 基础方法,但想取得好的分割结果需要高质量的输入图片。 |
| 邻接连续阈值法 | 用邻近像素值来代替当前像素值,可以降低小结构被并人生长区域的概率。这相当于对当前像素应用连续阈值法后,再对其进行一次数学形态上的腐蚀。 |
| 梯度法 | 一般会和其他准则组合使用,单独使用时,容易出现过渡生长的情况,尤其对于边界不明显的图片。 |
| 置信连接阈值法 | 基于统计特性,对部分图像能够起到较好的分割效果,但对具有较多噪声的图像效果并不理想。 |
代码实现
生长准则区域生长算法的思想核心。在实现上,有多种策略可以选择,在前面的几篇关于种子点生长的文章中介绍了3种种子点生长算法,分别是“泛洪法”、“扫描线法”,“区段法”,这几种算法本是用作区域填充,但经过一定的改善即可以用做区域生长算法的迭代逻辑,无论采用什么样的迭代逻辑,只要生长准则一样,生长结果也必然一样。
除了置信连接阈值法之外,另外三种生长准则对应的是不同的IncludePredicate函数,连续阈值法、邻接连续阈值法、梯度法对应的IncludePredicate函数如下。
连续阈值法:
protected virtual bool IncludePredicate(Int16Double p) { byte v = bmp.GetPixel(p.X, p.Y); return v >= min && v <= max; }
邻接连续阈值法:
List<Int16Double> radiusWin = new List<Int16Double>(); private void InitRadiusRange() { int Radius = radius; for (int i = 0; i < 2 * Radius + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 2 * Radius + 1; j++) { int d2=(i-Radius)*(i-Radius)+(j-Radius)*(j-Radius); if(d2<=Radius*Radius) { Int16Double t=new Int16Double(i-Radius,j-Radius); radiusWin.Add(t); } } } } protected override bool IncludePredicate(Int16Double p) { bool ret1 = base.IncludePredicate(p); if (ret1) { if (CheckRange(p.X, p.Y)) { return true; } else return false; } else { return false; } } bool CheckRange(int x, int y) { for (int i = 0; i < radiusWin.Count; i++) { int rx = x + radiusWin[i].X; int ry = y + radiusWin[i].Y; if (!InRange(rx, ry)) continue; if (!base.IncludePredicate(new Int16Double(rx, ry))) return false; } return true; }
梯度法:
protected virtual bool IncludePredicate(Int16Double p, Int16Double or) { byte v = bmp.GetPixel(p.X, p.Y); byte vr = bmp.GetPixel(or.X, or.Y); return Math.Abs(vr - v) < r; }
对于置信连接阈值法,由于其带有有迭代的逻辑,所以需要重新实现一些上层逻辑,这些逻辑用伪代码描述如下:
- 计算出Initializing Radius所确定区域的像素值的均值和方差,作为初始均值和方差。使用该均值方差以及Confidence Factor值来确定初始像素值上下界。
- 初始化队列Q与备用队列BQ
- 将种子点推入Q
- 若未到达最大循环次数并且上一次迭代有新像素进入Q
- 对Q执行种子生长迭代,其中访问到的不在范围内的体素放入BQ
- 计算新区域的均值和方差,更新上下界范围
- 检查BQ中的像素是否在新范围内,若在则加入Q
- 算法结束
使用C#实现相应的代码如下:
public class Confidence { public Confidence(BitMap2d bmp,Int16Double seed,int iterTime,double factor,int radius) { this.bmp = bmp; this.seed = seed; this.factor = factor; this.radius = radius; this.iterTime = iterTime; container = new Container_Queue<Int16Double>(); container2 = new Container_Queue<Int16Double>(); flagsMap = new FlagMap2d(bmp.width, bmp.height); } protected double sum; protected double sum2; protected double mean; protected double deviation; protected double cmin; protected double cmax; protected int iterTime; protected double factor; protected int radius; protected Int16Double seed; protected BitMap2d bmp; protected FlagMap2d flagsMap; protected Container<Int16Double> container; protected Container<Int16Double> container2; public List<Int16Double> results = new List<Int16Double>(); protected int count = 0; protected virtual bool IncludePredicate(Int16Double p,ref double value) { byte v = bmp.GetPixel(p.X, p.Y); value = v; return value >= cmin && value <= cmax; } protected virtual bool InRange(int x, int y) { return x < bmp.width && x >= 0 && y < bmp.height && y >= 0; } protected virtual void Process(Int16Double p) { results.Add(p); count++; return; } public virtual void ExcuteFloodFill() { flagsMap.SetFlagOn(seed.X, seed.Y, true); container.Push(seed); Process(seed); FirstCaculate(); for (int l = 0; l < iterTime; l++) { FloodFill(); ReCaluete(); bool haschanged = ReEnqueue(); if (!haschanged) break; } } protected void FirstCaculate() { int Radius = radius; double sum = 0; double sum2 = 0; Int16Double[,] radiusRange = new Int16Double[2 * Radius + 1, 2 * Radius + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < 2 * Radius + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 2 * Radius + 1; j++) { radiusRange[i, j].X = seed.X - Radius + i; radiusRange[i, j].Y = seed.Y - Radius + j; } } int c = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 2 * Radius + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 2 * Radius + 1; j++) { int d2 = (i - Radius) * (i - Radius) + (j - Radius) * (j - Radius); if (d2 <= Radius * Radius) { Int16Double t = radiusRange[i, j]; if (!InRange(t.X, t.Y)) continue; float v = bmp.GetPixel(t.X, t.Y); sum += v; sum2 += v * v; c++; } } } this.mean = sum / c; this.deviation = Math.Sqrt(sum2 / c - this.mean * this.mean); this.cmin = mean - factor * deviation; this.cmax = mean + factor * deviation; } protected void ReCaluete() { this.mean = sum / count; this.deviation = Math.Sqrt(sum2 / count - mean * mean); this.cmin = mean - factor * deviation; this.cmax = mean + factor * deviation; } protected void FloodFill() { double v=0; Int16Double[] adjPoints4 = new Int16Double[4]; while (!container.Empty()) { Int16Double p = container.Pop(); InitAdj4(ref adjPoints4, ref p); for (int adjIndex = 0; adjIndex < 4; adjIndex++) { Int16Double t = adjPoints4[adjIndex]; if (InRange(t.X, t.Y)) { if (!flagsMap.GetFlagOn(t.X, t.Y) && IncludePredicate(t, ref v)) { flagsMap.SetFlagOn(t.X, t.Y, true); container.Push(t); Process(t); } } } } return; } protected bool ReEnqueue() { bool haschanged = false; while (!container2.Empty()) { Int16Double t = container2.Pop(); double v=0; if (IncludePredicate(t, ref v)) { haschanged = true; flagsMap.SetFlagOn(t.X,t.Y,true); Process(t); sum += v; sum2 += v * v; container.Push(t); } } return haschanged; } protected void InitAdj4(ref Int16Double[] adjPoints4, ref Int16Double p) { adjPoints4[0].X = p.X - 1; adjPoints4[0].Y = p.Y; adjPoints4[1].X = p.X + 1; adjPoints4[1].Y = p.Y; adjPoints4[2].X = p.X; adjPoints4[2].Y = p.Y - 1; adjPoints4[3].X = p.X; adjPoints4[3].Y = p.Y + 1; } }
实验效果对比
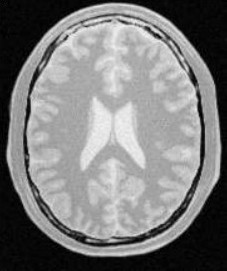
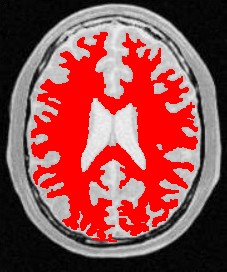
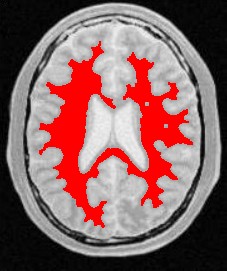
使用人体大脑截面图作为输入图像,选择合适的像素点作为种子像素,生长的结果如下图所示:
| 原始图像 | 连续阈值法 | 邻接连续阈值法 | 置信连接阈值法 |
 |
 |
 |
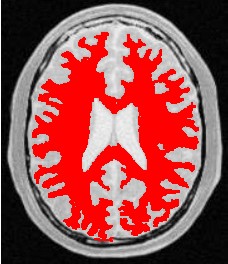 |
| 参数 | [150,180] | [150,180] R:3 | Iter:10 factor:2.5 r:5 |
| 结果点数 | 15011 | 7854 | 14643 |
相应源码下载地址如下:https://github.com/chnhideyoshi/SeededGrow2d/tree/master/GrowingStrategies
爬网的太疯狂了,转载本文要注明出处啊:http://www.cnblogs.com/chnhideyoshi/

 区域生长(Region Growing)是指将成组的像素或区域发展成更大区域的过程。从种子点的集合开始,从这些点的区域增长是通过将与每个种子点有相似属性像强度、灰度级、纹理颜色等的相邻像素合并到此区域。在二维图像中实现区域生长可以采用之前的文章中所介绍的种子点生长算法,但在实际应用中,可以有不同的生长准则可以选择,这依赖于用户的需求,本文简要的介绍几种在ITK库(Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit)中提到的几种生长准则。
区域生长(Region Growing)是指将成组的像素或区域发展成更大区域的过程。从种子点的集合开始,从这些点的区域增长是通过将与每个种子点有相似属性像强度、灰度级、纹理颜色等的相邻像素合并到此区域。在二维图像中实现区域生长可以采用之前的文章中所介绍的种子点生长算法,但在实际应用中,可以有不同的生长准则可以选择,这依赖于用户的需求,本文简要的介绍几种在ITK库(Insight Segmentation and Registration Toolkit)中提到的几种生长准则。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号