java动态绑定
入博客园第一天,记录个java动态绑定一个小知识,先铺代码
场景1
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
A a = B.class.newInstance();
Field field = A.class.getDeclaredField("str");
field.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(field.get(a));
}
static class A {
private String str = "AAA";
}
static class B extends A {
private String str = "BBB";
}
以学java时候的知识,子类指向父类,想当然的会以为这里的输出是BBB,但是这里的结果并不是。
通过编译器输出的结果为AAA
场景二
代码稍加改造
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
A a = B.class.newInstance();
Field field = A.class.getDeclaredField("str");
field.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(a.getStr());
}
static class A {
private String str = "AAA";
public String getStr() {
return this.str;
}
}
static class B extends A {
private String str = "BBB";
}
这个场景依然输出的是 AAA
打个断点分析分析
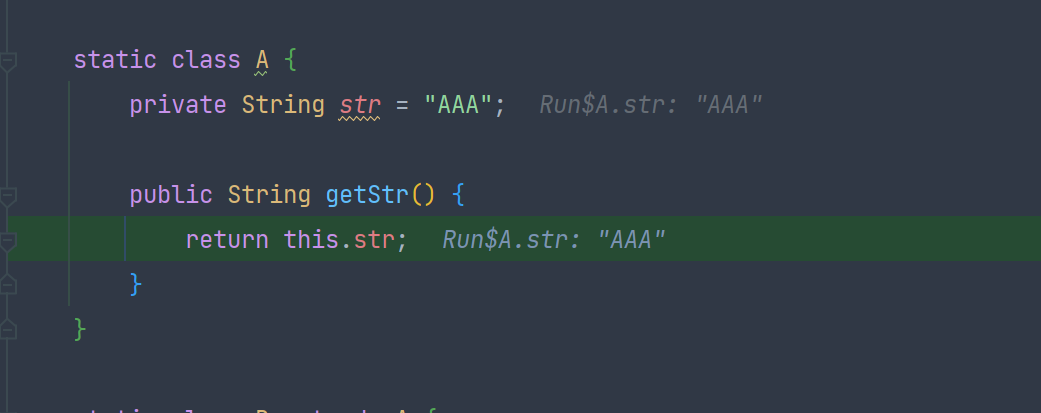
虽然运行的是类B,但B里面没有这个方法,就找父类里面的此方法,this.str 即为 A里面 声明的str,理所当然输出的是 AAA
场景三
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException { A a = B.class.newInstance(); Field field = A.class.getDeclaredField("str"); field.setAccessible(true); System.out.println(a.getStr()); } static class A { private String str = "AAA"; public String getStr() { return this.str; } } static class B extends A { private String str = "BBB"; @Override public String getStr() { return this.str; } }
这个就是经典的调用子类指向父类,输出BBB
最后小小总结一波
动态绑定原则
- 方法看对象的运行类型
- 属性看对象的编译类型
感觉没说明白
首先说说啥事运行类型,啥是编译类型
A a = new B(); A是编译的类型,B是运行的类型
拿属性看你声明的是啥,拿方法看你具体创建的对象。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号