记一次java简易计算器的实现(windows&android)
事情的起因是想在一个项目里摸鱼结果摸成了技术组,由于什么也不会被要求在一周内写出一个计算器app(虽然最后一共花了两天半)。写程序的时候参考了很多大佬的博客,特此也把自己的代码贴来,用作参考与交流。
记一次java简易计算器的实现(windows&android) - Chi4ki - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
1、windows计算器
主要用的是swing和awt框架,参考网站Java Swing教程:30分钟玩转Swing界面设计 (biancheng.net)。先看了网格布局和按钮以及文本框的设置写出布局,然后是重点事件监听,根据事件监听搭好框架,最后就是数据处理了,用StringBuilder作为数据的反馈。代码如下:
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Calculator3 { public static void main(String[] args) { CalculatorDemo cal = new CalculatorDemo(); } } class CalculatorDemo { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); JTextField fi = new JTextField(60); int j = 0, equal = 0, point = 0, sy = 0; double sum = 0; double num1 = 0, num2, num3; String[] num = { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "0" }; String[] s = { " ", " ", "DEL", "AC", "7", "8", "9", "/", "4", "5", "6", "*", "1", "2", "3", "-", "0", ".", "=", "+" }; String[] symbol = { "+", "-", "*", "/" }; public CalculatorDemo() { JFrame frame = new JFrame("计算器"); JPanel p1 = new JPanel(); fi.setFont(new Font("楷体", Font.BOLD, 16)); p1.add(fi); frame.add(p1, BorderLayout.NORTH); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(5, 4, 10, 5)); JButton[] button = new JButton[20]; for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { button[i] = new JButton(s[i]); panel.add(button[i]); } class button1ActionListener implements ActionListener { @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String a = e.getActionCommand(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if (a.equals(num[i])) { if (equal == 1) { sb = new StringBuilder(); equal = 0; } sb.append(num[i]); fi.setText(sb.toString()); if (j != 0) { sy = j; j = 0; } break; } } if (a.equals(".")) { if (j == 0 && point != 1) { point = 1; sb.append("."); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } } for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { if (j == 0 && a.equals(symbol[i]) && sy != 0) { num3 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); if (sy == 1) sum = num1 + num3; if (sy == 2) sum = num1 - num3; if (sy == 3) sum = num1 * num3; if (sy == 4) sum = num1 / num3; sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(sum); break; } } if (a.equals("+")) { if (j == 0) { j = 1; point = 0; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); fi.setText("+"); } else { j = 1; fi.setText("+"); } } if (a.equals("-")) { if (j == 0) { j = 2; point = 0; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); fi.setText("-"); } else { j = 2; fi.setText("-"); } } if (a.equals("*")) { if (j == 0) { j = 3; point = 0; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); fi.setText("*"); } else { j = 3; fi.setText("*"); } } if (a.equals("/")) { if (j == 0) { j = 4; point = 0; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); fi.setText("/"); } else { j = 4; fi.setText("/"); } } if (a.equals("=")) { num2 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); if (sy == 0) { sum = num1 + num2; sb.append(sum); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 1) { sum = num1 + num2; sb.append(sum); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 2) { sum = num1 - num2; sb.append(sum); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 3) { sum = num1 * num2; sb.append(sum); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 4) { if (num2 == 0) { sb.append("error"); fi.setText(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); } else { sum = num1 / num2; sb.append(sum); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } } j = 0; sy = 0; num1 = 0; num2 = 0; equal = 1; } if (a.equals("AC")) { sb = new StringBuilder(); j = 0; sy = 0; sum = 0; num1 = 0; num2 = 0; fi.setText(String.valueOf(sum)); } if (a.equals("DEL")) { if (sb.length() > 0 && !"null".equals(sb.toString()) && !"".equals(sb.toString())) { if (j != 0) { j = 0; sb.append(num1); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } if (j == 0) { sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1); fi.setText(sb.toString()); } } else { sb.append("error"); fi.setText(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); } } } } for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) button[i].addActionListener(new button1ActionListener()); frame.add(panel); frame.setBounds(600, 300, 600, 450); frame.setVisible(true); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); } }
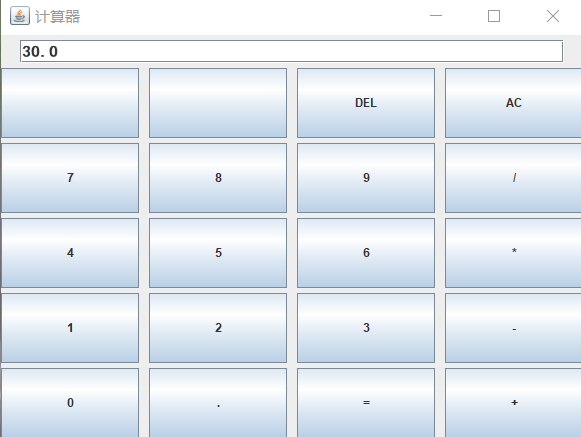
运行后的效果
2、Anroid 计算器app
编程软件:Android studio,教程有1.0 Android基础入门教程 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)。相比于windows上的布局是直接在xml里设置的,会舒服很多。布局的计算器代码我是照着菜鸟教程上的修改的,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <GridLayout android:id="@+id/GridLayout1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:columnCount="4" android:orientation="horizontal" android:rowCount="6" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"> <TextView android:layout_height="78dp" android:layout_columnSpan="4" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:layout_marginLeft="5dp" android:layout_marginRight="5dp" android:background="#FFCCCC" android:text="0" android:id="@+id/txv" android:textSize="50sp" /> <Button android:layout_columnSpan="2" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:id="@+id/DEL" android:text="DEL" /> <Button android:layout_columnSpan="2" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:id="@+id/AC" android:text="AC" /> <Button android:text="+" android:id="@+id/plus" /> <Button android:text="1" android:id="@+id/one"/> <Button android:text="2" android:id="@+id/two"/> <Button android:text="3" android:id="@+id/three"/> <Button android:text="-" android:id="@+id/minus"/> <Button android:text="4" android:id="@+id/four"/> <Button android:text="5" android:id="@+id/five"/> <Button android:text="6" android:id="@+id/six"/> <Button android:text="*" android:id="@+id/multiply"/> <Button android:text="7" android:id="@+id/seven"/> <Button android:text="8" android:id="@+id/eight"/> <Button android:text="9" android:id="@+id/nine" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:text="/" android:id="@+id/divide"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:text="." android:id="@+id/point"/> <Button android:text="0" android:id="@+id/zero"/> <Button android:text="=" android:id="@+id/equals"/> </GridLayout> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
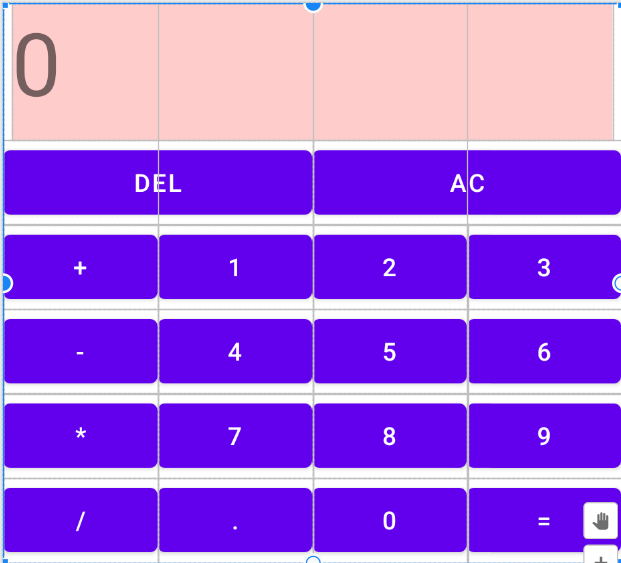
计算器布局效果
然后就是java的代码了,与之前类似,搭好监听数据处理就行。这里需要注意findViewById必须在onCreate之后使用,不然直接keeps stopping怎么找也找不到原因……java部分的代码如下:
package com.example.myapplication02; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.app.Activity; import android.widget.TextView; import android.widget.EditText; public class MainActivity extends Activity { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); int j = 0, sy = 0,equal=0,point=1; //j作为符号判断,sy作为计算时的符号判断,equal作为等于号判断 double sum = 0; double num1 = 0, num2, num3; String[] num = { "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "0" }; Button[] button=new Button[18]; Integer[] id= new Integer[]{ R.id.one, R.id.two, R.id.three, R.id.four, R.id.five, R.id.six, R.id.seven, R.id.eight, R.id.nine, R.id.zero, R.id.point, R.id.plus, R.id.minus, R.id.multiply, R.id.divide, R.id.equals, R.id.DEL, R.id.AC}; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); for(int i=0;i<18;i++){ //对每个按钮设置监听 button[i]= findViewById(id[i]); button[i].setOnClickListener(new BtnClickListener()); } } class BtnClickListener implements View.OnClickListener { @Override public void onClick(View v) { TextView text= findViewById(R.id.txv); Integer name=v.getId(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { if (name.equals(id[i])) { if (equal == 1) { //增加equal参数判断上一个按钮是不是等号,满足时重置StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); point=1; equal = 0; } sb.append(num[i]); text.setText(sb.toString()); if (j != 0) { sy = j; j = 0; } break; } } //当字符为空且符号为加减乘除DEL中任意一个时 if (!(sb.length() > 0 && !"null".equals(sb.toString()) && !"".equals(sb.toString()))){ for (int i = 11; i < 17; i++){ if (name.equals(id[i])) { name=(Integer)R.id.AC; break;} } } //当只有小数点且输入运算符时 if (".".equals(sb.toString())) for (int i = 11; i < 15; i++){ if (name.equals(id[i])) { name=(Integer)R.id.AC; break;} } if (name.equals(id[10])) { if (!sb.toString().contains(".")) { //小数点的判断 sb.append("."); text.setText(sb.toString()); } } //对结果显示整数还是小数的判断 if(sb.toString().contains(".")) point=0; for (int i = 11; i < 15; i++) { if (j == 0 && name.equals(id[i]) && sy != 0) { //判断:当第三次及以上按下符号键,且每两符号之间输入过数字,计算前两个运算的结果储存为num1 num3 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); if (sy == 1) sum = num1 + num3; if (sy == 2) sum = num1 - num3; if (sy == 3) sum = num1 * num3; if (sy == 4) { if (num3 == 0) { //处理多次计算时除数为0的情况:直接AC重置 name=(Integer)R.id.AC; } else { sum = num1 / num3; }; } sb = new StringBuilder(); if(point==1&&sy!=4) sb.append((int)sum); else sb.append(sum); break; } } if (name.equals(id[11])) { //加 equal = 0; if (j == 0) { j = 1; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); text.setText("+"); } else { j = 1; text.setText("+"); } } if (name.equals(id[12])) { //减 equal = 0; if (j == 0) { j = 2; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); text.setText("-"); } else { j = 2; text.setText("-"); } } if (name.equals(id[13])) { //乘 equal = 0; if (j == 0) { j = 3; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); text.setText("*"); } else { j = 3; text.setText("*"); } } if (name.equals(id[14])) { //除 equal = 0; if (j == 0) { j = 4; num1 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); text.setText("/"); } else { j = 4; text.setText("/"); } } if (name.equals(id[15])) { num2 = Double.parseDouble(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); //等于时根据sy判断运算符号 if (sy == 0) { sum = num1 + num2; sb.append(sum); text.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 1) { sum = num1 + num2; sb.append(sum); text.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 2) { sum = num1 - num2; sb.append(sum); text.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 3) { sum = num1 * num2; sb.append(sum); text.setText(sb.toString()); } else if (sy == 4) { if (num2 == 0) { //当除数为零时的处理 sb.append("error"); text.setText(sb.toString()); sb = new StringBuilder(); } else { sum = num1 / num2; sb.append(sum); text.setText(sb.toString()); } } //eaual变为1,其余参数重置 if(point==1&&sy!=4) { sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append((int)sum); text.setText(sb.toString()); } j = 0; sy = 0; num1 = 0; num2 = 0; sum = 0; equal=1; } if (name.equals(id[17])) { //AC时重置所有参数 sb = new StringBuilder(); j = 0; sy = 0; sum = 0; num1 = 0; num2 = 0; equal = 0; point=1; text.setText("0"); } if (name.equals(id[16])) { if (j != 0) { j = 0; sb.append(num1); text.setText(sb.toString()); }if (j == 0) { sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1); text.setText(sb.toString()); } } } } }
最后参考(25条消息) Android Studio 打包APK(详细版)_初学者-Study的博客-CSDN博客_安卓打包apk将程序打包成apk,一个简易的计算器就完成了~
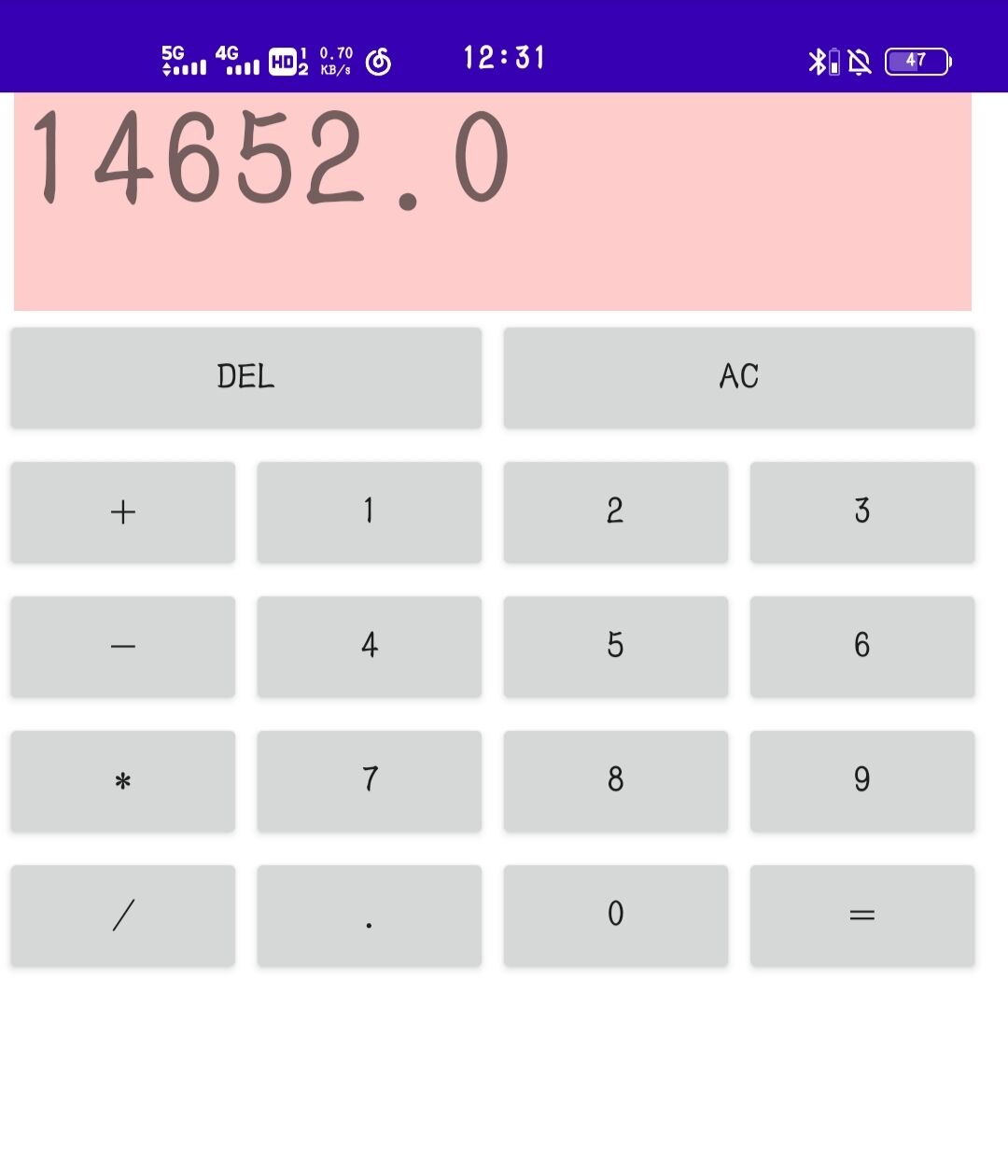
app运行效果
目前来说计算器还有不少问题,在一些按键之后会出现闪退之类……等之后有时间再修改一下。
 windows上用的是swing&awt框架,android用的是android studio。总的来说设置好监听之后就是熟悉的数据处理环节了。
windows上用的是swing&awt框架,android用的是android studio。总的来说设置好监听之后就是熟悉的数据处理环节了。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号