2023河南萌新联赛第(八)场
A. 唯物丁真遇上唯心王源:到了群星就要拿出真本事(并查集+dfs)

输入
7 6 3 3
5 8 9 4 5 4 5
1 2 3 1 1 1 1
1 2
2 3
2 4
4 5
3 6
3 7
输出
19
说明
样例中,4和5是相互连接的,用星门将1,4,5,7连通,最大的矿产流通资源量为19
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using i64 = int64_t;
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, m, k, w;
cin >> n >> m >> k >> w;
vector<int> a(n), b(n);
for (int &ai : a) { cin >> ai; }
for (int &bi : b) { cin >> bi; }
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (int i = 0, u, v; i < m; i += 1) {
cin >> u >> v;
u -= 1;
v -= 1;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
vector<bool> vis(n);
vector<i64> res;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 1) {
if (not vis[i] and b[i] == 1) {
i64 p = 0;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int u) {
vis[u] = 1;
p += a[u];
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (not vis[v] and b[v] == 1) { dfs(v); }
}
};
dfs(i);
res.push_back(p);
}
}
i64 ans = 0;
sort(res.rbegin(), res.rend());
for (int i = 0; i < res.size() and i < k; i += 1) { ans += res[i]; }
cout << ans;
}
B. 小分分(选点覆盖+打表)
输入
3
1 2 1 4
2 3 3 4
1 4 2 3
输出
9
说明
对于1 第二组没有一个线段对其覆盖,所以1不是好点
对于2 第一组[1,2],[1,4]第二组[2,3]第三组[1,4],[2,3]都能将其覆盖,因此2是好点,并且它有4种覆盖方式
对于3 第一组[1,4]第二组[2,3],[3,4]第三组[1,4],[2,3]都能将其覆盖,因此3是好点,并且它有4种覆盖方式
对于4 第一组[1,4],第二组[3,4],第三组[1,4],都能将其覆盖,因此4是好点,并且它有1种覆盖方式
其他所有点都不是好点
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define yes "yes\n"
#define YES "YES\n"
#define no "no\n"
#define NO "NO\n"
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 10, inf = 1e18;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
namespace DEFINITION
{
#define scanfll(a) scanf("%lld",&a)
#define read(n) cin >> n
#define write(n) cout << n;
#define lowbit(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define RESET(A) memset(A, 0, sizeof A)
#define ALL(A) A.begin(),A.end()
#define SORT(A) sort(ALL(A))
#define Presentation(i,r) " \n"[i==r]
#define FORLL(i,l,r) for(int i=l;i<=r;i++)
#define FORLL_rev(i,r,l) for(int i=r;i>=l;i--)
#define Get_Mod(a) (((a) + mod) % mod)
#define NO "NO\n"
#define YES "YES\n"
#define endl '\n'
}
struct node
{
int l, r;
}aa[N], bb[N], cc[N];
int f[N], a[N], b[N], c[N];
int n, ans;
void init()
{
f[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i ++)
f[i] = f[i - 1] * 2 % mod;
// for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++)
// cout << f[i] << ' ';
// cout << '\n';
}
bool cmp(node a, node b)
{
return a.l < b.l;
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
cin >> aa[i].l >> aa[i].r;
a[aa[i].l] ++, a[aa[i].r + 1] --;
cin >> bb[i].l >> bb[i].r;
b[bb[i].l] ++, b[bb[i].r + 1] --;
cc[i].l = min(aa[i].l, bb[i].l);
cc[i].r = max(aa[i].r, bb[i].r);
c[cc[i].l] ++, c[cc[i].r + 1] --;
}
ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 500000; i ++)
{
a[i] += a[i - 1];
b[i] += b[i - 1];
c[i] += c[i - 1];
}
for(int i = 1, t; i <= 500000; i ++)
{
if(c[i] >= n)
{
t = a[i] + b[i] - n;
ans = (ans + f[t]) % mod;
}
// cout << ans << " ";
}
// printf("%lld", ans);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
init();
int T = 1;
while(T --)
solve();
return T ^ T;
}
D. 鼠鼠的机器人(数学+模拟)
输入1
1
1 1
1
URL
输出1
Yes
说明
操作一次指令,机器人从(0,0)先移动到(0,1),再由(0,1)移动到(1,1),此时能拾起废品,所以结果输出“Yes”。
输入2
1
2 2
2
UL
输出2
No
说明
操作一次指令,机器人由(0,0)移动到(0,1),由(0,1)移动到(-1,1),操作第二次指令,机器人由(-1,1)移动到(-1,2),再由(-1,2)移动到(-2,2),操作两次指令后没有拾起废品,所以输出“No”。
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef double db;
typedef long double ld;
const int N = 1e5, M = 1e5 + 10, B = 500, mod = 998244353, inf = 1e18;
const ld eps = 1e-12;
int lowbit(int x) { return x & -x; }
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
ll qmi(ll a, ll b, ll mod)
{
ll res = 1;
a %= mod;
assert(b >= 0);
for (; b; b >>= 1)
{
if (b & 1)
res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
// head
void solve()
{
int x, y, n;
string s;
cin >>x >>y >>n >>s;
int m = s.size();
vector<int> a(m + 1, 0), b(m + 1, 0);
s = " " + s;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
a[i] = a[i - 1], b[i] = b[i - 1];
if(s[i] == 'U') b[i]++;
if(s[i] == 'D') b[i]--;
if(s[i] == 'L') a[i]--;
if(s[i] == 'R') a[i]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i <= m; ++i)
{
int nx = a[i], ny = b[i];
int v1 = n + 1, v2 = n + 1;
if(a[m] != 0)
{
if((x - nx)%a[m] == 0 && (x - nx) * a[m] >= 0) v1 = (x - nx)/a[m];
}
else
{
if(nx == x) v1 = 0;
}
if(b[m] != 0)
{
if((y - ny)%b[m] == 0 && (y - ny) * b[m] >= 0) v2 = (y - ny)/b[m];
}
else
{
if(ny == y) v2 = 0;
}
if(max(v1, v2)+(i > 0) <= n)
{
cout<<"Yes\n";
return;
}
}
cout<<"No\n";
}
signed main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(12);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
}
E. bilabila(数学)
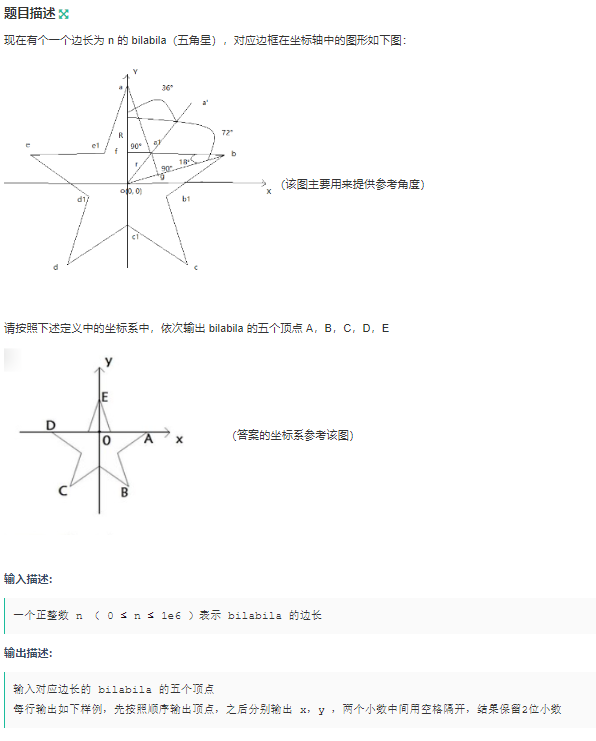
输入
0
输出
A: 0.00 0.00
B: 0.00 0.00
C: 0.00 0.00
D: 0.00 0.00
E: 0.00 0.00
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define yes "yes\n"
#define YES "YES\n"
#define no "no\n"
#define NO "NO\n"
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, inf = 1e18;
double a[10][2];
void init()
{
double pi = 3.141592653579;
double rad = pi / 180;
double s18 = sin(pi / 10), s36 = sin(pi / 5), c18 = cos(pi / 10), c36 = cos(pi / 5);
// cout << s18 << ' ' << s36 << '\n';
// cout << c18 << ' ' << c36 << '\n';
a[1][0] = (1.0 + 1.0 * s18);
a[2][0] = c36, a[2][1] = (c18 - c36 * c18 / s18);
a[3][0] = -c36, a[3][1] = (c18 - c36 * c18 / s18);
a[4][0] = -(1.0 + s18);
a[5][1] = c18;
}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
printf("A: %.2lf %.2lf\n", a[1][0] * n, a[1][1] * n);
printf("B: %.2lf %.2lf\n", a[2][0] * n, a[2][1] * n);
printf("C: %.2lf %.2lf\n", a[3][0] * n, a[3][1] * n);
printf("D: %.2lf %.2lf\n", a[4][0] * n, a[4][1] * n);
printf("E: %.2lf %.2lf\n", a[5][0] * n, a[5][1] * n);
// cout << a[i][0] * n << ' ' << a[i][1] * n << '\n';
}
signed main()
{
// ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
// cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
init();
int T = 1;
// cin >> T;
while(T --)
solve();
return T ^ T;
}
F. 小前前(前缀和)

输入
5 5
4 11 8 2 2
3 4 5
1 1 13
1 1 17
1 4 5
1 1 8
输出
15
13
21
15
12
点击查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define yes "yes\n"
#define YES "YES\n"
#define no "no\n"
#define NO "NO\n"
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 65, inf = 1e18;
int f[N][M], a[N];
int n, m, l, r, q, x, ans;
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= 61; j ++)
f[i][j] = a[i] & 1, a[i] >>= 1;
for(int j = 1; j <= 61; j ++)
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
f[i][j] += f[i - 1][j];
while(m --)
{
cin >> l >> r >> x;
ans = 0;
string s;
for(int i = 1, j = 1; i <= 61; i ++)
{
s += ((f[r][i] - f[l - 1][i]) & 1) + '0';
ans += j * ((f[r][i] - f[l - 1][i] + (x & 1)) >= 1);
x >>= 1, j *= 2;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int T = 1;
while(T --)
solve();
return T ^ T;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号