浅探SpringMVC中HandlerExecutionChain之handler、interceptor
讲解HandlerExecutionChain之前,先大致了解下SpringMVC的核心开发步骤:
- 在web.xml中部署DispaterServlet,并配置springmvc.xml等文件;
- 将映射文件请求到处理器HandlerMapping;
- HandlerMapping会把请求映射为HandlerExecutionChain类型的handler对象;
- 将handler对象作为参数传递给HandlerAdapter的实例化对象,调用其handler方法会生成一个ModelAndView对象;
- 通过ViewResolver视图解析器,将上一步骤中生成的ModelAndView解析为View;
- DispatcherServlet根据获取到View,将视图返回给用户。
本文分为两个部分进行讲解,第一部分分析Handler, 第二部分分析Interceptor
(一) Handler
首先可以明确HandlerExecutionChain与HanderMapping关系非常紧密,HandlerExecutionChain只能通过HanderMapping接口中的唯一方法来获得,HanderMapping接口定义如下:
package org.springframework.web.servlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
public interface HandlerMapping {
String PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".pathWithinHandlerMapping";
String BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".bestMatchingPattern";
String INTROSPECT_TYPE_LEVEL_MAPPING = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".introspectTypeLevelMapping";
String URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".uriTemplateVariables";
String MATRIX_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".matrixVariables";
String PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE = HandlerMapping.class.getName() + ".producibleMediaTypes";
//该方法是HandlerMapping接口中的唯一方法,此方法可以利用用户请求request中的信息来生成HandlerExecutionChain对象
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
}
HandlerMapping架构设计图如下:

可以看到HandlerMapping家族有两个分支,分别是AbstractUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping,它们又统一继承于AbstractHandlerMapping。
AbstractHandlerMapping是接口HandlerMapping的抽象实现,AbstractHandlerMapping抽象类中实现了部分方法提供给它的子类使用,它还覆了getHandler方法,源码如下:
@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// AbstractUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping均对getHandlerInternal(request)进行了覆写
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);//该方法在本类中有定义,是一个protected型的抽象方法,
//根据给定的request查找handler,如果没有找到handler,则返回一个null
//如果经过上步没有获取到handler实例,则通过本类中setDefaultHandler(Object defaultHandler)设置默认handler,然后使用getDefaultHandler获得。
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
}
上面的getHandlerInternal在AbstractUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中均有实现:
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping中的getHandlerInternal方法会根据用户请求信息中的URL查找handler:
/** Look up a handler for the URL path of the given request. -- 通过匹配URL,将URL与handler联系起来 */ @Override protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { ... //略 }
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中的getHandlerInternal方法则会根据用户request信息中提供的Method来查找handler:
/** Look up a handler method for the given request. -- 普遍用于@requestMaping,匹配内容将它的Method作为handler */ @Override protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { ... //略 }
回到上文中的getHandler方法,它最终返回了一个HandlerExecutionChain,getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request)方法属于 AbstractHandlerMapping 类的一个受保护类型方法,该方法定义如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 如果已经是HandlerExecutionChain,则直接使用,否则创建新的
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
//向chain中加入mappedInterceptor类型的拦截器
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
// 向chain中共加入拦截器
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
简而言之就是:当用户请求到到DispaterServlet中后,配置的HandlerMapping会根据用户请求(也就是handler)会将它与所有的interceptors封装为HandlerExecutionChain对象,HandlerExecutionChain的作用在源码注释部分简要解释如下:
Handler execution chain, consisting of handler object and any handler interceptors.
Returned by HandlerMapping's HandlerMapping.getHandler method.
可知通过HandlerMapping实例对象的getHandler方法可以获得一个HandlerExecutionChain对象实例,该实例封装了一个handler处理对象和一些interceptors。HandlerExecutionChain类定义代码不长,其中所有的属性,方法如下:

(二) Interceptor 拦截器
HandlerExecutionChain中介绍到了拦截器,那这个拦截器是何方圣神?下文来简单介绍一下。
首先引入拦截器。
上文中指出了HandlerMapping继承了AbstractHandlerMapping,AbstractHandlerMapping又继承于WebApplicationObjectSupport,进而继承了ApplicationObjectSupport。
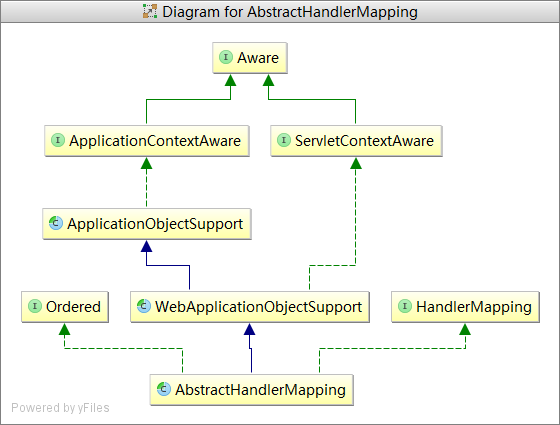
ApplicationObjectSupport实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,在Spring容器中如果该bean类实现了ApplicationContextAware,那么通过容器获取这个bean时,void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context)方法将被调用。
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
//探测容器中所有拦截器
detectMappedInterceptors(this.mappedInterceptors);
//初始配置这些拦截器
initInterceptors();
}
其中,initInterceptors()方法如下,主要作用是返回一个HandlerInterceptor对象,然后将这个对象放到 this.adaptedInterceptors 集合中(ps: adaptedInterceptors很重要哟)。
/**
* Initialize the specified interceptors, checking for {@link MappedInterceptor}s and
* adapting {@link HandlerInterceptor}s and {@link WebRequestInterceptor}s if necessary.
* @see #setInterceptors
* @see #adaptInterceptor
*/
protected void initInterceptors() {
if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) {
Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i);
if (interceptor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null");
}
this.adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor));
}
}
}
至此,了解了拦截器来龙,那接下来说一下拦截器的去脉。
拦截器的总接口 HandlerInterceptor 定义如下:
public interface HandlerInterceptor {
boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;
void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception;
void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception;
}
在spring-webmvc-4.3.1.RELEASE-sources.jar中,HandlerIntercetor共有13个实现类,如MappedInterceptor、webContentInterceptor、ThemeChangeInterceptor、HandlerIntercetorAdapter等,这里就不一一列出来了。
当客户端发送请求后,DispatcherServlet.doDispatch方法中会处理请求,下面贴出doDispatch(req, res)中与拦截器相关的代码:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
...(前面代码略)
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.//获取根据请求获取handler
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.//获取handler适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
...(略)
// 拦截器执行拦截,对客户端请求响应requset进行拦截
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 核心逻辑,处理handler,返回ModerAndView对象
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 拦截器执行拦截,对客户端响应response进行拦截
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
...(后面代码略)
}
}
}
这里以mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(req, res)为例,简要分析一下doDispatch中的处理请求前拦截逻辑:
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// 获取所有初始化的拦截器
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
// 遍历拦截器
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
// 遍历执行每个拦截器中的preHandle方法(即对某一个handler,要遍历执行所有的拦截器preHandle方法)
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
// 最终调用interceptor.afterCompletion(req, res, handler, ex)
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}
当然也可以自定义拦截器,只要实现HandlerInterceptor 接口中的preHandle、postHandle、afterCompletion方法就可以啦。
写在最后
其实看源码是最好的,也是最优效果的,本文只希望能在阅读源码的时候提供一点参考作用就够了。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号