java常用API
1.Math类
常用方法如下

public class TestDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println(Math.abs(-88)); //System.out.println(Math.absExact(-2147483648));//会检测是否越界 System.out.println(Math.ceil(-12.54));//-12.0 向上取整 System.out.println(Math.round(12.54));//13.0 四舍五入 System.out.println(Math.floor(12.54));//12.0 向下取整 System.out.println(Math.max(20,30));//30 取较大值 System.out.println(Math.min(20.5,20.3));//20.3 取较小值 System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3));//8 2的3次方 System.out.println(Math.pow(4,0.5));//2.0 4的平方根 System.out.println(Math.sqrt(4));//2.0 4的平方根 System.out.println(Math.random());//0.0~1.0之间的随机数 左闭右开不包含1 System.out.println(Math.floor(Math.random()*100)+1);//1.0~100.0之间的随机数 } }
2.System工具类
计算机中的时间原点 1970年1月1日 08:00:00(东八区)
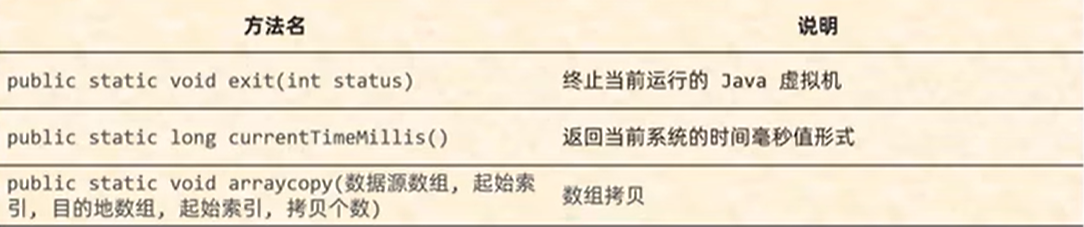
方法3注意事项:
1.如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是基本数据类型,那么两者的类型必须保持一致,否则会报错
2.在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,如果超出范围也会报错
3.如果数据源数组和目的地数组都是引用数据类型,那么子类类型可以赋值给父类类型
public class TestDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { //方法的形参(状态码) //0:表示当前虚拟机是正常停止 //非0:表示当前虚拟机异常停止 //System.exit(0);//虚拟机停止,下方不会继续走(需要把程序停止的时候用 long l = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前系统时间的毫秒值 System.out.println(l); int arr1[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; int[] arr2=new int[10]; System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,0,5);//只复制了前五个 for(int i=0;i<arr2.length;i++){ System.out.println(arr2[i]); } } }
3.Runtime表示当前虚拟机的运行环境

4.Object 是java中的顶级父类,所有的类都直接或间接的继承于Object类(Object类中的方法可以被所有子类访问)
方法名 public Object() 空参构造
顶级父类中只有无参构造方法

- toString方法的结论:如果打印一个对象想要看到属性值的话,重写toString方法就可以了。在重写的方法中,把对象的属性值进行拼接。
String s = "abc"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("abc"); System.out.println(s.equals(sb))//false //因为equals方法是被s调用的,而s是字符串,所以equals要看String类中的 //字符串中的equals方法先判断参数是否为字符串,如果是字符串再比较内部的属性,如果不是字符串直接返回false System.out.println(sb.equals(s));//false //因为equals方法时被sb调用的,而sb是StringBuilder,所以这里的equals要看StringBuilder中的 //在StringBuilder中没有重写equals方法,使用的是object中的,而object中默认使用==号比较两个对象的地址值,而这里的s和sb记录的地址值不同,所以结果为false
- clone把A对象的属性值圈圈拷贝给B对象,也叫对象拷贝,对象复制
User u2 = (User) u1.clone() //方法在底层会帮我们创建一个对象,并把原对象中的数据拷贝过去
浅克隆:不管对象内部的属性是基本数据类型还是引用数据类型,都完全拷贝过来。
深克隆:基本数据类型拷贝过来,字符串复用,引用数据类型会创建新的
Object中的克隆是浅克隆。可以在类中重写克隆方法,实现深克隆/使用第三方工具类
Objects的成员方法:

Student s1 = null; Student s2 = new Student("zhangsan",23); boolean result = Objects.equals(s1,s2); System.out.println(result);//false //方法的底层会判断是s1是否为null,如果是直接返回false //如果s1不是null,那么就利用s1再次调用equals方法 //此时s1是Student类型,所以最终还是会调用Student中的equals方法。 //如果没有重写,比较地址值。如果重写了,比较属性值
5.BigInteger基本使用和原理解析: 对象一旦创建,内部记录的值不能发生改变



public class Java01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.获取一个随机的大整数 Random r = new Random(); BigInteger bd1 = new BigInteger(4,r);//0~2^4-1 System.out.println(bd1); //2.获取一个指定的大整数 BigInteger bd2 = new BigInteger("9999999999"); System.out.println(bd2); //3.大整数的加减乘除 System.out.println(bd1.add(bd2));//加法 System.out.println(bd1.subtract(bd2));//减法 System.out.println(bd1.multiply(bd2));//乘法 System.out.println(bd1.divide(bd2));//除法 //4.获取指定进制的大整数 BigInteger bd3 = new BigInteger("10000",2);//2进制的123 System.out.println(bd3); //5.静态方法获取BigInteger的对象,内部有优化 BigInteger bd5 = BigInteger.valueOf(100); System.out.println(bd5.add(bd5)); } }
注意:
1.如果BigInteger表示的数字没有超出long的范围,可以用静态方法获取。
2.如果BigInteger表示的超出long的范围,可以用构造方法获取。
3.对象一旦创建,BigInteger内部记录的值不能发生改变
4.只要进行计算都会产生一个新的BigInteger对象
6.BigDecima
作用:表示较大的小数和解决小数运算精度失真问题
public class Java01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.通过传递double类型跨小数来创建对象 BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("1.23"); BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.09"); System.out.println(bd1); System.out.println(bd2); //2.通过传递字符串表示的小数来创建对象 BigDecimal bd3 = bd1.add(bd2); System.out.println(bd3); //3.通过静态方法获取对象 BigDecimal bd4=BigDecimal.valueOf(10); System.out.println(bd4); //如果要表示的数字不大没有超出double的取值范围使用静态方法,否则建议使用构造方法 //如果传递的是0-19之间的整数,包含0包含10,那么方法会返回已经创建好的对象不会重新new } }

舍入模式:
UP:远离零方向舍入的舍入模式
DOWN:向零方向舍入的舍入模式
CEILING:向正无限大方向舍入的舍入模式
FLOOR:向负无限大方向舍入的舍入模式
RoundingMode.HALF_UP 四舍五入
7.正则表达式:
作用:(1)校验字符串是否满足规则(2)在一段文本中查找满足规则的内容


转义字符\ 改变后面那个字符的含义
数量词:

本地爬虫:
public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ /*如有以下文本,按照要求爬取数据 Java自从95年问世以来,经历了很多版本,目前企业中用的最多的是Java8和Java11, 因为这两个是长期支持版本,下一个长期支持版本是Java17,相信在未来不久Java17也会逐渐登上历史舞台 要求:找出里面所有的JavaXX */ String str="Java自从95年问世以来,经历了很多版本,目前企业中用的最多的是Java8和Java11," + "因为这两个是长期支持版本,下一个长期支持版本是Java17,相信在未来不久Java17也会逐渐登上历史舞台"; //Pattern表示正则表达式 //Matcher:文本匹配器,作用按照正则表达式的规则去读取字符串,从头开始读取 //在大串中去找符合匹配规则的子串 Pattern p = Pattern.compile("Java\\d{0,2}"); Matcher m = p.matcher(str); //利用循环获取 while(m.find()){ String s = m.group(); System.out.println(s); } } private static void method1(String str){ Pattern p = Pattern.compile("Java\\d{0,2}"); Matcher m = p.matcher(str); boolean b = m.find(); String s1=m.group(); System.out.println(s1); } }
捕获分组:后续还要继续使用本组的数据
正则内部使用:\\组号 正则外部使用:$组号
public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ String str="我要学学编编编编程程程程程程"; //需求:把重复的内容 替换为单个的 String res=str.replaceAll("(.)\\1+","$1"); System.out.println(res);//我要学编程 } }
非捕获分组:分组之后不需要再使用本组数据,仅仅把数据括起来,不占组号
(?:正则) 获取所有
(?=正则)获取前面部分
(?!正则)获取不是指定内容的前面部分
8.JDK7-Date时间
- 时间:以前使用格林威治时间(Greenwich Mean Time)简称GMT
现在:原子钟利用铯原子的振动频率计算出来的时间作为世界时间UTC
中国时间=世界标准时间+8h
- Date时间类:是一个JDK写好的Javabean类,用来描述时间,精确到毫秒。
利用空参构造创建的对象,默认表示系统当前时间。利用有参构造创建的对象,表示指定的时间
public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ //1.创建对象表示一个时间 Date d1 = new Date(); //创建对象表示一个指定的时间 Date d2=new Date(0L); System.out.println(d2); //setTime修改时间 1000毫秒=1秒 d2.setTime(1000L); System.out.println(d2); //getTime获取当前时间的毫秒值 long time = d2.getTime(); System.out.println(time); } }
- SimpleDateFormat类作用
格式化:把时间变成我们喜欢的格式
解析:把字符串表示的时间变成Date对象


模式定义:
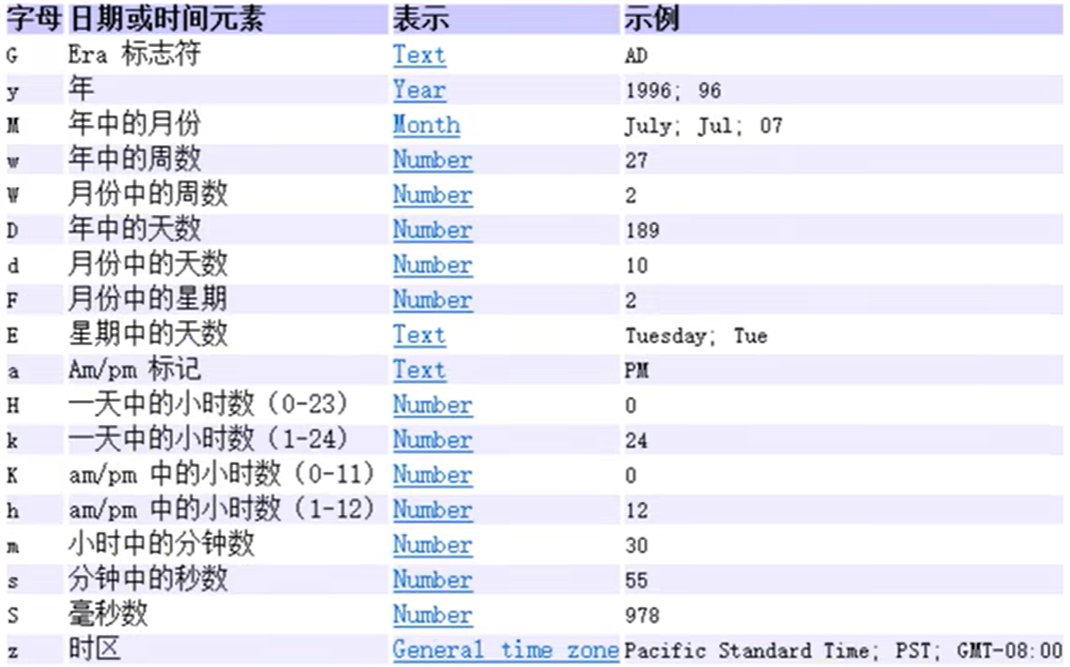
public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ //1.利用空参构造创建SimpleDateFormat对象,默认格式 SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat(); Date d1 = new Date(0L); String str1=sdf1.format(d1); System.out.println(str1);//1970/1/1 08:00 //2.利用带参构造创建SimpleDateFormat对象,指定格式 SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); String str2=sdf2.format(d1); System.out.println(str2);//1970年01月01日 08:00:00 } }
9.Calendar:代表当前系统时间的日历对象,可以单独修改、获取时间中的年月日
注意:Calendar是一个抽象类,不能直接创建对象。
获取Calendar日历类对象的方法:public static Calendar getInstance()获取当前时间的日历对象
常用方法:
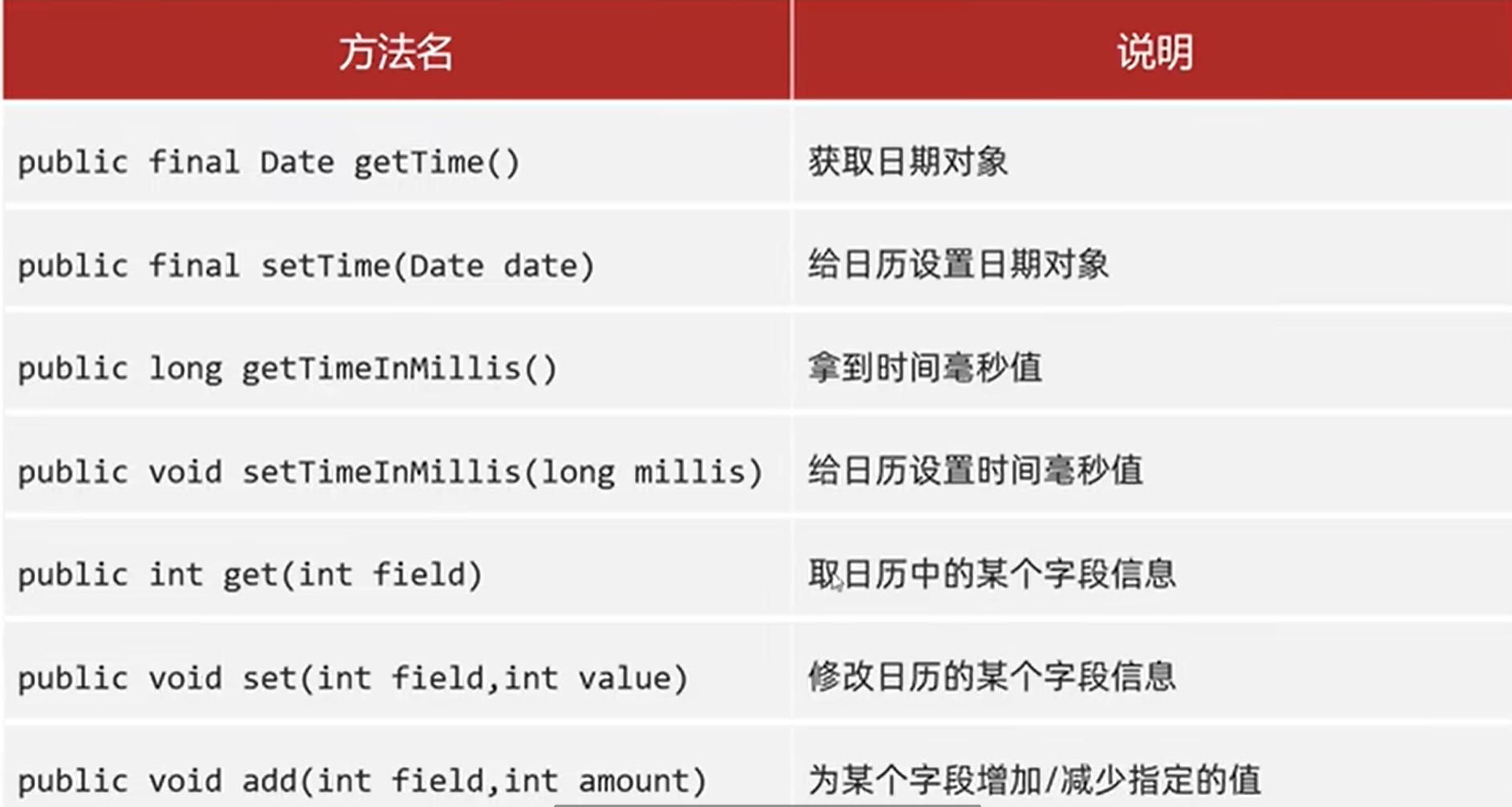
public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ /*获取日历对象 *细节:Calendar是一个抽象类,不能直接new,而是通过一个静态方法获取到了子类对象 *底层原理:会根据系统的不同时区来获取不同的日历对象。会把时间中的0:纪元,1:年,2:月,日,时,分,秒,星期,等等的都放到一个数组当中 * 细节2: * 月份范围0~11,如果取出来是0,那么实际上是1月;星期:在外国星期日是一周中的第一天 1星期日 2星期一... * */ Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); //2.修改下日历代表的时间 Date d = new Date(0L); c.setTime(d); System.out.println(c); //修改日历 c.set(Calendar.YEAR, 2000); c.set(Calendar.MONTH, 11); //为某个字段增加/减少指定的值 c.add(Calendar.MONTH, 2); //取日期中的某个字段信息 int year=c.get(Calendar.YEAR); int month=c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1; int day=c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); //int Week=c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); System.out.println(year+"-"+month+"-"+day); } }
10.JDK8时间类
Date类:ZoneId:时区;Instant:时间戳;ZoneDateTime:带时区的时间
日期格式化类SimpleDateFormat:DateTimeFormatter用于时间的格式化和解析
Calendar日历类:LocalDate:年、月、日;LocalTime:时、分、秒;LocalDateTime:年月日时分秒
工具类:Duration:时间间隔(秒、纳秒);Period:时间间隔(年、月、日);ChronoUnit:时间间隔(所有单位)
//ZoneId public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ //1.获取所有的时区名称 Set<String>zoneIds= ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds(); System.out.println(zoneIds.size()); System.out.println(zoneIds); //2.获取当前系统的默认时区 ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault(); System.out.println(zoneId); //3.获取指定的时区 ZoneId zoneId1=ZoneId.of("Asia/Pontianak"); System.out.println(zoneId1); } }
//Instant public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ //1.获取当前的Instant对象(标准时间( Instant now = Instant.now(); System.out.println(now); //2.根据(秒/毫秒/纳秒)获取Instant对象 Instant instant1=Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L); System.out.println(instant1);//1970-01-01T00:00:00Z Instant instant2=Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L); System.out.println(instant2);//1970-01-01T00:00:01Z Instant instant3=Instant.ofEpochSecond(1L,1000000000L); System.out.println(instant3);//1970-01-01T00:00:02Z //3.指定时区 ZonedDateTime time =Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai")); System.out.println(time); //4.isXxx判断 Instant instant4=Instant.ofEpochMilli(0L); Instant instant5=Instant.ofEpochMilli(1000L); boolean res=instant4.isBefore(instant5); System.out.println(res);//true instant4参数在5前面 //5.Instant minusXxx(long millisToSubtract)减少时间系列的方法 Instant instant6 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(3000L); System.out.println(instant6); Instant instant7 = instant6.minusSeconds(1); System.out.println(instant7); } }
11.包装类 基本数据类型对应的引用类型
byte-Byte, short-Short, char-Character, int-Integer, long-Long, float-Float, double- Double, boolean- Boolean
JDK5以后对包装类新增了自动装箱、自动拆箱的特性(即基本数据类型和对象之间的转换)
public class Demo { public static void main(String []args){ //1.利用构造方法获取Integer的对象(JDK5以前的方式) Integer i1 = new Integer(1); Integer i2 = new Integer("1"); System.out.println(i1); System.out.println(i2); //2.利用静态方法获取Integer的对象 Integer i3=Integer.valueOf(123); System.out.println(i3); //3.这两种方法获取对象的区别 //因为在实际开发中-128~127之间的数据使用率高 //如果每次使用new对象太浪费内存了 //所以提前把该范围内的每一个数据都创建好对象 //如果用到 不会创建新的而是返回已经创建好的对象 Integer i6 = Integer.valueOf(127); Integer i7 = Integer.valueOf(127); System.out.println(i6==i7);//true Integer i8 = Integer.valueOf(128); Integer i9 = Integer.valueOf(128); System.out.println(i8==i9);//false //因为使用new关键字创建,每次都是创建了一个新的对象,因此下面的两个对象地址值不一样 Integer i10 = new Integer(127); Integer i11 = new Integer(127); System.out.println(i10==i11);//false Integer i12 = new Integer(128); Integer i13 = new Integer(128); System.out.println(i12==i13);//false } }
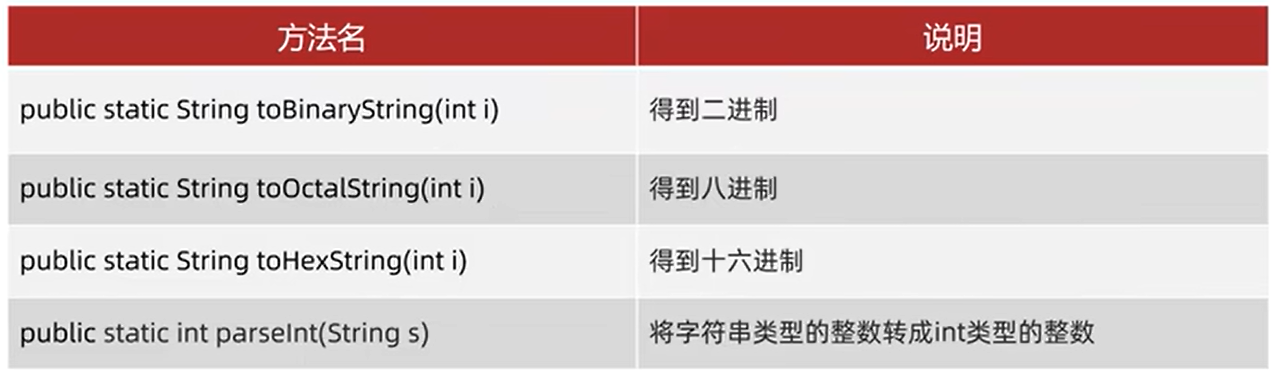
- Integer成员方法




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号