算法15:冷门面试题_队列实现栈,栈实现队列
经常有些面试官很变态,一般都是老阴逼级别的,喜欢问一些变态的问题。但是,反过来思考一下,这些题目也确实具备一些动手的能力,变相能够考查面试者的coding能力。
面试一:怎么样用数组实现不产过固定大小的队列和栈?
队列实现:
package code2.数组实现栈和队列_02;
public class Queue_02 {
class MyQueue {
private int pollIndex;
private int pushIndex;
private int size;
private int[] arr;
private int limit;
MyQueue(int limit) {
pollIndex = 0;
pushIndex = 0;
arr = new int[limit];
size = 0;
this.limit = limit;
}
private int nexIndex(int index) {
return index == limit-1 ? 0 : ++index;
}
public void push(int data) {
if (size == limit) {
System.out.println("队列满了,无法添加元素:" + data);
return;
}
arr[pushIndex] = data;
pushIndex = nexIndex(pushIndex);
size++;
}
public int poll () {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("队列为空,无法取出元素");
return -1;
}
int temp = arr[pollIndex];
pollIndex = nexIndex(pollIndex);
size--;
return temp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue_02 test = new Queue_02();
MyQueue queue = test.new MyQueue(5);
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
queue.push(i);
}
System.out.println("取出对应元素" + queue.poll());
System.out.println("取出对应元素" + queue.poll());
System.out.println("取出对应元素" + queue.poll());
queue.push(11);
queue.push(12);
queue.push(13);
queue.push(14);
//遍历队列
System.out.println("=========遍历============");
for(int i =0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("取出对应元素" + queue.poll());
}
}
}
栈实现:
package code2.数组实现栈和队列_02;
public class Stack_01 {
class MyStack {
private int[] arr = null;
private int index;
private int size;
public MyStack(int limit) {
arr = new int[limit];
size = limit;
index = 0;
}
public void pushElement (int data)
{
if (size == index) {
System.out.println("准备插入数据:" + data + " ,由于栈已满,无法插入成功");
return;
}
arr[index] = data;
index++;
}
public int pollElement()
{
if (index == 0) {
System.out.println("栈为空, 无法获取数据");
return -1;
}
index--;
int temp = arr[index];
return temp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack_01 test = new Stack_01();
MyStack stack =test.new MyStack(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
stack.pushElement(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
System.out.println(stack.pollElement());
}
}
}
面试题二:
实现一个特殊的栈,在基本功能的基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的功能
1)pop、push、getMin操作的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
2)设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构
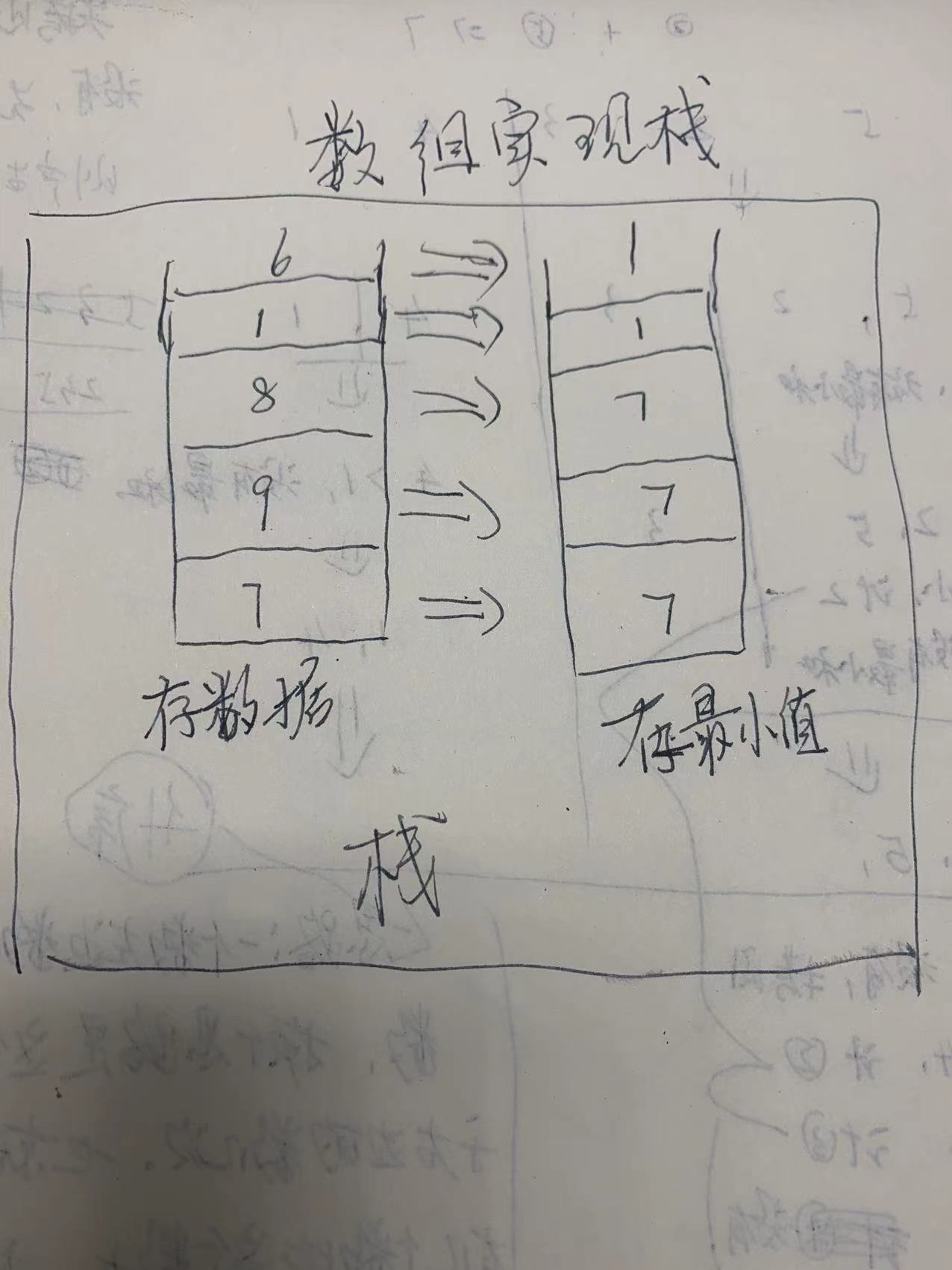
解题思路就是用2个数组,一个数组存储栈的元素,另一个数组这是存储栈中的最小值,下图是我手绘的流程:
package code2.数组实现栈和队列_02;
/**
* 实现一个特殊的栈,在基本功能的基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的功能
* 1)pop、push、getMin操作的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
* 2)设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构。
*/
public class Stack_03 {
class MyStack {
private int[] arr = null;
private int[] minArr = null;
private int index;
private int limit;
public MyStack(int limit) {
arr = new int[limit];
minArr = new int[limit];
this.limit = limit;
index = 0;
}
public void pushElement (int data)
{
if (index == limit) {
System.out.println("准备插入数据:" + data + " ,由于栈已满,无法插入成功");
return;
}
arr[index] = data;
setMin(data);
index++;
}
public int pollElement()
{
if (index == 0) {
System.out.println("栈为空, 无法获取数据");
return -1;
}
index--;
int temp = arr[index];
arr[index] = 0;
minArr[index] = 0;
return temp;
}
public void setMin(int data) {
if (index != 0) {
int temp = index;
int value = minArr[--temp];
if (data < value) {
minArr[index] = data;
}
else {
minArr[index] = value;
}
}
else {
minArr[0] = data;
}
}
public int getMin() {
int temp = index;
return minArr[--temp];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack_03 test = new Stack_03();
MyStack stack =test.new MyStack(5);
for (int i = 8; i > 6; i--) {
stack.pushElement(i);
}
stack.pushElement(11);
stack.pushElement(2);
stack.pushElement(13);
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
stack.pushElement(14);
System.out.println("删除:" + stack.pollElement());
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
System.out.println("删除:" + stack.pollElement());
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
System.out.println("删除:" + stack.pollElement());
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
stack.pushElement(6);
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
System.out.println("删除:" + stack.pollElement());
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
System.out.println("删除:" + stack.pollElement());
System.out.println("获取最小值:" + stack.getMin());
//8, 7,11,2,13
}
}
面试题三:用栈结构实现队列
package code2.数组实现栈和队列_02;
import java.util.Stack;
//栈实现队列
public class StackImpmentQueue {
private Stack stackPush;
private Stack stackPop;
public StackImpmentQueue()
{
stackPush = new Stack<Integer>();
stackPop = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push (int data)
{
if (!stackPop.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("stackPop中还有数据待取出,无法添加新元素");
}
stackPush.push(data);
}
public int pop () {
while (!stackPush.isEmpty()) {
stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());
}
if (stackPop.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
}
return (int) stackPop.pop();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StackImpmentQueue t = new StackImpmentQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
t.push(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("get :" + t.pop());
}
for (int i = 11; i < 15; i++) {
t.push(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("get :" + t.pop());
}
}
}
面试题四:用队列实现栈:
package code2.数组实现栈和队列_02;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
//队列实现栈
public class QueueImplementStack {
private Queue queuePush;
private Queue queueBak;
public QueueImplementStack() {
queueBak = new LinkedList();
queuePush = new LinkedList();
}
public void push(int value) {
queuePush.add(value);
}
public int pop() {
if (queuePush.isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无法获取有效数据");
}
while(queuePush.size() > 1) {
queueBak.add(queuePush.poll());
}
Object val = queuePush.poll();
Queue temp = queueBak;
queueBak = queuePush;
queuePush = temp;
return (int)val;
}
public boolean isEmpty () {
return queuePush.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueImplementStack stack = new QueueImplementStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
System.out.println("获取栈元素" + stack.pop());
stack.push(5);
System.out.println("获取栈元素" + stack.pop());
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("获取栈元素" + stack.pop());
}
}
}





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号