python日志篇-基础版
对常用python日志语法做记录,方便以后重复使用
日志等级:
DEBUG(调试)<INFO(一般信息输出)<WARNING(警告信息)<ERRO(程序报错信息)<CRITICAL(程序崩溃信息)
print内容记录到文件:
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- ##______________________命令行执行test.py文件并写入执行结果到abc.log文件_____________________ # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for i in range(1,21): print("the number is {}".format(i)) ''' 在cmd中运行 python test.py>adc.log '''
##————————————————————————直接运行就可以记录打印内容———————————————————————————————— #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import sys origin = sys.stdout#标准输出文件 #打开文件并执行控制台 f = open('file.txt', 'w') sys.stdout = f print ('开始记录打印内容') a=555 print('a=',a) print ('Start of progeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeram') # 你的程序放到这里,过程中所有print到屏幕的内容都同时保存在file.txt里面了。 print ('End of program') sys.stdout = origin f.close()
#——————————————————print_wire.py模块——————直接执行或通过导入模块名执行即可———————————————————————————————— #!/usr/bin/env python # encoding: utf-8 import sys import time class Logger(object): def __init__(self, filename="Default.log"): self.terminal = sys.stdout self.log = open(filename, "a")#a表示追加,w覆盖写入 def write(self, message): self.terminal.write(message) if '下载进度' not in message:#过滤下载进度的日志 #a=str(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time()))) self.log.write(message) def flush(self): pass now = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d", time.localtime())#获取当前日期 sys.stdout = Logger('123456.txt')#存放文件名 if __name__ == '__main__': __console__=sys.stdout print('---------start---------') print('1234567890123456789') print('---------stop---------') sys.stdout=__console__ time.sleep(10) ''' 如果在其他模块需要记录print内容,只需import rint_wire即可 '''
python logging日志封装:
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Author: zhangjun # @Date : 2018/7/26 9:20 # @Desc : Description import logging import logging.handlers import os import time class logs(object): def __init__(self): self.logger = logging.getLogger("") ## 设置输出的等级 LEVELS = {'NOSET': logging.NOTSET, 'DEBUG': logging.DEBUG, 'INFO': logging.INFO, 'WARNING': logging.WARNING, 'ERROR': logging.ERROR, 'CRITICAL': logging.CRITICAL} ##_________________________同时打印控制台并写入文件____________________________________ ## 创建文件目录 logs_dir="logs2" if os.path.exists(logs_dir) and os.path.isdir(logs_dir): pass else: os.mkdir(logs_dir) ## 修改log保存位置 timestamp=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d",time.localtime()) logfilename='%s.txt' % timestamp logfilepath=os.path.join(logs_dir,logfilename) rotatingFileHandler = logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler(filename =logfilepath, maxBytes = 1024 * 1024 * 50, backupCount = 5) ## 设置输出格式 formatter = logging.Formatter('[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') rotatingFileHandler.setFormatter(formatter) ## 控制台句柄 console = logging.StreamHandler() console.setLevel(logging.NOTSET) console.setFormatter(formatter) ## 添加内容到日志句柄中 self.logger.addHandler(rotatingFileHandler) self.logger.addHandler(console) self.logger.setLevel(logging.NOTSET) ##___________________________只打印控制台不写入文件____________________________________________ # logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, # format='%(asctime)s - %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s') #__________________________只写入文件不打印控制台______________________________________________ # ## 创建文件目录 # logs_dir="logs2" # if os.path.exists(logs_dir) and os.path.isdir(logs_dir): # pass # else: # os.mkdir(logs_dir) # ## 修改log保存位置 # timestamp=time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d",time.localtime()) # logfilename='%s.txt' % timestamp # logfilepath=os.path.join(logs_dir,logfilename) # rotatingFileHandler = logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler(filename =logfilepath, maxBytes = 1024 * 1024 * 50,backupCount = 5) # ## 设置输出格式 # formatter = logging.Formatter('[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] %(message)s', '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') # rotatingFileHandler.setFormatter(formatter) # ## 添加内容到日志句柄中 # self.logger.addHandler(rotatingFileHandler) # self.logger.setLevel(logging.NOTSET) def info(self, message): self.logger.info(message) def debug(self, message): self.logger.debug(message) def warning(self, message): self.logger.warning(message) def error(self, message): self.logger.error(message) if __name__ == '__main__': logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) logger=logs() logger.info("this is info") logger.debug("this is debug") logger.error("this is error") #logger.warning("this is warning") # #在其他模块调用日志 # import logging # logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # import 日志的模块 # if __name__ == '__main__': # logger=日志模块.logs() # logger.info("this is info") # logger.debug("this is debug") # logger.error("this is error") # logger.warning("this is warning")
第三方loguru模块处理日志:
如果想更简洁,可用loguru库,python3安装:pip3 install loguru。
loguru默认的输出格式是上面的内容,有时间、级别、模块名、行号以及日志信息,不需要手动创建 logger,直接使用即可,另外其输出还是彩色的,看起来会更加友好。
from loguru import logger ##########################默认格式################################### logger.debug('this is a debug message') logger.info('this is another debug message') logger.warning('this is another debug message') logger.error('this is another debug message') logger.info('this is another debug message') logger.success('this is success message!') logger.critical('this is critical message!')
#########################自定义格式################################## import sys logger.remove() # 移除默认的日志处理器 logger.add(sys.stderr, format="{time:YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss} | {level} | {message}") # 测试日志 logger.debug('this is a debug message') logger.info('this is another debug message') logger.success('this is success message!')
执行结果如下:
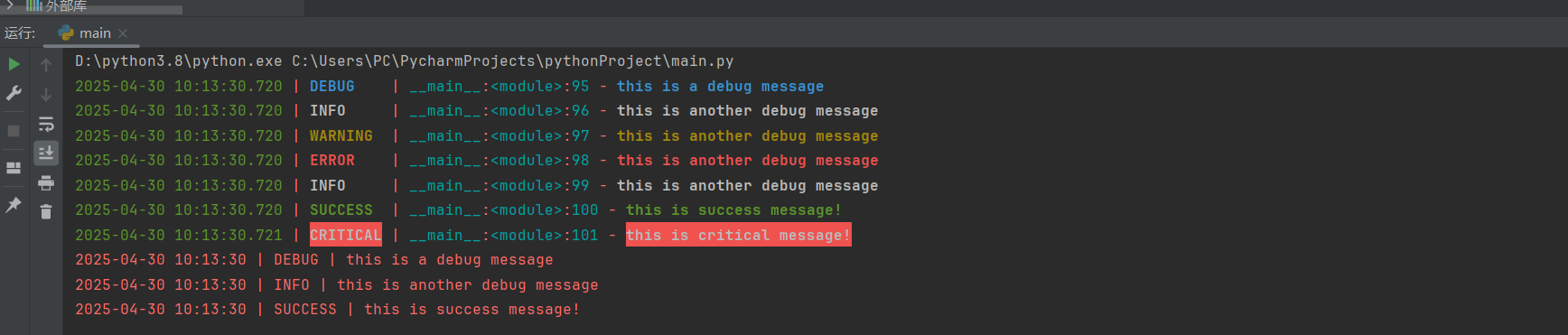
日志写入文件及设置
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from loguru import logger #______________________________日志写入文件为json格式_________________________________ logger.add("json.log",serialize=True,encoding="utf-8") logger.debug('this is a debug message') logger.info('this is a info message123456') #_____________________________日志写入文件普通模式____________________________________ logger.add('my_log.log') logger.debug('this is a debug') logger.debug('this is a info') logger.error('this is another error message') #_________________________________日志绕接__________________________________________ logger.add('my_log1.log',rotation="500MB") #自动循环过大的文件 logger.add('my_log2.log',rotation="12:00") #每天中午创建新文件 logger.add('my_log3.log',rotation="1 week") #一旦文件太旧进行循环 logger.add('my_log4.log',rotation="10 days") #定期清理 logger.add('my_log4.log',compression="zip") #压缩节省空间
运行之后会发现目录下 my_log.log 出现了刚刚控制台输出的 DEBUG 信息
其他写法:
######################################配置抽离,更适合实际场景(不封装)############################### #!/usr/bin/env python import sys,time from loguru import logger folder_ = "./log/" prefix_ = "polaris-" rotation_ = "10 MB" retention_ = "30 days" encoding_ = "utf-8" backtrace_ = True diagnose_ = True # 格式里面添加了process和thread记录,方便查看多进程和线程程序 format_ = '<green>{time:YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS}</green> | <level>{level: <8}</level> ' \ '| <magenta>{process}</magenta>:<yellow>{thread}</yellow> ' \ '| <cyan>{name}</cyan>:<cyan>{function}</cyan>:<yellow>{line}</yellow> - <level>{message}</level>' # 这里面采用了层次式的日志记录方式,就是低级日志文件会记录比他高的所有级别日志,这样可以做到低等级日志最丰富,高级别日志更少更关键 # debug logger.add(folder_ + prefix_ + "debug.log", level="DEBUG", backtrace=backtrace_, diagnose=diagnose_, format=format_, colorize=False, rotation=rotation_, retention=retention_, encoding=encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no == logger.level("DEBUG").no) # info logger.add(folder_ + prefix_ + "info.log", level="INFO", backtrace=backtrace_, diagnose=diagnose_, format=format_, colorize=False, rotation=rotation_, retention=retention_, encoding=encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no == logger.level("INFO").no) # warning logger.add(folder_ + prefix_ + "warning.log", level="WARNING", backtrace=backtrace_, diagnose=diagnose_, format=format_, colorize=False, rotation=rotation_, retention=retention_, encoding=encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no >= logger.level("WARNING").no) # error logger.add(folder_ + prefix_ + "error.log", level="ERROR", backtrace=backtrace_, diagnose=diagnose_, format=format_, colorize=False, rotation=rotation_, retention=retention_, encoding=encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no >= logger.level("ERROR").no) # critical logger.add(folder_ + prefix_ + "critical.log", level="CRITICAL", backtrace=backtrace_, diagnose=diagnose_, format=format_, colorize=False, rotation=rotation_, retention=retention_, encoding=encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no >= logger.level("CRITICAL").no) logger.add(sys.stderr, level="CRITICAL", backtrace=backtrace_, diagnose=diagnose_, format=format_, colorize=True, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no >= logger.level("CRITICAL").no) if __name__ == '__main__': logger.debug("This is a debug message") time.sleep(1) logger.info("This is an info message") ###在其他模块调用 import 日志模块 日志模块.logger.info("This is an info message") ######################################配置抽离并封装起来###################################### # !/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -* import sys from loguru import logger class logs(object): folder_ = "./log/" prefix_ = "polaris-" rotation_ = "10 MB" retention_ = "30 days" encoding_ = "utf-8" backtrace_ = False diagnose_ = False format_ = '<green>{time:YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS}</green> | <level>{level: <8}</level> ' \ '| <magenta>{process}</magenta>:<yellow>{thread}</yellow> ' \ '| <cyan>{name}</cyan>:<cyan>{function}</cyan>:<yellow>{line}</yellow> - <level>{message}</level>' def debug(self, debug): logger.add(self.folder_ + self.prefix_ + "debug.log", level="DEBUG", backtrace=self.backtrace_, diagnose=self.diagnose_, format=self.format_, colorize=False, rotation=self.rotation_, retention=self.retention_, encoding=self.encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no == logger.level("DEBUG").no) logger.debug(debug) def info(self, info): logger.add(self.folder_ + self.prefix_ + "info.log", level="INFO", backtrace=self.backtrace_, diagnose=self.diagnose_, format=self.format_, colorize=False, rotation=self.rotation_, retention=self.retention_, encoding=self.encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no == logger.level("INFO").no) logger.info(info) def error(self, error): logger.add(self.folder_ + self.prefix_ + "error.log", level="ERROR", backtrace=self.backtrace_, diagnose=self.diagnose_, format=self.format_, colorize=False, rotation=self.rotation_, retention=self.retention_, encoding=self.encoding_, filter=lambda record: record["level"].no == logger.level("ERROR").no) logger.error(error) if __name__ == '__main__': log = logs() log.debug("这是debug信息") log.info("这是info信息") log.error("这是error信息") # 在其他模块调用 import 日志所在模块 log = 日志所在模块.logs() log.debug("这是debug信息") log.info("这是info信息") ############################################设置不同级别的日志并输出到文件####################################### from loguru import logger ##设置不同级别的日志输出文件(rotation:超过xx就新生成文件, filter:当日志级别是 "DEBUG" 时,才会被写入到指定的日志文件) logger.add("debug.log", level="DEBUG", rotation="10 MB", filter=lambda record: record["level"].name == "DEBUG") logger.add("info.log", level="INFO", rotation="10 MB", filter=lambda record: record["level"].name == "INFO") logger.add("warning.log", level="WARNING", rotation="10 MB", filter=lambda record: record["level"].name == "WARNING") logger.add("error.log", level="ERROR", rotation="10 MB", filter=lambda record: record["level"].name == "ERROR") logger.add("critical.log", level="CRITICAL", rotation="10 MB", filter=lambda record: record["level"].name == "CRITICAL") ##输出不同级别的日志消息 logger.debug("This is a debug message") logger.info("This is an info message") logger.warning("This is a warning message") logger.error("This is an error message") logger.critical("This is a critical message")
相关连接:
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzkxNDI3NjcwMw==&mid=2247493818&idx=1&sn=1b913b843f60b522041dcd0807f2ba2f .....................loguru一行代码搞定Python日志
https://blog.csdn.net/cui_yonghua/article/details/107498535 ........................................................................................................................loguru详细用法(好处:不用学代码直接调用即可)
日志服务相关连接(详情在数据分类):
https://c4ys.com/archives/552 ....................................................................python+logstash+elasticsearch+Kibana日志方案
https://www.cnblogs.com/xuzhongtao/p/12466351.html ..............................Kibana搭建
https://www.jianshu.com/p/9d2316693a1e ................................................kibana查询基础使用


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号