2020软件工程作业04
区间第k大数
解题思路
- 获取输入的数字
- 获取序列的长度
- 获取序列具体的值
- 输入需要查询几次
- 输入查询arr数组中的哪一个区间,和区间内第几个值
- 定义temp数组保存指定区间的值
- 调用quickSort(temp)方法进行从小到大排序
![BMzG6O.jpg]()
- 输出指定区间内,从大到小的第k个值。
代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入序列的长度:");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入序列的具体数字:");
int arr[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("请输入查询数:");
int m = sc.nextInt();//指定询问个数
System.out.println("请输入l、r、k:");
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int l = sc.nextInt();
int r = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
//输入起始位置、结束位置、指定索引元素
int temp[] = new int[r-l+1];
int index=0;
//将指定范围元素赋给新的数组
for (int j = l-1; j <= r-1; j++) {
temp[index++]=arr[j];
}
quickSort(temp);//对该数组进行排序
//输出新数组指定索引位置元素
System.out.println(temp[r-l+1-k]);
}
}
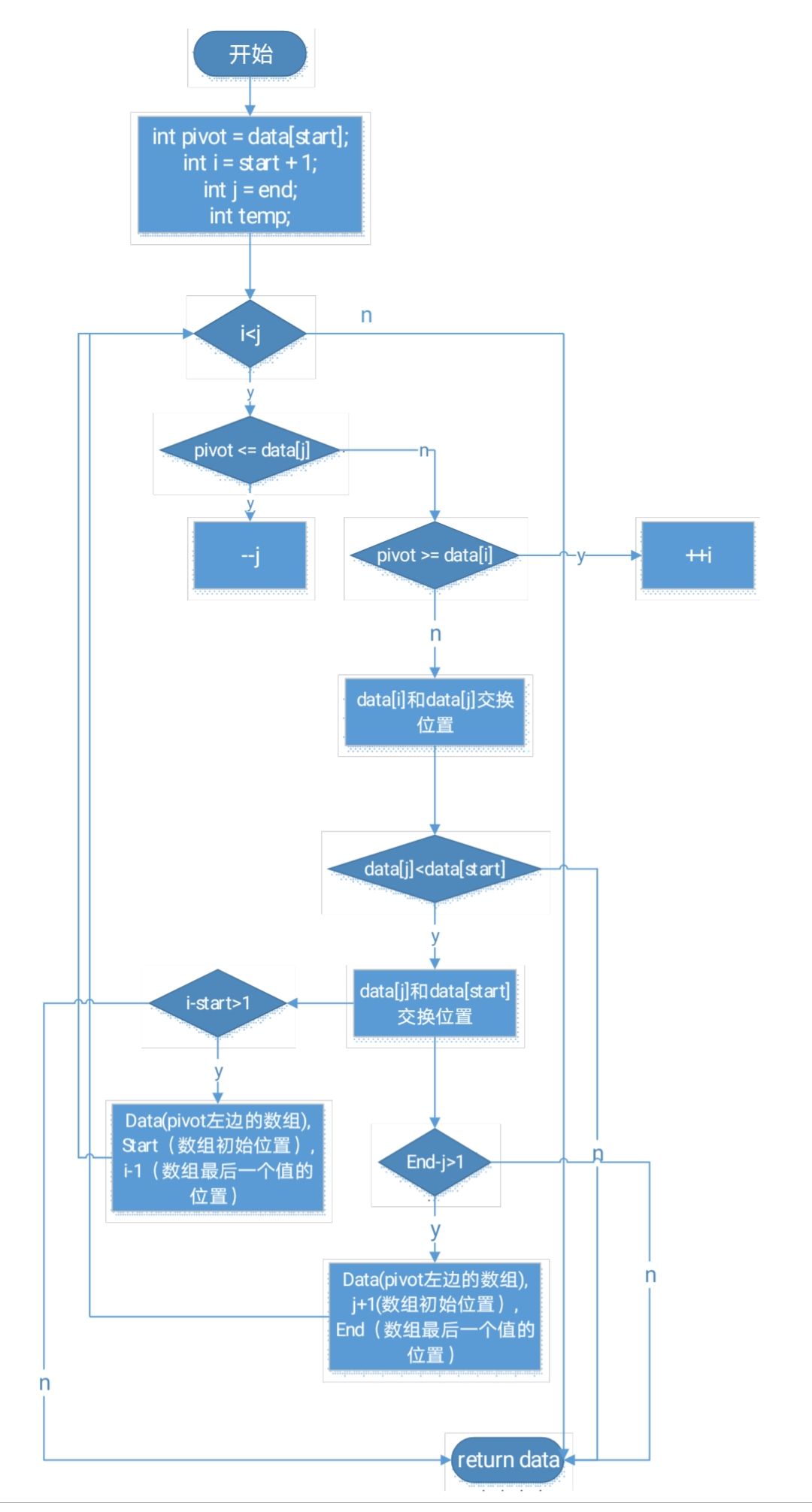
public static int[] quickSort(int[] data){
return quickSort(data,0,data.length-1);
}
public static int[] quickSort(int[] data,int start,int end){
int pivot = data[start];
int i = start + 1;
int j = end;
int temp;
while (i<j){
while((j>i) && (pivot <= data[j])){
--j;
}
while((i<j) && (pivot >= data[i])){
++i;
}
if(i < j){
temp = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = temp;
}
}
if(data[j] <data[start]){
temp = data[start];
data[start] = data[j];
data[j] = temp;
}
if(i - start > 1){
quickSort(data,start,i-1);
}
if(end -j >1){
quickSort(data,j + 1,end);
}
return data;
}
}
![BKwf4e.png]()
二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
解题思路
- 先序遍历:访问根结点,先序遍历根结点的左子树,先序遍历根结点的右子树
- 中序遍历:中序遍历根结点的左子树,访问根结点,中序遍历根节点的右子树
- 后序遍历:后序遍历根结点的左子树,后序遍历根结点的右子树,访问根结点
以上通过递归的方式遍历整个二叉树结构
- 层次遍历:设置队列,将根结点引用入队,当队列非空时,循环:
- 从队列中取出一个结点并访问该结点
- 判断他的左右子树是否为空,非空则加入队列。
代码实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台
*/
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
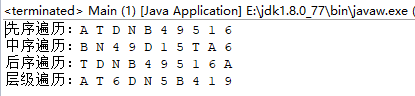
System.out.print("先序遍历:");
A(root);
System.out.println();
// 中序遍历
System.out.print("中序遍历:");
B(root);
System.out.println();
// 后续遍历
System.out.print("后序遍历:");
C(root);
System.out.println();
// 层级遍历
System.out.print("层级遍历:");
D(root);
}
private static void A(Node root) {
// TODO 先序遍历
if(root != null){
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
A(root.getLchild());
A(root.getRchild());
}
}
private static void B(Node root) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if(root != null){
B(root.getLchild());
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
B(root.getRchild());
}
}
private static void C(Node root) {
// TODO 后续遍历
if(root != null){
A(root.getLchild());
A(root.getRchild());
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
}
private static void D(Node root) {
// TODO 层级遍历
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<Node>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node tmp = q.poll();
System.out.print(tmp.data+" ");
if(tmp.getLchild() != null){
q.add(tmp.getLchild());
}
if(tmp.getRchild() != null){
q.add(tmp.getRchild());
}
}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
}
class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
public Node getLchild(){
return l;
}
public Node getRchild(){
return r;
}
}
![BKwA1A.png]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号