spring cloud(2):ribbon
一 ribbon是什么?
定义
Spring Cloud Ribbon是基于Netflix Ribbon实现的一套客户端负载均衡的工具。
简单的说,Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,将Netflix的中间层服务连接在一起。Ribbon客户端组件提供一系列完善的配置项如连接超时,重试等。简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出Load Balancer(简称LB)后面所有的机器,Ribbon会自动的帮助你基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随机连接等)去连接这些机器。我们也很容易使用Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法。
客户端负载均衡与服务端负载均衡?
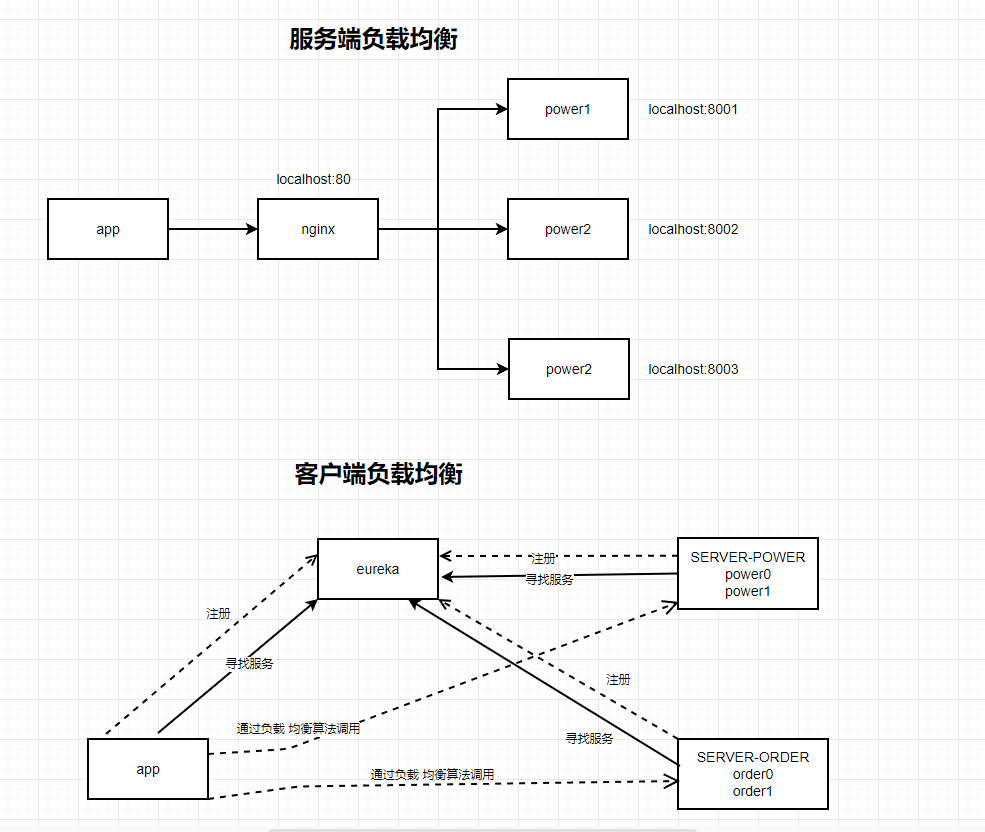
服务端的负载均衡是一个url先经过一个代理服务器(这里是nginx),然后通过这个代理服务器通过算法(轮询,随机,权重等等..)反向代理你的服务,来完成负载均衡。
而客户端的负载均衡则是一个请求在客户端的时候已经声明了要调用哪个服务,然后通过具体的负载均衡算法来完成负载均衡。
二 java中如何使用ribbon?
首先,我们还是要引入依赖,但是,eureka已经把ribbon集成到他的依赖里面去了,所以这里不需要再引用ribbon的依赖,如图:
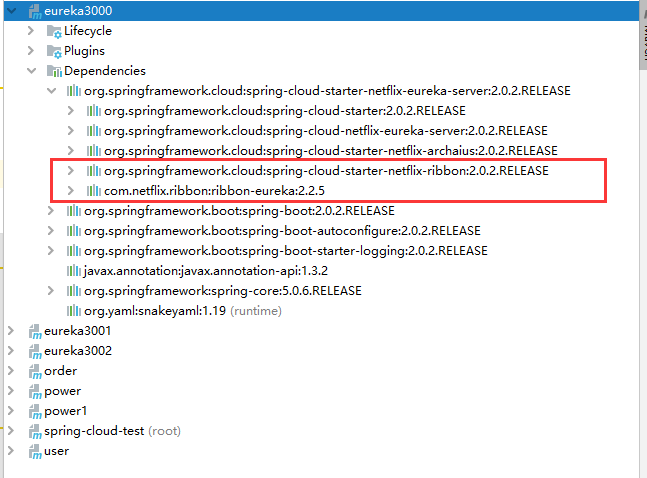
要使用ribbon,只需要一个注解@LoadBalanced:
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
return restTemplate;
}
我们这里现在启动了eureka集群(3个eureka) 和Power集群(2个power) 和一个服务调用者(User)
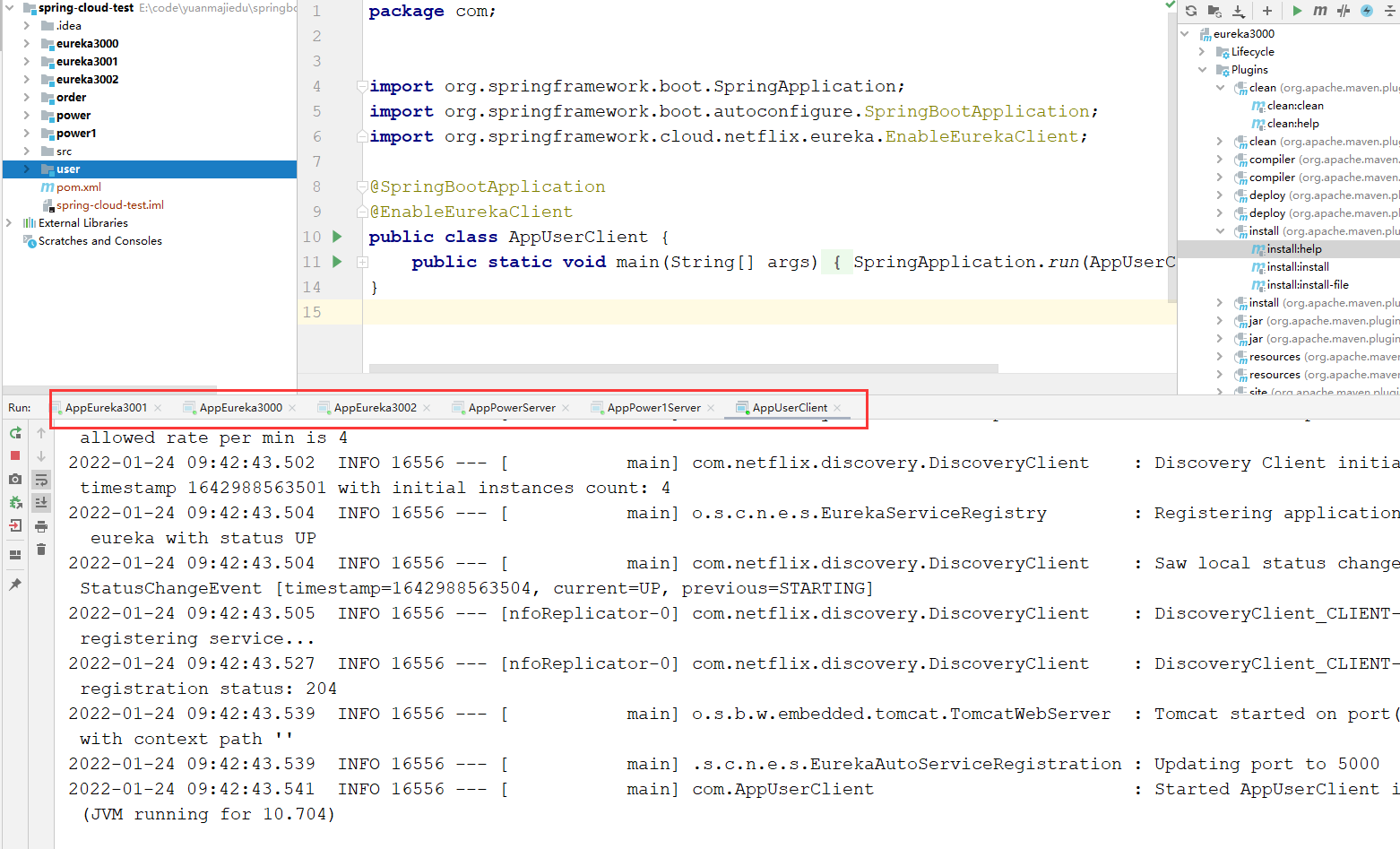
我们能看见 微服务名:SERVER-POWER 下面有2个微服务(power-1,power2),现在我们来通过微服务名调用这个服务
这是我们的user项目的调用代码:
package com.luban.controller;
import com.luban.util.R;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
RestTemplate restTemplate;
private static final String POWER_URL="http://SERVER-POWER";
@RequestMapping("/getUser.do")
public R getUser(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("key","user数据");
return R.success("返回成功",map);
}
@RequestMapping("/getPower.do")
public R getPower(){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("key1","value1");
R.success().set("key1","value1").set("key1","value1");
return R.success("操作成功",restTemplate.getForObject(POWER_URL+"/getPower.do",Object.class));
}
}
结果如下:
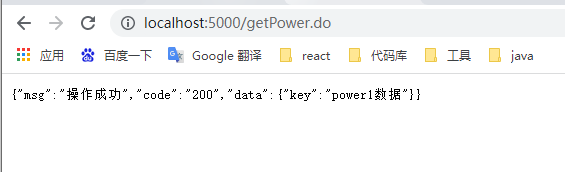
他默认的负载均衡是轮询策略。
三 核心组件IRule
IRule是什么? 它是Ribbon对于负载均衡策略实现的接口, 怎么理解这句话? 说白了就是你实现这个接口,就能自定义负载均衡策略, 自定义我们待会儿来讲, 我们先来看看他有哪些默认的实现
- RoundRoRounbinRule:轮询。
- RandomRule:随机。
- AvailabilityFilteringRule:会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器 跳闸状态的服务,还有并发的连接数量超过阈的服务,然后对于剩余的服务列表按照轮询策略进行选取。
- WeightedResponseTimeRule:根据平均响应时间计算所有服务的权重,响应时间越快服务权重越大,刚启动时如果统计信息不足,则使用RoundRobinRule策略,等统计信息足够后,会切换WeightedResponseTimeRule。
- RetryRule:先按照RoundRoRounbinRule的策略获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定的时间内重试,再获取不到则放弃。
- BestAvailableRule:会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务。
- ZoneAvoidanceRule:默认规则,符合判断server所在区域的性能和server的可用性选择服务器。
具体实现代码:
package com.luban.config;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.*;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
@ComponentScan("com")
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Bean
public IRule iRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
}
在Spring 的配置类里面把对应的实现作为一个Bean返回出去就行了。
还有一个重点就是,怎么调用不同的微服务,配置不同的负载均衡策略,比如说我user调用power服务,user调用order服务,调用这两个微服务调用两种负载均衡策略。
首先上面那种情况,IRule这个bean不能放在ComponentScan的目录下,由于扫描的是目录是 com,所以需要在com同目录下创建一个config的目录,然后在这个config目录里面操作
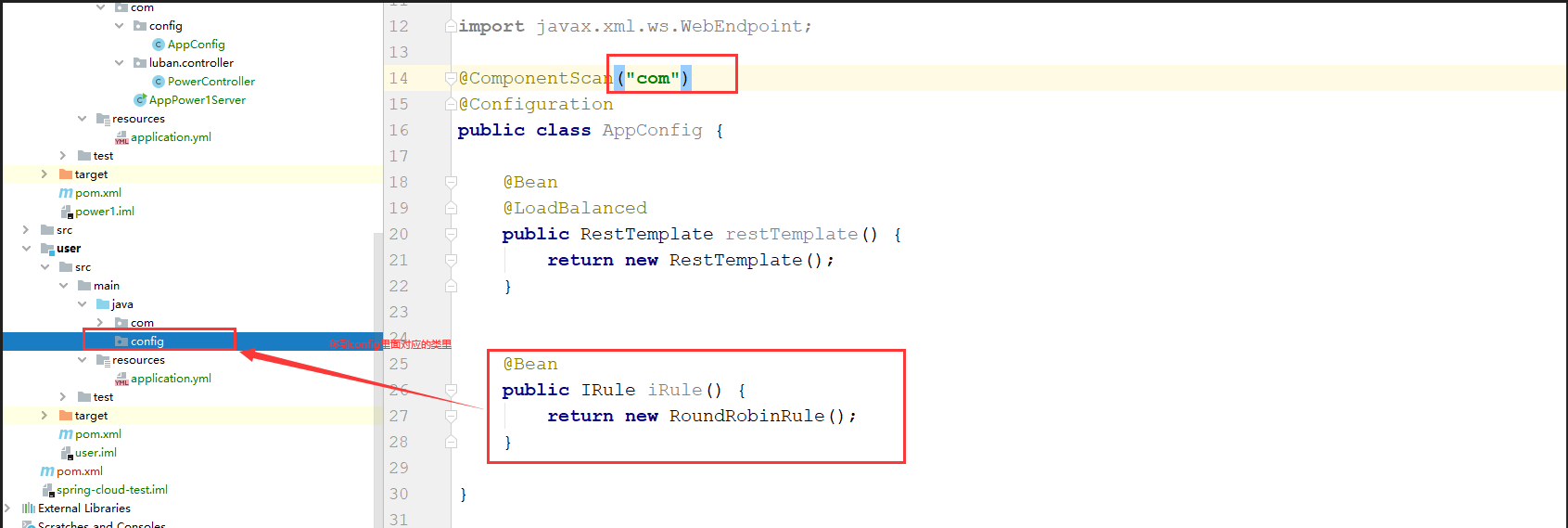
如下图:

创建俩个config类
package config;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class OrderRuleConfig {
@Bean
public IRule iRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
}
package config;
import com.luban.rule.LuBanRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class PowerRuleConfig {
@Bean
public IRule iRule(){
return new LuBanRule();
}
}
然后在启动类配置如下:
package com;
import config.OrderRuleConfig;
import config.PowerRuleConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClients;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@RibbonClients({
@RibbonClient(name = "SERVER-ORDER",configuration = OrderRuleConfig.class),
@RibbonClient(name = "SERVER-POWER",configuration = PowerRuleConfig.class)
})
@EnableFeignClients
public class AppUserClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppUserClient.class);
}
}
这样user在调用power服务和order服务就可以是不同的负载均衡策略了
3.1 自定义实现负载均衡
我们刚刚讲过,只要实现了IRule就可以完成自定义负载均衡,至于具体怎么来,我们先看看他默认的实现
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.netflix.loadbalancer;
import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;
import edu.umd.cs.findbugs.annotations.SuppressWarnings;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
Random rand = new Random();
public RandomRule() {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"RCN_REDUNDANT_NULLCHECK_OF_NULL_VALUE"})
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
} else {
Server server = null;
while(server == null) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
return null;
}
int index = this.rand.nextInt(serverCount);
server = (Server)upList.get(index);
if (server == null) {
Thread.yield();
} else {
if (server.isAlive()) {
return server;
}
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
}
return server;
}
}
public Server choose(Object key) {
return this.choose(this.getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
}
}
我们来看看这个类AbstractLoadBalancerRule
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.netflix.loadbalancer;
import com.netflix.client.IClientConfigAware;
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalancerRule implements IRule, IClientConfigAware {
private ILoadBalancer lb;
public AbstractLoadBalancerRule() {
}
public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb) {
this.lb = lb;
}
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer() {
return this.lb;
}
}
这里我们能发现,还是我们上面所说过的,实现了IRule就能够自定义负载均衡即使是他默认的策略也实现了IRule
package com.luban.rule;
import com.netflix.client.config.IClientConfig;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.AbstractLoadBalancerRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.Server;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class MyRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
//原来是纯随机策略 我们现在改为。 如果一个下标已经被随机到了2次了,第三次还是同样的下标的话,那就再随机一次
Random rand;
private int lastIndex = -1;
private int nowIndex = -1;
private int skipIndex = -1;
public MyRule() {
rand = new Random();
}
/**
* Randomly choose from all living servers
*/
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
return null;
}
Server server = null;
while (server == null) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
return null;
}
List<Server> upList = lb.getReachableServers();
List<Server> allList = lb.getAllServers();
int serverCount = allList.size();
if (serverCount == 0) {
/*
* No servers. End regardless of pass, because subsequent passes
* only get more restrictive.
*/
return null;
}
int index = rand.nextInt(serverCount);
System.out.println("当前下标为:"+index);
if (skipIndex>=0&&index == skipIndex) {
System.out.println("跳过");
index = rand.nextInt(serverCount);
System.out.println("跳过后的下标:"+index);
}
skipIndex=-1;
nowIndex = index;
if (nowIndex == lastIndex) {
System.out.println("下一次需要跳过的下标"+nowIndex);
skipIndex = nowIndex;
}
lastIndex = nowIndex;
server = upList.get(index);
if (server == null) {
/*
* The only time this should happen is if the server list were
* somehow trimmed. This is a transient condition. Retry after
* yielding.
*/
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive()) {
return (server);
}
// Shouldn't actually happen.. but must be transient or a bug.
server = null;
Thread.yield();
}
return server;
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
这里我们就把自己写的Rule给new出来交给spring 就好了
package com.luban.config;
import com.luban.rule.MyRule;
import com.netflix.loadbalancer.*;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
@ComponentScan
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Bean
public IRule iRule(){
return new MyRule();
}
}
这样就可以了
四 feign负载均衡
4.1 feign是什么?
Feign是一个声明式WebService客户端。使用Feign能让编写Web Service客户端更加简单, 它的使用方法是定义一个接口,然后在上面添加注解,同时也支持JAX-RS标准的注解。Feign也支持可拔插式的编码器和解码器。SpringCloud对Feign进行了封装,使其支持了Spring MVC标准注解和HttpMessageConverters。Feign可以与Eureka和Ribbon组合使用以支持负载均衡。
feign 能干什么
Feign旨在使编写Java Http客户端变得更容易。 前面在使用Ribbon+RestTemplate时,利用RestTemplate对http请求的封装处理,形成了一套模版化的调用方法。但是在实际开发中,由于对服务依赖的调用可能不止一处,往往一个接口会被多处调用,所以通常都会针对每个微服务自行封装一些客户端类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。所以,Feign在此基础上做了进一步封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现依赖服务接口的定义。在Feign的实现下,我们只需创建一个接口并使用注解的方式来配置它(以前是Dao接口上面标注Mapper注解,现在是一个微服务接口上面标注一个Feign注解即可),即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用Spring cloud Ribbon时,自动封装服务调用客户端的开发量。
4.2 如何使用?
在客户端(User)引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
在启动类上面加上注解:@EnableFeignClients
package com;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class AppUserClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppUserClient.class);
}
}
然后编写一个service类加上@FeignClient()注解 参数就是你的微服务名字
package com.luban.service;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@FeignClient("SERVER-POWER")
public interface PowerServiceClient {
@RequestMapping("/getPower.do")
public Object power();
}
下面是调用代码:
package com.luban.controller;
import com.luban.service.PowerServiceClient;
import com.luban.util.R;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
RestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
PowerServiceClient power;
private static final String POWER_URL="http://SERVER-POWER";
@RequestMapping("/getUser.do")
public R getUser(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("key","user数据");
return R.success("返回成功",map);
}
@RequestMapping("/getPower.do")
public R getPower(){
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("key1","value1");
R.success().set("key1","value1").set("key1","value1");
return R.success("操作成功",restTemplate.getForObject(POWER_URL+"/getPower.do",Object.class));
}
@RequestMapping("/feignPower.do")
public Object feignPower(){
return power.power();
}
}
这里拿了RestTemplate做对比 可以看看2者区别。
Feign集成了Ribbon,利用Ribbon维护了服务列表信息,并且融合了Ribbon的负载均衡配置,也就是说之前自定义的负载均衡也有效,而与Ribbon不同的是,通过feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法,优雅而简单的实现了服务调用



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号