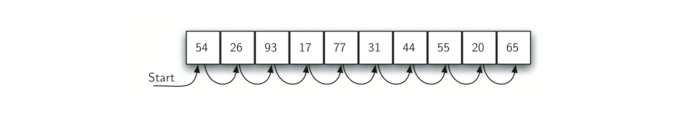
顺序查找
按照基本的顺序排序,简单地从一个项移动到另一个项,直到找到我们正在寻找的项或遍历完整个列表。
def sequentialSearch(alist,item):
pos = 0
found = False
while pos < len(alist) and not found:
if alist[pos] == item:
found = True
else:
pos += 1
return found
testlist = [1, 2, 32, 8, 17, 19, 42, 13, 0]
print(sequentialSearch(testlist, 3))
print(sequentialSearch(testlist, 13))
查找性能情况:
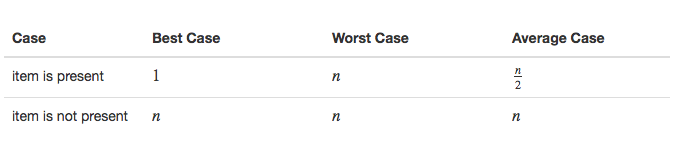
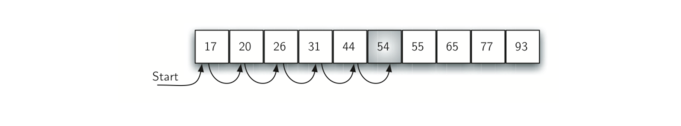
假设项的列表按升序排列。如果我们正在寻找的项存在于列表中,它在 n 个位置中的概率依旧相同。我们仍然会有相同数量的比较来找到该项。然而,如果该项不存在,则有一些优点。
def orderedSequentialSearch(alist,item):
pos = 0
found = False
stop = False
while pos < len(alist) and not found and not stop:
if alist[pos] == item:
found = True
else:
if alist[pos] > item:
stop = True
else:
pos += 1
return found
testlist = [0, 1, 2, 8, 13, 17, 19, 32, 42,]
print(orderedSequentialSearch(testlist, 3))
print(orderedSequentialSearch(testlist, 13))
查找性能情况:

在最好的情况下,我们通过只查看一项会发现该项不在列表中。 平均来说,我们将只了解 n/2 项就知道。然而,这种复杂度仍然是 O(n)。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号