201871010104-陈园园 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
201871010104-陈园园 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://www.cnblogs.com/lily-2018/p/11441372.html |
| 作业学习目标 |
(1) 掌握事件处理的基本原理,理解其用途; (2) 掌握AWT事件模型的工作机制; (3) 掌握事件处理的基本编程模型; (4) 了解GUI界面组件观感设置方法; (5) 掌握WindowAdapter类、AbstractAction类的用法; (6) 掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。 |
第一部分:总结理论知识
第十一章 事件的处理
11.1事件处理基础
1)事件源:能够产生事件的组件对象,如:文本框、按钮等。事件源能够注册监听器并向监听器发送事件对象。
2)事件监听器;事件监听器接收事件源发送的通告(事件对象)后,对发生的事件作出响应,一个事件监听器就是一个实现专门监听器接口的实例,该类必须实现接口中的方法。这些方法当事件发生时,被自动执行。
事件对象:java将事件的相关信息封装在事件对象中,不同的事件源可以产生不同类别的事件,所有的事件对象都派生于java.util.EventObject类。
AWT事件处理机制的概要:
监听器对象:是一个实现了特定监听器接口(listener interface)的类实例。
事件源:是一个能够注册监听器并发送事件对象的对象。
当事件发生时,事件源将事件对象自动传递给其所有注册的监听器。
监听器对象利用事件对象中的信息决定如何对事件作出响应。
GUI设计中,需要对组件某种事件进行响应和处理时,程序员必须完成的两个步骤:
1)定义实现某种事件监听器接口的事件接听器类,并具体化接口中声明的事件处理抽象方法。
2)为组件注册实现了规定接口的事件监听器对象。
注册监听器的方法:
eventSourceObject.addEventListener(eventListenerObject)
注册监听器的实例:
ActionListener listener=...;
JButton button=new JButton("Ok");
button.addActionListener(listener);
动作事件(ActionEvent):当特定组件动作(点击按钮)发生时,该组件自动生成此动作事件。
该事件被传递给组件注册的每一个ActionListener对象,并调用监听器对象的actionPerformed方法以接收这类事件对象。
动作事件主要包括:
(1)点击按钮
(2)双击一个列表中的选项
(3)选择菜单项
(4)在文本框中输入回车
监听器接口的实现:
监听器接口必须与事件源相对应的监听器接口,即必须提供接口中方法的实现。
class Mylistener implements ActionnListener
(
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{.....}
}
命令按钮Jbutton主要API(见教材444页)
在例ButtonTest,java中,各按钮需要同样的处理:
1)使用字符串构造按钮对象
2)把按钮添加到面板上
3)用对应的颜色构造一个动作监听器
4)注册动作监听器
用匿名类、lambda表达式简化程序见实验。
命令按钮Jbutton主要API
创建按钮对象
Jbutton类常用的一组构造方法;
(1) JButton(String text):创建一个带文本的按钮。
(2) JButton(Icon icon) :创建一个带图标的按钮。
(3)JButton(String text, Icon icon) :创建一个带文本和图标
的按钮
按钮对象的常用方法:
1) getLabel( ):返回按钮的标签字符串;
2)setLabel(String s):设置按钮的标签为字符串s。
注册事件监听器
可将一个Terminator对象注册为事件监听器:
WindowListener listener=new Terminator();
frame.addWindowListener(listener);
只要框架产生一个窗口事件,该事件就会传递给
监听器对象。
创建扩展于WindowAdapter的监听器类是很好的
改进,但还可以进一步将上面语句也可简化为:
frame.addWindowListener(new Terminator());
鼠标事件
– MouseEvent
鼠标监听器接口
– MouseListener
– MouseMotionListener
鼠标监听器适配器
– MouseAdapter
– MouseMotionAdapter
用户点击鼠标按钮时,会调用三个监听器方法:
1) 鼠标第一次被按下时调用mousePressed方法;
2)鼠标被释放时调用mouseReleased方法;
3) 两个动作完成之后,调用mouseClicked方法。
鼠标在组件上移动时,会调用mouseMoved方法。
如果鼠标在移动的时候还按下了鼠标,则会调用
mouseDragged方法
鼠标事件返回值
– 鼠标事件的类型是MouseEvent,当发生鼠标事件时:
MouseEvent类自动创建一个事件对象,以及事件发生
位置的x和y坐标,作为事件返回值。
第二部分:实验部分
实验1: 导入第11章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
1)在elipse IDE中调试运行教材443页-444页程序11-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2) 在事件处理相关代码处添加注释;
3) 用lambda表达式简化程序;
4)掌握JButton组件的基本API;
5)掌握Java中事件处理的基本编程模型。
代码如下:
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.35 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ButtonTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {//lambda表达式
var frame = new ButtonFrame();
frame.setTitle("ButtonTest");//设置标题
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);//设置可见性
});
}
}
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame with a button panel.
*/
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame//继承关系,ButtonFrame的父类是JFrame类。
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public ButtonFrame()//构造器
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
// create buttons
var yellowButton = new JButton("Yellow");
var blueButton = new JButton("Blue");
var redButton = new JButton("Red");
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
// add buttons to panel
buttonPanel.add(yellowButton);
buttonPanel.add(blueButton);
buttonPanel.add(redButton);
// add panel to frame
add(buttonPanel);
// create button actions
var yellowAction = new ColorAction(Color.YELLOW);
var blueAction = new ColorAction(Color.BLUE);
var redAction = new ColorAction(Color.RED);
// associate actions with buttons
yellowButton.addActionListener(yellowAction);
blueButton.addActionListener(blueAction);
redButton.addActionListener(redAction);
}
/**
* An action listener that sets the panel's background color.
*/
private class ColorAction implements ActionListener//实现监听器接口
{
private Color backgroundColor;//定义背景色
public ColorAction(Color c)
{
backgroundColor = c;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)//按钮单机操作
{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgroundColor);
}
}
}
用lambda表达式简化程序如下:
package button;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame with a button panel.
*/
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public ButtonFrame() {
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
makeButton("yellow", Color.yellow);
makeButton("blue", Color.blue);
makeButton("red", Color.red);
add(buttonPanel);
}
protected void makeButton(String name,Color backgound) {
// create buttons
JButton button = new JButton(name);
// add buttons to panel
buttonPanel.add(button);
button.addActionListener((e)->{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgound);
});
}
}
}
运行结果:

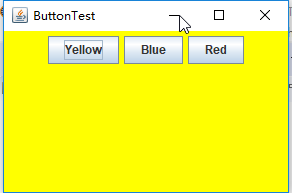

测试程序2:
1) 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材449页程序11-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2) 在组件观感设置代码处添加注释;
3) 了解GUI程序中观感的设置方法。
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.32 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PlafTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new PlafFrame();
frame.setTitle("PlafTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.UIManager;
/**
* 带有按钮面板的框架,用于更改外观和感觉
*/
public class PlafFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
public PlafFrame()//构造器
{
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo[] infos = UIManager.getInstalledLookAndFeels();
for (UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo info : infos)
makeButton(info.getName(), info.getClassName());
add(buttonPanel);
pack();
}
/**
* 创建一个按钮来更改可插入的外观.
* @param name the button name
* @param className the name of the look-and-feel class
*/
private void makeButton(String name, String className)
{
//添加按钮到面板
JButton button = new JButton(name);
buttonPanel.add(button);
//设置按钮要进行的操作
button.addActionListener(event -> {
// 按钮操作结果: 切换到新的外观
try //可能出错的代码放入try子句中
{
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(className);
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(this);
pack();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
运行结果:
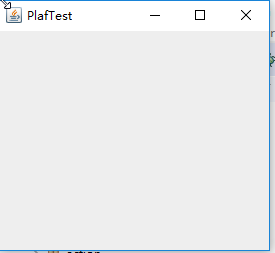
测试程序3:
1)在elipse IDE中调试运行教材457页-458页程序11-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2)掌握AbstractAction类及其动作对象;
3)掌握GUI程序中按钮、键盘动作映射到动作对象的方法。
package action;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ActionTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {//lamda表达式
var frame = new ActionFrame();
frame.setTitle("ActionTest");//设置标题
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//设置关闭操作
frame.setVisible(true);//设置可见性
});
}
}
package action;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame with a panel that demonstrates color change actions.
*/
public class ActionFrame extends JFrame//继承关系,ActionFrame的父类JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
public ActionFrame()//构造器
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
// 定义按钮
var yellowAction = new ColorAction("Yellow", new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"),
Color.YELLOW);
var blueAction = new ColorAction("Blue", new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), Color.BLUE);
var redAction = new ColorAction("Red", new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif"), Color.RED);
// add buttons for these actions
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(yellowAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(blueAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(redAction));
// add panel to frame
add(buttonPanel);
// 将Y、B和R键与名称关联起来
InputMap inputMap = buttonPanel.getInputMap(JComponent.WHEN_ANCESTOR_OF_FOCUSED_COMPONENT);
inputMap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl Y"), "panel.yellow");
inputMap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl B"), "panel.blue");
inputMap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl R"), "panel.red");
// associate the names with actions
ActionMap actionMap = buttonPanel.getActionMap();
actionMap.put("panel.yellow", yellowAction);
actionMap.put("panel.blue", blueAction);
actionMap.put("panel.red", redAction);
}
public class ColorAction extends AbstractAction
{
/**
* Constructs a color action.
* @param name the name to show on the button
* @param icon the icon to display on the button
* @param c the background color
*/
public ColorAction(String name, Icon icon, Color c)
{
putValue(Action.NAME, name);
putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, icon);
putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, "Set panel color to " + name.toLowerCase());
putValue("color", c);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
var color = (Color) getValue("color");
buttonPanel.setBackground(color);
}
}
}
运行结果:
程序运行时只需同时按Ctrl+Y或R或B键,窗口就会自动显示某种颜色,如下:
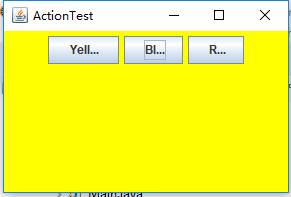
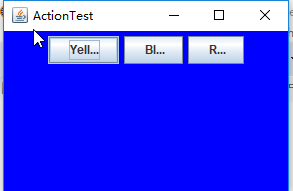
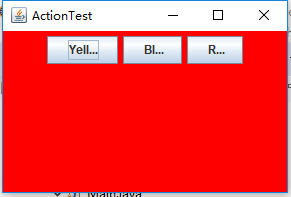
测试程序4:
1) 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材462页程序11-4、11-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2)掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。
package mouse;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* @version 1.35 2018-04-10
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class MouseTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {//构造器
var frame = new MouseFrame();
frame.setTitle("MouseTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package mouse;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A frame containing a panel for testing mouse operations
*/
public class MouseFrame extends JFrame
{
public MouseFrame()//构造器
{
add(new MouseComponent());
pack();
}
}
package mouse;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
/**
* A component with mouse operations for adding and removing squares.
*/
public class MouseComponent extends JComponent//继承组件类
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
private static final int SIDELENGTH = 10;
private ArrayList<Rectangle2D> squares;
private Rectangle2D current; // 包含鼠标光标的正方形
public MouseComponent()//构造器
{
squares = new ArrayList<>();
current = null;
addMouseListener(new MouseHandler());
addMouseMotionListener(new MouseMotionHandler());
}
public Dimension getPreferredSize()
{
return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
}
public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
var g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
//画出所有方块
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
g2.draw(r);
}
/**
* Finds the first square containing a point.
* @param p a point
* @return the first square that contains p
*/
public Rectangle2D find(Point2D p)
{
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
{
if (r.contains(p)) return r;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a square to the collection.
* @param p the center of the square
*/
public void add(Point2D p)
{
double x = p.getX();
double y = p.getY();
current = new Rectangle2D.Double(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2,
SIDELENGTH, SIDELENGTH);
squares.add(current);
repaint();
}
/**
* Removes a square from the collection.
* @param s the square to remove
*/
public void remove(Rectangle2D s)
{
if (s == null) return;
if (s == current) current = null;
squares.remove(s);
repaint();
}
private class MouseHandler extends MouseAdapter
{
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果光标不在正方形内,则添加一个新的正方形
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current == null) add(event.getPoint());
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果双击,则删除当前方块
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current != null && event.getClickCount() >= 2) remove(current);
}
}
private class MouseMotionHandler implements MouseMotionListener
{
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果鼠标指针在内部,则将其设置为十字线
if (find(event.getPoint()) == null) setCursor(Cursor.getDefaultCursor());
else setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.CROSSHAIR_CURSOR));
}
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent event)
{
if (current != null)
{
int x = event.getX();
int y = event.getY();
// 拖动当前矩形到(x, y)的中心
current.setFrame(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2, SIDELENGTH, SIDELENGTH);
repaint();
}
}
}
}
运行结果:

实验2:结对编程练习
利用班级名单文件、文本框和按钮组件,设计一个有如下界面(图1)的点名器,要求用户点击开始按钮后在文本输入框随机显示2018级计算机科学与技术(1)班同学姓名,如图2所示,点击停止按钮后,文本输入框不再变换同学姓名,此同学则是被点到的同学姓名,如图3所示。


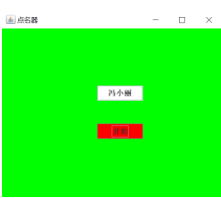
图一 图二 图三
代码如下:
package chart13;
import java.util.*;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//serialVersionUID适用于Java的序列化机制,简单来说,Java的序列化机制是通过判断类的
private JButton but ;
private JButton show;
private static boolean flag = true;
public static void main(String arguments []) {
new ButtonFrame();
}
public ButtonFrame(){
but = new JButton("START");//创建一个“开始”按钮
but.setBounds(100,150,100,40);
show = new JButton("随机点名");//创建一个“随机点名”按钮
show.setBounds(80,80,180,30);
add(but);//将按钮添加到面板中
add(show);
setLayout(null);
setVisible(true);//面板的可视化处理
setResizable(false);
setBounds(100,100,300,300);
this.getContentPane().setBackground(Color.black);//面板背景色为白色
setTitle("随机点名");//设置框架标题
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭该面板
but.addActionListener(this);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
int i=0;
String names[]=new String[50];//创建一个数组,大小为50
try {
Scanner in=new Scanner(new File("D:\\student.txt"));//将文件写入程序
while(in.hasNextLine())
{
names[i]=in.nextLine();//读取文件,遍历全班姓名
i++;
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();//异常处理
}
//点击开始后的操作
if(but.getText()=="START"){
show.setBackground(Color.GREEN);
flag=true;
new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(ButtonFrame.flag){
Random r = new Random(); //随机点名
int i= r.nextInt(43);
show.setText(names[i]);
}
}
}.start();
but.setText("STOP");
but.setBackground(Color.BLUE);
}
else if(but.getText()=="STOP"){
flag = false;
but.setText("START");
but.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
show.setBackground(Color.magenta);
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
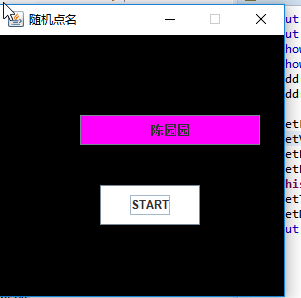
实验总结:
对于本节课的内容,我觉得java很神奇,可以通过写代码制作不同的窗口类型,也学习了好多关于事件处理的知识,通过前三个代码,也了解到了通过不同的方法来控制窗口页面的颜色,以及通过匿名内部类和lambda表达式简化程序,在学长的细心教导之下,慢慢听懂了好多内容。也在课后自己看了一些课件上的预习知识。还有,就是结对编程方面,仍然有一些问题,希望老师和学长能详解一下,知识模块有点疏散,之后慢慢总结吧。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号