第三章:流
本章内容:
1. 什么是流
2. 集合与流
3. 中间操作和终端操作
3.1 什么是流
流是javaAPI的新成员,它允许你以声明式方式处理集合数据(通过查询语句来表达,类似于mysql等数据库的查询sql)
public class Dish { private final String name; private final boolean vegetarian; private final int calories; private final Type type; public Dish(String name, boolean vegetarian, int calories, Type type) { this.name = name; this.vegetarian = vegetarian; this.calories = calories; this.type = type; } public String getName() { return name; } public boolean isVegetarian() { return vegetarian; } public int getCalories() { return calories; } public Type getType() { return type; } public enum Type { MEAT, FISH, OTHER } @Override public String toString() { return name; } public static final List<Dish> menu = Arrays.asList( new Dish("pork", false, 800, Dish.Type.MEAT), new Dish("beef", false, 700, Dish.Type.MEAT), new Dish("chicken", false, 400, Dish.Type.MEAT), new Dish("french fries", true, 530, Dish.Type.OTHER), new Dish("rice", true, 350, Dish.Type.OTHER), new Dish("season fruit", true, 120, Dish.Type.OTHER), new Dish("pizza", true, 550, Dish.Type.OTHER), new Dish("prawns", false, 400, Dish.Type.FISH), new Dish("salmon", false, 450, Dish.Type.FISH)); }
现在有这么一个需求:返回低热量(卡路里小于400)的菜肴名称,并按照卡路里排序
之前写法(java7)
public static List<String> getLowCaloricDishesNamesInJava7(List<Dish> dishes){ List<Dish> lowCaloricDishes = new ArrayList<>(); for(Dish d: dishes){ if(d.getCalories() < 400){ lowCaloricDishes.add(d); } } List<String> lowCaloricDishesName = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.sort(lowCaloricDishes, new Comparator<Dish>() { public int compare(Dish d1, Dish d2){ return Integer.compare(d1.getCalories(), d2.getCalories()); } }); for(Dish d: lowCaloricDishes){ lowCaloricDishesName.add(d.getName()); } return lowCaloricDishesName; }
之后(java8)
import static java.util.Comparator.comparing;
import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList;
//import static java.util.Comparator.*;
//import static java.util.stream.Collectors.*;
public static List<String> getLowCaloricDishesNamesInJava8(List<Dish> dishes){ return dishes.stream()//将集合转化成流 .filter(d -> d.getCalories() < 400)// 选出低于400卡路里的菜肴 .sorted(comparing(Dish::getCalories))// 按照卡路里排序 .map(Dish::getName)// 提取菜肴的名称 .collect(toList());// 将所有的名称保存在List中 }
显而易见的好处:
1. 代码是声明性方式写的:说明想要完成什么问不是说明如何实现一个操作(利用循环和if等控制流语句)
2. 你可以把几个基础的操作连接起来,来表达复杂的数据处理流水线(filter后面接上sorted、map和collect操作)
3.2 流简介
流的定义:从支持数据处理操作的源生成的元素序列。
List<String> collect = Dish.menu.stream().filter(d -> d.getCalories() > 300) .map(Dish::getName) .limit(3) .collect(toList());
1. filter:接受Lambda,从流中排除某些元素
2. map:接受一个Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息
3. limit:截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量
4. collect:将流转换为其他形式
3.2.1 只能遍历一次
流只能遍历一次,准确的来说,流只能被消费一次。
List<String> title = Arrays.asList("java8", "in", "Action");
Stream<String> stream = title.stream();
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
// stream.forEach(System.out::println); // 再次执行将报错
3.3 流操作
可以连接起来的流操作称为中间操作,关闭流的操作称为终端操作。
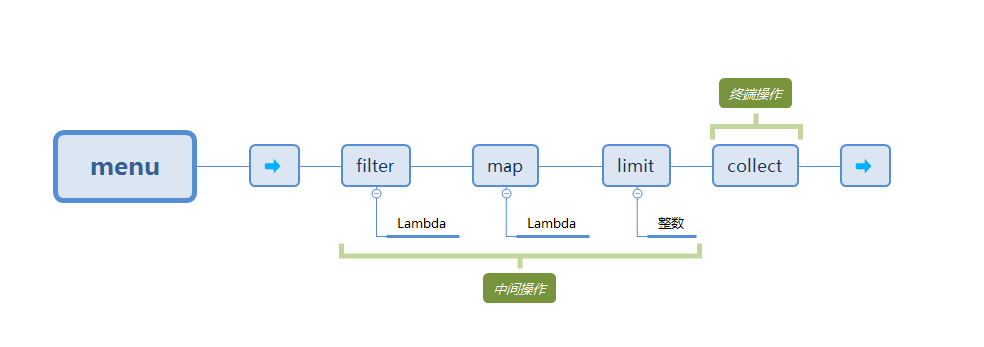
3.3.1 中间操作
诸如filter或sorted等中间操作会返回另外一个流。这让多个操作可以连接起来形成一个查询。
// 中间操作 collect = Dish.menu.stream().filter( d -> { System.out.println("filtering:" + d.getName()); return d.getCalories() > 300; }) .map(d -> { System.out.println("maping:" + d.getName()); return d.getName(); }) .limit(3) .collect(toList());
3.3.2 终端操作
终端操作会从流的流水线生成结果。其结果是任何不是流的值,比如List、Integer、甚至是void。例如forEach是一个返回void的终端操作
// 终端操作 Dish.menu.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
3.3.3 使用流
1. 一个数据源(如集合)来执行一个查询
2. 一个中间操作链,形成一条流的流水线
3. 一个终端操作,执行流水线,并能生成结果
备注:
摘自文献:《Java8实战》(中文版)《Java8 in Action》(英文版)
代码(GitHub地址): https://github.com/changlezhong/java8InAction
posted on 2018-06-04 07:30 changlezhong 阅读(134) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号