【java】javaSE知识梳理-反射机制
反射机制,即动态的处理类信息
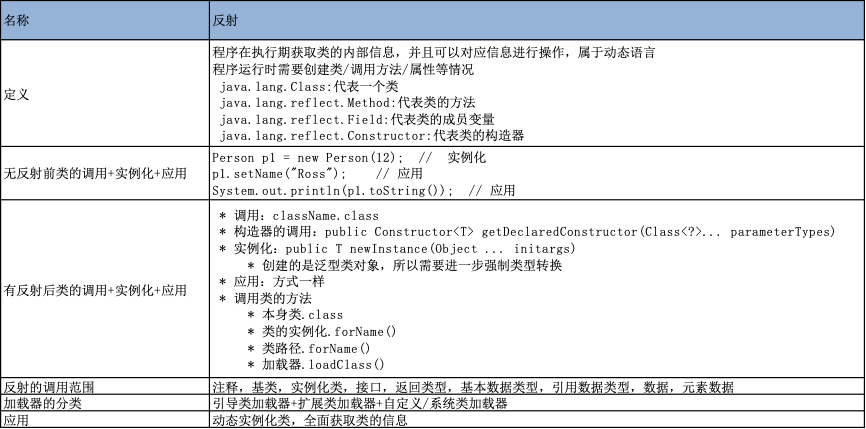
反射的应用

package javaLang.reflect.methods; import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-03 * @desc */ public class ReflectTest { /** * 对应Class实例可以是如下结构 */ @Test public void test4() { Class c1 = Object.class; // 类 Class c2 = Comparable.class; // 接口 Class c3 = String[].class; // 饮用数据类 Class c4 = ElementType.class; // 元素类型 Class c5 = Override.class; // 注解 Class c6 = int.class; // 基本数据类型 Class c7 = void.class; // 数据返回类型 Class c8 = Class.class; // 基类 Class c9 = Object.class; int[] i = new int[12]; Class c10 = i.getClass(); // 数组类 } /** * 关于java.lang.Class类的理解 * 1.类的加载过程: * 程序经过javac.exe命令以后,会生成一个或多个字节码文件(.class结尾)。 * 接着我们使用java.exe命令对某个字节码文件进行解释运行。相当于将某个字节码文件 * 加载到内存中。此过程就称为类的加载。加载到内存中的类,我们就称为运行时类,此 * 运行时类,就作为Class的一个实例。 * 2.换句话说,Class的实例就对应着一个运行时类。 * 3.加载到内存中的运行时类,会缓存一定的时间。在此时间之内,我们可以通过不同的方式来获取此运行时类。 * 类的属性:.class * 类对象的方法:public final native Class<?> getClass() * 类的目录:public static Class<?> forName(String className) * 加载器:ReflectTest.class.getClassLoader() */ @Test public void test3() throws Exception{ // 1,通过类的属性调用类.class Class clazz = Person.class; System.out.println(clazz); // 2,通过对象调用类.getClass() Person person = new Person(); Class clazz1 = person.getClass(); System.out.println(clazz1); // 通过Class的静态方法调用类 Class clazz2 = Class.forName("javaLang.reflect.methods.Person"); System.out.println(clazz2); // 通过加载器classLoader调用类 ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectTest.class.getClassLoader(); Class clazz3 = classLoader.loadClass("javaLang.reflect.methods.Person"); System.out.println(clazz3); } /** * 有了反射之后的类的初始化+调用 * Class clazz = Person.class; * 获取构造函数 * public Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) * 实例化:public T newInstance(Object ... initargs) * 获取属性 * public Field getDeclaredField(String name) * 调用:public void set(Object obj, Object value) * 获取方法 * public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) * 调用:public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args),返回参数 * 私有类型访问 * public void setAccessible(boolean flag)-true */ @Test public void test2() throws Exception{ Class clazz = Person.class; // 通过反射创建Person对象:类+获取对应构造方法+实例化+强制类型转换 Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class,int.class); Object obj = cons.newInstance("Joey",43); Person p = (Person) obj; System.out.println(p.toString()); // 通过反射调用对象指定的属性+方法 Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age"); age.set(p,54); System.out.println(p.toString()); // Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name"); //IllegalAccessException // name.set(p,"Phoebe"); Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show"); show.invoke(p); // 通过反射,调用类中的私有结构-构造器+方法+属性 Constructor cons1 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class); cons1.setAccessible(true); Person p1 = (Person) cons1.newInstance("Rachel"); System.out.println(p1); Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name"); name.setAccessible(true); name.set(p1,"Monica"); System.out.println(p1); Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class); showNation.setAccessible(true); String nation = (String)showNation.invoke(p1, "中国"); System.out.println(nation); } // 反射之前,类的初始化+调用 @Test public void test1() { Person p1 = new Person("Ross",32); p1.age = 67; System.out.println(p1.toString()); p1.show(); } }
关联自定义类

package javaLang.reflect.methods; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-03 * @desc */ public class Person { private String name; public int age; @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } private Person(String name) { this.name = name; } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Person() { System.out.println("Person()"); } public void show() { System.out.println("你好,我是一个人"); } private String showNation(String nation) { System.out.println("我的国际是:" + nation); return nation; } }
使用反射动态创建类

package javaLang.reflect.methods; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Random; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc 通过反射创建对应的运行时类的对象 */ public class NewInstanceTest { //使用反射的动态性,实例化对象 @Test public void test2() throws Exception { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { int num = new Random().nextInt(3);//0,1,2 String classPath = ""; switch(num){ case 0: classPath = "java.util.Date"; break; case 1: classPath = "java.lang.Object"; break; case 2: classPath = "javaLang.reflect.methods.Person"; break; } Object obj = getInstance(classPath); System.out.println("i=" + i + ": " + obj); } } /* 创建一个指定类的对象。 classPath:指定类的全类名 */ public Object getInstance(String classPath) throws Exception { Class clazz = Class.forName(classPath); return clazz.newInstance(); } @Test public void test1() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException { Class<Person> clazz = Person.class; Person person = clazz.newInstance(); System.out.println(person); } }
加载器的应用-只能用扩展类+自定义加载器

package javaLang.reflect.methods; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Properties; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc */ public class ClassLoaderTest { /** * Properties:用来读取配置文件。 */ @Test public void test2() throws IOException { Properties properties = new Properties(); //方式一:FileInputStream流读取--默认地址在当前module下--不建议默认地址 // FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src///jdbc1.properties"); properties.load(fis); String user = properties.getProperty("user"); String password = properties.getProperty("password"); System.out.println("user = " + user + ",password = " + password); fis.close(); // 方式二:ClassLoader读取--默认地址在当前的src下 ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader(); InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("jdbc1.properties"); properties.load(is); String user1 = properties.getProperty("user"); String password1 = properties.getProperty("password"); System.out.println("user = " + user1 + ",password = " + password1); is.close(); } /** * 加载器分类 * 引导类:系统自动,核心模块类 * 扩展类:java.ext.jar下的jar库 * 自定义类-系统类:自己定义的类 */ @Test public void test1(){ // 自定义类-系统类 ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader(); // 自定义类加载器 System.out.println(classLoader); // 扩展类 ClassLoader classLoader1 = classLoader.getParent(); // 扩展类加载器 System.out.println(classLoader1); // 自定义类-系统类 ClassLoader classLoader2 = classLoader1.getParent(); // 系统类加载器 System.out.println(classLoader2); // 当前类使用的哪种加载器 ClassLoader classLoader3 = ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader(); System.out.println(classLoader3); } }
全面获取类的信息

package javaLang.reflect.other; import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import java.lang.reflect.*; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc */ public class ReflectionTest { Class clazz = Person.class; /** * 权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型1 形参名1,...) throws XxxException{} */ @Test public void testOther() throws Exception { Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); // Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); // Annotation[] declaredAnnotations = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotations(); // Constructor[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();// 接口 Package aPackage = clazz.getPackage();// 包名 Class superclass = clazz.getSuperclass();// 父类 Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass();// 泛型 System.out.println(aPackage); System.out.println(superclass); System.out.println(genericSuperclass); for (Method method:declaredMethods) { // 方法名 System.out.print(method.getName() + "\t"); // 注释 Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations(); for (Annotation annotation:annotations) { System.out.print("annotations:" + annotation + "\t"); } // 权限修饰符 System.out.print("modifier:" + Modifier.toString(method.getModifiers()) + "\t"); // 返回类型 System.out.print("returnType:" + method.getReturnType() + "\t"); // 参数变量 System.out.print("parameterTypes:"); Type[] parameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes(); for (Type para:parameterTypes) { System.out.print(para.getTypeName() + "\t"); } // 抛出的异常 System.out.print("exceptionTypes:"); Type[] exceptionTypes = method.getExceptionTypes(); for (Type exception:exceptionTypes) { System.out.print(exception.getTypeName() + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } } /** * 获取指定构造器 * 获取构造器-public:public Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) * 获取构造器-所有:public Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) * 实例化构造器:public T newInstance(Object ... initargs) */ @Test public void testConstructor() throws Exception { // 获取构造器-public Constructor constructor1 = clazz.getConstructor(); Person person1 = (Person) constructor1.newInstance(); System.out.println(person1.toString()); // 获取构造器-所有 Constructor constructor2 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class); constructor2.setAccessible(true); Person person2 = (Person) constructor2.newInstance("Ross"); System.out.println(person2.toString()); // 获取构造器-默认 Constructor constructor3 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,int.class); Person person3 = (Person) constructor3.newInstance("Rachel",12,43); System.out.println(person3.toString()); } /** * 获取方法 * 获取方法-public:public Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) * 获取方法-所有:public Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) * 方法调用:public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) * 返回类型Object是数据的变量 */ @Test public void testMethod() throws Exception { Person person = (Person)clazz.newInstance(); // 获取方法-public Method info = clazz.getMethod("info"); info.invoke(person); // 获取方法-所有 Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show",String.class); show.setAccessible(true); System.out.println(show.invoke(person,"China")); // 获取方法-所有-静态-invoke中的参数可以是基类 Method showDesc = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showDesc"); showDesc.setAccessible(true); System.out.println(showDesc.invoke(Person.class)); } /** * 获取属性 * 获取属性-public:public Field getField(String name) * 获取属性- 所有:public Field getDeclaredField(String name) * 赋值:public void set(Object obj, Object value) * 获取:public Object get(Object obj) * ** 私有化可访问:public void setAccessible(boolean flag) */ @Test public void testField() throws Exception{ Person person = (Person)clazz.newInstance(); Field id = clazz.getField("id"); // 只能获取类的public字段 id.set(person,123); System.out.println(person.id); System.out.println(id.get(person)); Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name"); // 可以获取一个类的所有字段. name.setAccessible(true); name.set(person,"Ross"); System.out.println(name.get(person)); } }

package javaLang.reflect.other; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc */ public class Person extends Creature<String> implements Comparable<String>,MyInterface{ private String name; int age; public int id; public Person() { } @MyAnnotation(value="abc") private Person(String name) { this.name = name; } Person(String name, int age, int id) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.id = id; } @MyAnnotation private String show(String nation){ System.out.println("我的国籍是:" + nation); return nation; } public String display(String interests,int age) throws NullPointerException,ClassCastException{ return interests + age; } @Override public void info() { System.out.println("我是一个人"); } @Override public int compareTo(String o) { return 0; } private static void showDesc(){ System.out.println("我是一个可爱的人"); } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", id=" + id + '}'; } }

package javaLang.reflect.other; import java.io.Serializable; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc */ public class Creature<T> implements Serializable { private char gender; public double weight; private void breath(){ System.out.println("生物呼吸"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("生物吃东西"); } }

package javaLang.reflect.other; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc */ public interface MyInterface { void info(); }

package javaLang.reflect.other; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.*; import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-06-06 * @desc */ @Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { String value() default "hello"; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号