【java】javaSE知识梳理-静态数组+动态数组(集合)
数组:同数据类型,同名称,一定顺序排列,编号[0,^]

数组声明+初始化

package javaUtil.arrays.constructor; import org.junit.Test; /** * @desc * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-23 */ public class ConstructorsTest { /** * 一维数 * // 静态初始化 * int arr1[] = {1,2,3}; * int arr2[] = new int[]{1,2,3}; * * // 动态初始化 * int arr3[] = new int[3]; * arr3[0] = 0; * arr3[1] = 0; * arr3[2] = 0; */ @Test public void test1() { // 静态初始化 int arr1[] = {1,2,3}; int arr2[] = new int[]{1,2,3}; // 动态初始化 int arr3[] = new int[3]; arr3[0] = 0; arr3[1] = 0; arr3[2] = 0; } /** * 二维数组 * 静态初始化 * int [][] arr1 = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8,9}}; * int[] arr2[] = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8,9}}; * 动态初始化 * int[][] arr3 = new int[3][4]; * int[][] arr4 = new int[3][]; * arr4[0] = new int[1]; * arr4[1] = new int[2]; * arr4[2] = new int[3]; */ @Test public void test2() { // 静态初始化 int [][] arr1 = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8,9}}; int[] arr2[] = {{1,2,3},{4,5},{6,7,8,9}}; // 动态初始化1 int[][] arr3 = new int[3][4]; for (int i = 0; i < arr3.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < arr3[i].length ; j++) { arr3[i][j] = i*j; } } // 动态初始化2 int[][] arr4 = new int[3][]; arr4[0] = new int[1]; arr4[1] = new int[2]; arr4[2] = new int[3]; } }
java.util.Arrays类的使用

package javaUtil.arrays.methods; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @desc * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-23 */ public class MethodsTest { int[] arr1 = new int[3]; int[][] arr2 = new int[3][]; /** * 数组遍历 */ @Test public void iterator() { for (int arr:arr1) { System.out.println(arr); } for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { for (int arr:arr2[i]) { System.out.println(arr); } } } /** * java.util.Arrays函数 * public boolean equals(Object obj) : 是否相等 * public static void fill(int[] a, int val):所有的下标都赋值 * public String toString():?+哈希值 * arr1.length:数组的长度 * public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key):key所在的位置 */ @Test public void testMethods() { System.out.println(arr1.equals(arr2)); Arrays.fill(arr1,43); System.out.println(arr1.toString()); System.out.println(arr1.length); Arrays.sort(arr1); Arrays.binarySearch(arr1,12); } @Before public void before() { for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) { arr1[i] = i; } for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { arr2[i] = new int[i]; for (int j = 0; j < arr2[i].length; j++) { arr2[i][j] = i * j; } } } }
集合是静态数组的延伸
列表和接口如下:
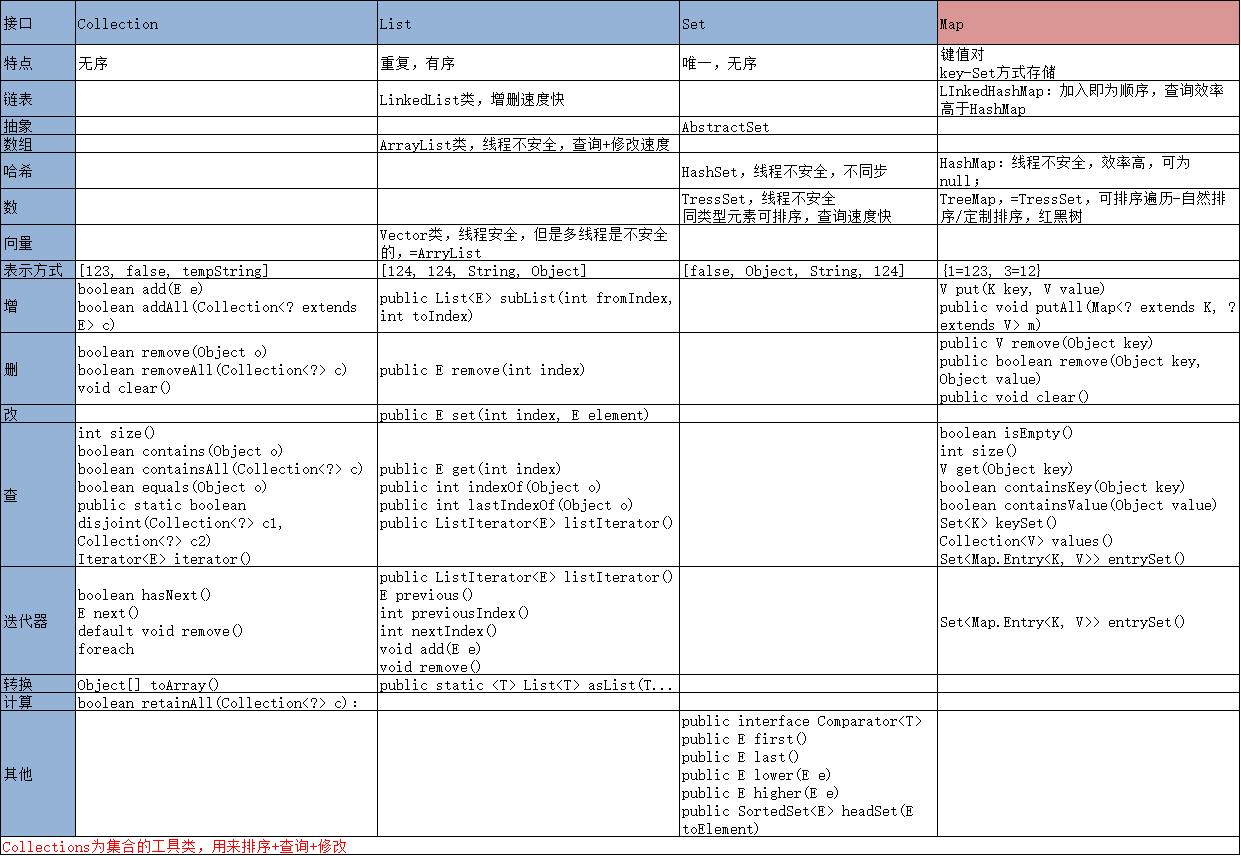
Interface Collection<E>接口

import org.junit.Test; import java.util.*; /** * Collection 方法 * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); /** * <p>addition:<pre> * boolean add(E e) * boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) * </pre> */ @Test public void addTest() { coll.add("123Temp"); coll1.addAll(coll); Iterator iterator = coll1.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } /** * <p>deletion:<pre> * boolean remove(Object o) * boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) * void clear()</pre> */ @Test public void deleTest() { coll.add(123); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); System.out.println(coll1); coll1.remove(new String("tempString")); coll1.remove(true); coll1.removeAll(coll); System.out.println(coll1); coll.clear(); System.out.println(coll); } /** * <p>modify:<pre></pre> */ @Test public void modifyTest() { coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); coll1.addAll(coll); System.out.println(coll1); } /** * <p>check:<pre> * boolean isEmpty() * int size() * boolean contains(Object o) * Iterator<E> iterator() * boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) * boolean equals(Object o) * boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) * public static boolean disjoint(Collection<?> c1, Collection<?> c2)</pre> */ @Test public void checkTest() { coll.add(123); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); System.out.println(coll1.isEmpty()); // 空? System.out.println(coll1.size()); // 长度 System.out.println(coll1.contains(true)); // 是否包含Object对象? System.out.println(coll1.containsAll(coll)); // 是否包含Collection对象? System.out.println(coll1.retainAll(coll)); // 获取两个集合的交集 System.out.println(coll1.equals(coll)); // 是否等于Object对象? System.out.println(Collections.disjoint(coll, coll1)); // 两个Collection对象有没有共同元素 } /** * <p>conversion:<pre> * Object[] toArray() * public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a)</pre> */ @Test public void converTest() { Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); System.out.println(coll1); Object[] objs = coll1.toArray(); // 集合->数组 for (Object obj:objs) { System.out.println(obj); } List list = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"AA", "BB", "CC"}); // 数组 -> 集合 System.out.println(list); } }
Interface List<E>接口

package javaUtil.list.method; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.*; /** * <p>List 有序可重复集合,序列 * @author ChenDan */ public class Methods { ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); Collection coll = new ArrayList(); /** * <p>addition <pre> * public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):获取集合中的子集合 * </pre> */ @Test public void addTest() { list.add(0,124); list.add(false); list.add("String"); list.add(3,124); list.add(new String("Object")); list.addAll(coll); System.out.println(list); List list1 = list.subList(1,4); // 获取集合中的部分元素 System.out.println(list1); } /** * <p>deletion <pre> * public E remove(int index):指定index元素删除 * </pre> */ @Test public void deleTest() { list.add(124); System.out.println(list); list.remove(0); // 指定index元素删除 } /** * <p>modify <pre> * public E set(int index, E element):指定index位置元素替换为element * </pre> */ @Test public void modifyTest() { list.add(124); list.add(1,124); list.add(false); list.add("String"); list.add(new String("Object")); System.out.println(list); list.set(1,123); System.out.println(list); } /** * <p>check <pre> * public E get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素 * public int indexOf(Object o):首次出现o对象的集合内的位置 * public int lastIndexOf(Object o):最后一次出现o对象的集合内的位置 * public ListIterator<E> listIterator():集合迭代器 * </pre> */ @Test public void checkTest() { list.add(124); list.add(1,124); list.add(false); list.add("String"); list.add(new String("Object")); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { // 长度 System.out.println(list.get(i)); // 获取1 } System.out.println(list.indexOf(124)); // 首次出现的位置 System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(124)); // 最后一次出现的位置 ListIterator listIterator = list.listIterator(); // 集合迭代器 while(listIterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(listIterator.next()); } } /** * <p>check <pre> * public ListIterator<E> listIterator():集合迭代器 * E previous():集合前一个元素 * int previousIndex():集合前一个元素的位置 * int nextIndex():集合下一个元素的位置 * void add(E e):下一个位置添加元素 * void remove():删除对应位置的元素 * </pre> */ @Test public void interatorTest() { list.add(124); list.add(1,124); list.add(false); list.add("String"); list.add(new String("Object")); ListIterator listIterator = list.listIterator(); // 集合迭代器 System.out.println(listIterator.nextIndex()); // 集合下一个元素的位置 listIterator.next(); System.out.println(listIterator.previous()); // 集合前一个元素 System.out.println(listIterator.previousIndex()); // 集合前一个元素的位置 System.out.println(list); listIterator.add("iterator"); // 下一个位置添加元素 System.out.println(list); listIterator.next(); listIterator.remove(); // 删除对应位置的元素 System.out.println(list); } /** * <p>ArrayList <pre> * Constructors * public ArrayList() * public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) * public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) * Methods--modify * public E set(int index, E element) * Methods--check * public boolean contains(Object o) * public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) * public boolean isEmpty() * public int size() * public E get(int index) * public int indexOf(Object o) * public int lastIndexOf(Object o) * public ListIterator<E> listIterator():集合迭代器 * </pre> */ @Test public void arrayListTest() { ArrayList arraylist = new ArrayList(); // 构建容量为10的空列表 ArrayList arraylist1 = new ArrayList(coll); // 构建以集合为基础的列表 ArrayList arraylist2 = new ArrayList(1); // 构建容量为1的空列表 arraylist.add(123); arraylist.add(true); arraylist.add(123); arraylist.add("123"); arraylist.set(1,"tmrp"); // 指定index位置元素替换为element System.out.println(arraylist.contains("123")); System.out.println(arraylist.containsAll(coll)); System.out.println(arraylist.isEmpty()); // 列表中是否为空 System.out.println(arraylist.size()); // 列表长度 System.out.println(arraylist); System.out.println(arraylist.get(0)); // 获取指定index位置的元素 System.out.println(arraylist.indexOf(123)); // 首次出现o对象的集合内的位置 System.out.println(arraylist.lastIndexOf(123)); // 最后一次出现o对象的集合内的位置 System.out.println(arraylist.contains("123")); // 列表中是否包含o对象 System.out.println(arraylist.containsAll(coll)); // 列表中是否包含Collection对象 ListIterator listIterator = arraylist.listIterator(); while(listIterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(listIterator.next()); } System.out.println(arraylist); } /** * <p>linkedList <pre> * Constructors * public LinkedList() * public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) * Methods--additon * void add(int index, E element) * boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) * public void addFirst(E e) * public void addLast(E e) * Methods--deletion * public E remove() * public boolean remove(Object o) * public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) * public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) * public E remove(int index) * public E removeFirst() * public E removeLast() * </pre> */ @Test public void linkedListTest() { coll.add(true); coll.add('C'); coll.add(456); coll.add(new String[]{"AA", "BB", "tempString"}); LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(); // 创建空列表 LinkedList linkedList1 = new LinkedList(coll); // 创建以集合为基础的列表 linkedList.add(0,"AA"); // 列表index中加入element元素 linkedList.addAll(1,coll); // 列表index中加入Collection对象 linkedList.addFirst(true); // 列表首中加入e元素 linkedList.addLast(new String("money")); // 列表尾中加入e元素 System.out.println(linkedList); linkedList.remove(); // 删除列表首的元素 linkedList.remove(true); // 删除列表第一个出现的元素 linkedList.removeFirstOccurrence(true); // 删除列表第一个出现的元素 linkedList.removeLastOccurrence(true); // 删除列表最后一个出现的元素 linkedList.remove(1); // 删除index=1的元素 linkedList.removeFirst(); // 删除列表首的元素 linkedList.removeLast(); // 删除列表尾的元素 System.out.println(linkedList); // ListIterator listIterator = list.listIterator(); // while(listIterator.hasNext()){ // System.out.println(listIterator.next()); // } } }
Interface Set<E>接口

package javaUtil.set.method; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.*; /** * <p>Set接口<pre> * 继承了Collection集合接口,未扩展对应信息</pre> * <p>HashSet类<pre> * 具体化Set接口,未扩展对应信息</pre> * <p>TreeSet类<pre> * * 具体化Set接口,扩展对应信息,使得集合可排序</pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { Collection coll = new ArrayList(); Set set = new HashSet(); HashSet hashSet = new HashSet(); TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet(); TreeSet treeSet1 = new TreeSet(); /** * <p>TreeSet <pre> * 同类型元素, 自然排序;如果想定制排序,就重写Comparator * public interface Comparator<T> * public E first() * public E last() * public E lower(E e) * public E higher(E e) * public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) * </pre> */ @Test public void treeSetTest() { TreeSet<Integer> treeSet1 = new TreeSet<Integer>(new Comparator<Integer>() { @Override public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) { if(i1 instanceof Integer && i2 instanceof Integer) { Integer str1 = (Integer) i1; Integer str2 = (Integer) i2; return -Integer.compare(i1,i2); } throw new RuntimeException("数据类型不一致!"); } }); treeSet1.add(1); treeSet1.add(3); treeSet1.add(6); treeSet1.add(4); System.out.println(treeSet1); System.out.println(treeSet1.first()); // 集合中最低元素 System.out.println(treeSet1.last()); // 集合中最高元素 System.out.println(treeSet1.lower(3)); // 小于给定元素的最大元素 System.out.println(treeSet1.higher(3)); // 大于给定元素的最小元素 System.out.println(treeSet1.headSet(4)); // 小于于给定元素的子集合 } /** * <p>addition <pre> * 继承了Collection集合接口,未扩展对应信息 * 哈希函数怎么理解?? * </pre> */ @Test public void addTest() { set.add(124); set.add(124); set.add(false); set.add(new String("Object")); set.add(new User("Object",12)); // 自定义的类,需要重写hashCode+equal方法,、 set.add(new User("Object",12)); set.addAll(coll); System.out.println(set); Iterator iterator = set.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.print(iterator.hashCode() + ": "); System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } }
相关类

package javaUtil.set.method; import java.util.Objects; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-18 * @desc */ public class User { private String name; private int age; public User() { } public User(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; User user = (User) o; return age == user.age && Objects.equals(name, user.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, age); } }
Interface Map<K,V>接口

package javaUtil.map.method; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.*; /** * <p>Map接口<pre> * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 默认容量为16 * </pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { Map map = new HashMap(); // 默认容量为16,加载因子0.75,扩容的临界值16 * 0.75 >= 12 HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); LinkedHashMap linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap(); TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap(); /** * <p>addition <pre> * V put(K key, V value) * public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m)</pre> */ @Test public void addTest() { map.put("1","123"); hashMap.put("3","123"); hashMap.put("3","12"); hashMap.putAll(map); System.out.println(hashMap); } /** * <p>deletion <pre> * public V remove(Object key) * public boolean remove(Object key, Object value) * public void clear() * </pre> */ @Test public void deleTest() { hashMap.put("1","123"); hashMap.put("3","123"); hashMap.put("2","12"); System.out.println(hashMap); hashMap.remove("1"); System.out.println(hashMap); hashMap.remove("2","12"); hashMap.clear(); System.out.println(hashMap); System.out.println(hashMap.size()); } /** * <p>modify <pre> * V put(K key, V value) * </pre> */ @Test public void modifyTest() { map.put("1","65"); map.put("1","63"); // 修改 System.out.println(map); } /** * <p>check <pre> * boolean isEmpty() * int size() * V get(Object key) * boolean containsKey(Object key) * boolean containsValue(Object value) * Set<K> keySet() * Collection<V> values() * Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() ?? * </pre> */ @Test public void checkTest() { map.put("1","123"); map.put("3",false); map.put(2,12); // System.out.println(map); // System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); // 为空? // System.out.println(map.size()); // 长度 // System.out.println(map.get("2")); // 获取value值 // System.out.println(map.containsKey(2)); // 是否有key=2? // System.out.println(map.containsValue(2)); //是否有value=2? // // Set keys = map.keySet(); // 获取所有的key // System.out.println(keys); // Collection values = map.values(); // 获取所有的value // System.out.println(values); Set mappings = map.entrySet(); // 方式一:获取所有的key-value集合 System.out.println(mappings); for (Object mapping:mappings) { Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) mapping; System.out.println("Key是:" + entry.getKey() + ", Value是:" + entry.getValue()); } Set keySet = map.keySet(); // 方式二:获得key,根据key去找value Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { Object key = iterator.next(); Object value = map.get(key); System.out.println(key + ":" + value); } } }
-
java.util.Properties 类
-
![]() View Code
View Codepackage javaUtil.properties.method; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Properties; /** * <p>Properties<pre> * 处理属性文件 * </pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { /** * <p>handling <pre> * public String getProperty(String key) * </pre> */ @Test public void addTest() { FileInputStream fis = null; Properties pros = new Properties(); try { fis = new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"); pros.load(fis); String name = pros.getProperty("name"); String password = pros.getProperty("password"); String stringName = pros.getProperty("StringName"); System.out.println("name= " + name + ", password= " + password); System.out.println("stringName= " + stringName); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
java.util.Collections 类

package javaUtil.collections.method; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.*; /** * Collections类<pre> * 是Set,List,Map的工具类 * 排序+查询+修改 * </pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { List list = new ArrayList(); /** * <p>check:<pre> * </pre> */ @Test public void checkTest() { list.add(12); list.add(23); list.add(3); list.add(389); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(Collections.max(list)); // 最大值 System.out.println(Collections.min(list)); // 最小值 System.out.println(Collections.frequency(list,3)); // 某元素出现的次数 System.out.println(Collections.replaceAll(list,3,44)); // 替换 } /** * <p>sort:<pre> * public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator * public static void reverse(List<?> list) * public static void shuffle(List<?> list) * public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) * public static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) * </pre> */ @Test public void sortTest() { list.add(12); list.add(23); list.add(3); list.add(389); System.out.println(list); Collections.sort(list); // 同类型排序 Collections.reverse(list); // 反转 Collections.shuffle(list); // 随机排序 // Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Object>() { // }); // 自定义比较排序-省略 Collections.swap(list,2,1); // 交换元素 System.out.println(list); } }
迭代器,遍历集合:
Interface Iterator<E>接口

package javaUtil.interator; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.*; /** * <p>Interator迭代器 <pre> * boolean hasNext():是否可以迭代 * E next():下一个元素 * default void remove() * foreach</pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { /** * <p>遍历 <pre> * hasNext + next</pre> */ @Test public void test1(){ // 迭代遍历输出 Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); Iterator iterator = coll1.iterator(); // 方法一:无法确定是否完成 // System.out.println(iterator.next()); // System.out.println(iterator.next()); // 方法二:为什么不推荐? // for (int i = 0; i < coll1.size(); i++) { // System.out.println(iterator.next()); // } // 方法三:推荐 while(iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } /** * <p>错误表达 */ @Test public void test2() { // 错误的迭代方式 Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); Iterator iterator = coll1.iterator(); // 错误方式一:迭代器调用了一次,每次的next也是一次访问 while(iterator.next() != null) { System.out.println(iterator.next()); } // // 错误方式二:每调用一次iterator方法都得到一个新的迭代器 // while(coll1.iterator().hasNext()){ // System.out.println(iterator.next()); // } } /** * <p>deletion <pre> * remove</pre> */ @Test public void test3() { // 删除集合元素 Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); Iterator iterator = coll1.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { Object obj = iterator.next(); if("tempString".equals(obj)) { iterator.remove(); System.out.println(obj); } } iterator = coll1.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(iterator.next()); } } /** * <p>foreach */ @Test public void test4() { Collection coll1 = new ArrayList(); coll1.add(123); coll1.add(false); coll1.add(new String("tempString")); for (Object coll:coll1) { System.out.println(coll); } String[] strs = new String[]{"AA", "BB", "CC"}; for (String str:strs) { System.out.println(str); } } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号