【java】javaSE知识梳理-java常用类
比较器

自定义类比较,直接使用(跟常用类一样)

package javaUtil.comparable.method; import javaLang.comparator.method.Goods; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 比较器<pre> * Comparable接口 * 常用类直接调用现成的compare即可实现 * 如果不满意现有的比较器,可以自己调用对应接口,重写对应方法 * </pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { /** * <p>比较器(内比较器)<pre> * 自己定义类,将Comparable重写compare(obj)方法 * 重写规则:[< == >] [<0 =0 >0] * public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c)</pre> */ @Test public void test1() { Goods[] goods = new Goods[5]; for (int i = goods.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { goods[4 - i] = new Goods(Character.toString((char) ('A' + i)), i); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goods)); Arrays.sort(goods); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goods)); } }
自定义类,调用Comparable接口,重写compare方法

package javaLang.comparator.method; /** * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-16 * @desc */ public class Goods implements Comparable{ private String name; private double price; public Goods(){} public Goods(String name, double price) { this.name = name; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Goods{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", price=" + price + '}'; } @Override public int compareTo(Object o) { if(o instanceof Goods) { Goods goods = (Goods) o; if(this.price > goods.price) { return 1; }else if(this.price < goods.price){ return -1; }else{ return 0; } } throw new RuntimeException("传入数据类型不一致!"); } }
调用类比较

package javaLang.comparator.method; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.TreeSet; /** * 比较器<pre> * Comparator接口 * 该接口不能直接调用,而是创建Comparator对象,重写compare方法 * </pre> * @author ChenDan * @create 2021-05-15 */ public class Methods { /** * <p>实例化1 */ @Test public void test1(){ Comparator com = new Comparator() { @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { if(o1 instanceof Goods && o2 instanceof Goods) { Goods goods1 = (Goods) o1; Goods goods2 = (Goods) o2; return Double.compare(goods1.getPrice(),goods2.getPrice()); } throw new RuntimeException("数据类型不一致!"); } }; TreeSet set = new TreeSet(com); set.add(new Goods("apple",12.3)); set.add(new Goods("pear",32.3)); set.add(new Goods("peach",2.3)); System.out.println(set); } /** * <p>实例化2 */ @Test public void test2(){ Goods[] goods = new Goods[5]; for (int i = goods.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { goods[4 - i] = new Goods(Character.toString((char) ('A' + i)), i); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goods)); Arrays.sort(goods, new Comparator<Goods>() { @Override public int compare(Goods o1, Goods o2) { if(o1 instanceof Goods && o2 instanceof Goods){ Goods goods1 = (Goods)o1; Goods goods2 = (Goods)o2; if(goods1.getName().equals(goods2.getName())) { return -Double.compare(goods1.getPrice(),goods2.getPrice()); }else{ return -goods1.getName().compareTo(goods2.getName()); } } throw new RuntimeException("输入的数据类型不一致!"); } }); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goods)); } }
基本数据类
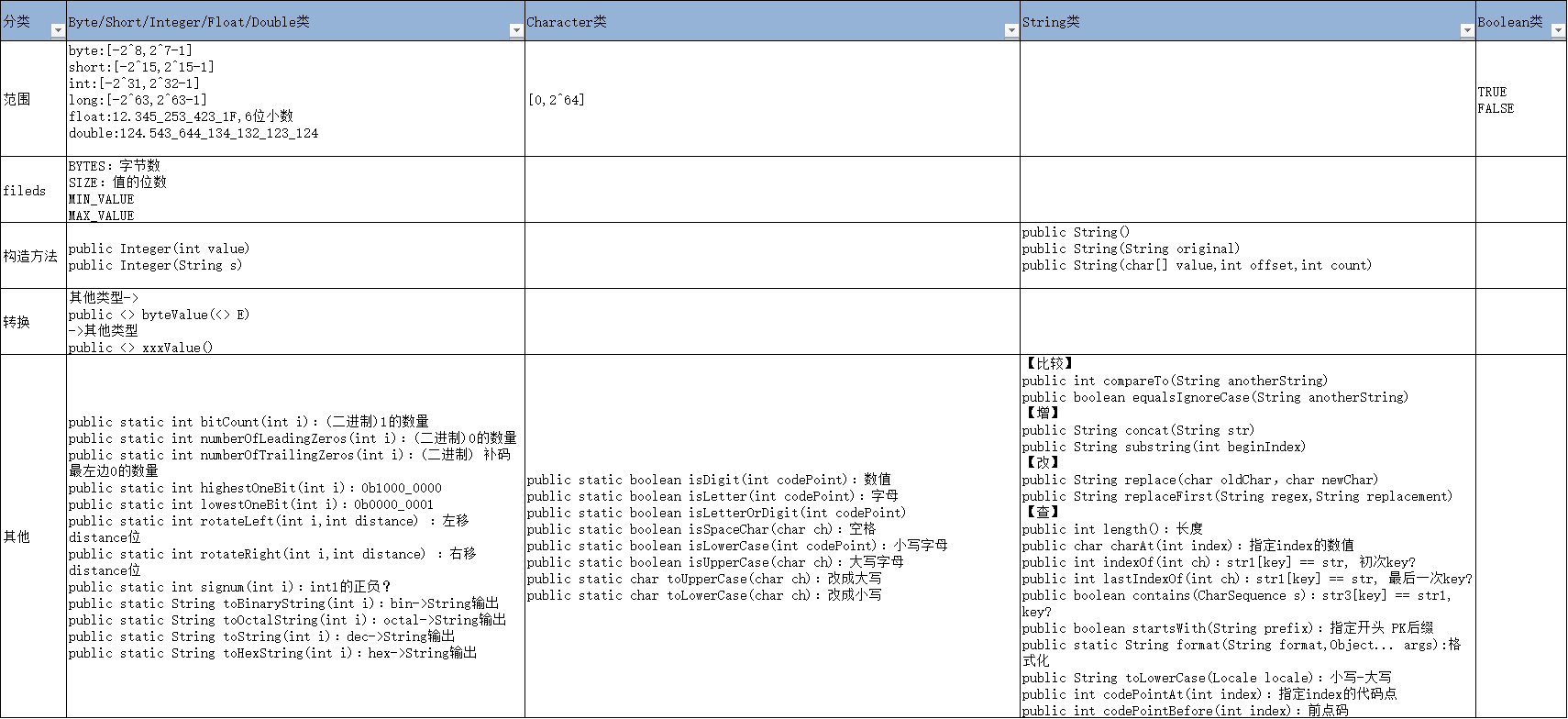
数据类型-基本数据类型

public class BaseDataType { /* * 数据类型-基本类型-整数型(byte-1/short-2/int-4/long-8)、浮点型(float-4/double-8)、布尔型(boolean) * 只声明不初始化不可使用(may not have been initialized) */ public static void main(String[] args) { byte b1 = -0b1000_0000 + 0b0111_1111; // 取值范围[-2^8,2^7-1] short s1 = -32768 + 32767; // 取值范围[-2^15,2^15-1] int i1 = -2147483648 + 2147483647; // 取值范围[-2^31,2^32-1] long l1 = -1; // 取值范围[-2^63,2^63-1] float f1 = 12.345_253_423_1F; // 输出12.345325,6位小数 double d1 = 124.543_644_134_132_123_124;// 输出124.543_644_134_132_12,14位小数 boolean bo1 = true; char c1 = 'C'; // 取值范围[0,2^64] b1 = (byte) (b1 + s1); // 高->低,需要强制类型转换,不然会报:Type mismatch: cannot convert from int to byte i1 = b1 + b1; // short,byte,int的加减,系统都会将其结果转换为int f1 = (float) d1 + b1; // 不同数据类型运算结果的类型为字节最大的那个类型 } }
java.lang.Byte/Short/Float/Double类

public class ReferenceDataTypeByte { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "127"; /* java.lang.Byte(引用数据类型) 字段 */ System.out.println(Byte.BYTES); // 1byte, 8bit,[-128,127] System.out.println(Byte.SIZE); System.out.println(Byte.MIN_VALUE); System.out.println(Byte.MAX_VALUE); /* java.lang.Byte 构造方法 */ Byte b1 = new Byte((byte) 12); Byte b2 = new Byte("124"); /* java.lang.Byte 方法-其他数据类型转换为Byte */ System.out.println(Byte.valueOf(b1)); // Byte->Byte System.out.println(Byte.valueOf(str)); // String->Byte /* java.lang.Byte 方法-其他(计数,找位置,比较,哈希) */ System.out.println(b1.compareTo(b2)); // b1>b2 ? [b1-b2] System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); // b1==b2 ? System.out.println(b1.hashCode()); // hashCode值 /* java.lang.Byte 方法-Byte以其他数据类型返回 */ System.out.println(b1.byteValue()); // Byte->byte System.out.println(b1.shortValue()); // Byte->short System.out.println(b1.intValue()); // Byte->int System.out.println(b1.longValue()); // Byte->long System.out.println(b1.floatValue()); // Byte->float System.out.println(b1.doubleValue()); // Byte->double System.out.println(Byte.parseByte(str)); // String->byte /* java.lang.Byte 方法-int数据类型(进制)以String的类型输出 */ System.out.println(Byte.toString(b1)); // bin->String输出 } }
java.lang.Integer类

public class ReferenceDataTypeInteger { public static void main(String[] args) { int bin = 0b0000_0001; int octal = 0110; int dec = 110; int hex = 0x10; String str = "999"; /* java.lang.Integer(引用数据类型) 字段 */ System.out.println(Integer.BYTES); // 4byte,32bit,取值范围[-2147483648, 2147483647] System.out.println(Integer.SIZE); System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE); /* java.lang.Integer 构造方法 */ Integer int1 = new Integer(90); // int/String 作为形参 Integer int2 = new Integer(str); /* java.lang.Integer 方法-其他(计数,找位置,比较,哈希) */ System.out.println(int1.bitCount(bin)); // (二进制)1的数量 System.out.println(int1.numberOfLeadingZeros(bin)); // (二进制)0的数量 System.out.println(int1.numberOfTrailingZeros(bin)); // (二进制) 补码最左边0的数量 System.out.println(int1.highestOneBit(bin)); // 0b1000_0000 System.out.println(int1.lowestOneBit(bin)); // 0b0000_0001 System.out.println(Integer.compare(int1, int2)); // int1>int2 ? [-1 0 1] [< = >] System.out.println(int1.equals(int2)); // int1 == int2 ? System.out.println(int1.hashCode()); // ihashCode值 System.out.println(int1.rotateLeft(bin, 1)); // 左移1位 System.out.println(int1.rotateRight(bin, 1)); // 右移1位 System.out.println(Integer.signum(int1)); // int1的正负? /* java.lang.Integer 方法-其他数据类型转换为Integer */ System.out.println(Integer.valueOf(bin)); // binary->Integer System.out.println(Integer.decode(str)); // String->Integer System.out.println(Integer.valueOf(str)); // Integer(String值) System.out.println(Integer.getInteger("sun.arch.data.model")); // 属性->Integer System.out.println(Integer.getInteger("90")); // String->Integer System.out.println(Integer.getInteger("sun.arch.data.modl", 5)); // 属性->Integer,属性无效->数值 /* java.lang.Integer 方法-Integer以其他数据类型返回 */ System.out.println(int1.byteValue()); // Integer->byte System.out.println(int1.shortValue()); // Integer->short System.out.println(int1.intValue()); // Integer->int System.out.println(int1.longValue()); // Integer->long System.out.println(int1.floatValue()); // Integer->float System.out.println(int1.doubleValue()); // Integer->double System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(str)); // Integer:String->int /* java.lang.Integer 方法-int数据类型(进制)以String的类型输出 */ System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(bin)); // bin->String输出 System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(octal)); // octal->String输出 System.out.println(Integer.toString(dec)); // dec->String输出 System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(hex)); // hex->String输出 } }
java.lang.Character类

public class ReferenceDataTypeCharacter { public static void main(String[] args) { // java.lang.Character(引用数据类型) 字段 System.out.println(Character.BYTES); // 2byte 16bit,[0,65535] System.out.println(Character.SIZE); System.out.println((int) Character.MIN_VALUE); System.out.println((int) Character.MAX_VALUE); System.out.println(Character.MIN_RADIX); // 基数:0-9,a-z=10+26,所以基数的范围在[2,36] System.out.println(Character.MAX_RADIX); // java.lang.Character(引用数据类型) 其他字段待理解 // java.lang.Character 构造方法 Character char1 = new Character('E'); Character char2 = new Character('D'); // java.lang.Character 方法 System.out.println(char1.charValue()); // char值? System.out.println(char1.compareTo(char2)); // char1>char2? System.out.println(char1.equals(char2)); // char1==char2? System.out.println(Character.isDigit(char1)); // 数值? System.out.println(Character.isLetter(char1)); // 字母? System.out.println(Character.isLetterOrDigit(char1)); // 字母/数值? System.out.println(Character.isSpaceChar(char1)); // 空格? System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase(char1)); // 小写字母? System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase(char1)); // 大写字母? System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase(char1)); // 改成小写字母 System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase(char1)); // 改成大写字母 System.out.println(Character.toString(char1)); // 输出字符 // java.lang.Character 继承的方法这个东西待理解 // 基数,代码点,代码单元,unicode这个东西待理解 } }
java.lang.String类

import java.util.Arrays; public class ReferenceDataTypeString { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "9"; char[] c1 = new char[] { '3', 'd', 'a' }; char[] c2 = new char[6]; /* java.lang.String 构造方法 */ String str1 = new String(str); String str2 = new String("3"); // 默认为空值 String str3 = new String("3ds4vf*dd32jjb*3ds4vf"); // 默认为空值 System.out.println(str1); System.out.println(str2); /* java.lang.String 方法-str1,str2比较 */ System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); // str1<str2 ? [str2 str1 str1] [< = >] System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2)); // str1<str2 && 忽略大小写 ? [str2 str1 str1] [< = >] System.out.println(str1.equals(str2)); // str1==str2 ? System.out.println(str1.concat(str2)); // str1+str2 /* java.lang.String 方法-处理String信息 */ System.out.println(str1.hashCode()); // hashCode值 System.out.println(str1.charAt(0)); // str1[0] System.out.println(str3.indexOf(str, 0)); // str1[key] == str, 初次key? System.out.println(str3.lastIndexOf(str)); // str1[key] == str, 最后一次key? System.out.println(str3.contains(str1)); // str3[key] == str1, key? System.out.println(str3.startsWith(str1)); // str3[key] == str1, key==0? System.out.println(str3.endsWith(str1)); // str3[key] == str1, key==str3.length? System.out.println(str3.substring(0, 4)); // str3[0,4] System.out.println(str3.length()); // str3.length System.out.println(str3.isEmpty()); // str3 == null? System.out.println(String.format("str3的长度为:%d", str3.length())); // format(str3.length) System.out.println(str3.replace('d', 'D')); // str3(d->D) System.out.println(str3.replaceFirst("vf", "vF")); // str3(第一个:"vf"->"vF") System.out.println(str3.replace("vf", "vF")); // str3(所有:"vf"->"vF") System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str3.split("\\*"))); // str3用"*"拆开 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c1)); // format(str3.length) System.out.println(String.format("str3的长度为:%d", str3.length())); // format(str3.length) System.out.println(str3.toLowerCase()); // 小写 System.out.println(str3.toUpperCase()); // 大写 /* java.lang.String 方法-String以其他数据类型返回 */ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str3.toCharArray())); // String->char[] /* java.lang.String 方法-其他数据类型转换为String */ System.out.println(String.valueOf((byte) 12)); // byte->String System.out.println(String.valueOf((byte) 123)); // short->String System.out.println(String.valueOf(123)); // int->String System.out.println(String.valueOf(123L)); // long->String System.out.println(String.valueOf(123.0432)); // float->String System.out.println(String.valueOf(123.123214798213928)); // double->String System.out.println(String.valueOf('A')); // char->String System.out.println(String.valueOf("hkjhdkwqd")); // String->String System.out.println(String.valueOf(str1)); // String->String } }
java.lang.Boolean类

public class BooleanTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Boolean b = false; /* java.lang.Boolean(引用数据类型) 字段 */ System.out.println(Boolean.TYPE); // 1Boolean true false System.out.println(Boolean.TRUE); System.out.println(Boolean.FALSE); /* java.lang.Boolean 构造方法 */ Boolean b1 = new Boolean(true); Boolean b2 = new Boolean("false"); /* java.lang.Boolean 方法-其他(计数,找位置,比较,哈希) */ System.out.println(b1.compareTo(b2)); // b1>b2 ? [1 0 1] [> = <] System.out.println(b1.equals(b2)); // b1==b2 ? System.out.println(b1.hashCode()); // hashCode值 /* java.lang.Boolean 方法-其他数据类型转换为Boolean */ System.out.println(b.booleanValue()); // Boolean->Boolean System.out.println(Boolean.valueOf(true)); // Boolean->Boolean System.out.println(Boolean.getBoolean("false")); // String->Boolean System.out.println(Boolean.valueOf("false")); // String->Boolean /* java.lang.Boolean 方法-boolean数据类型(进制)以String的类型输出 */ System.out.println(Boolean.toString(b1)); // bin->String输出 } }
基础类
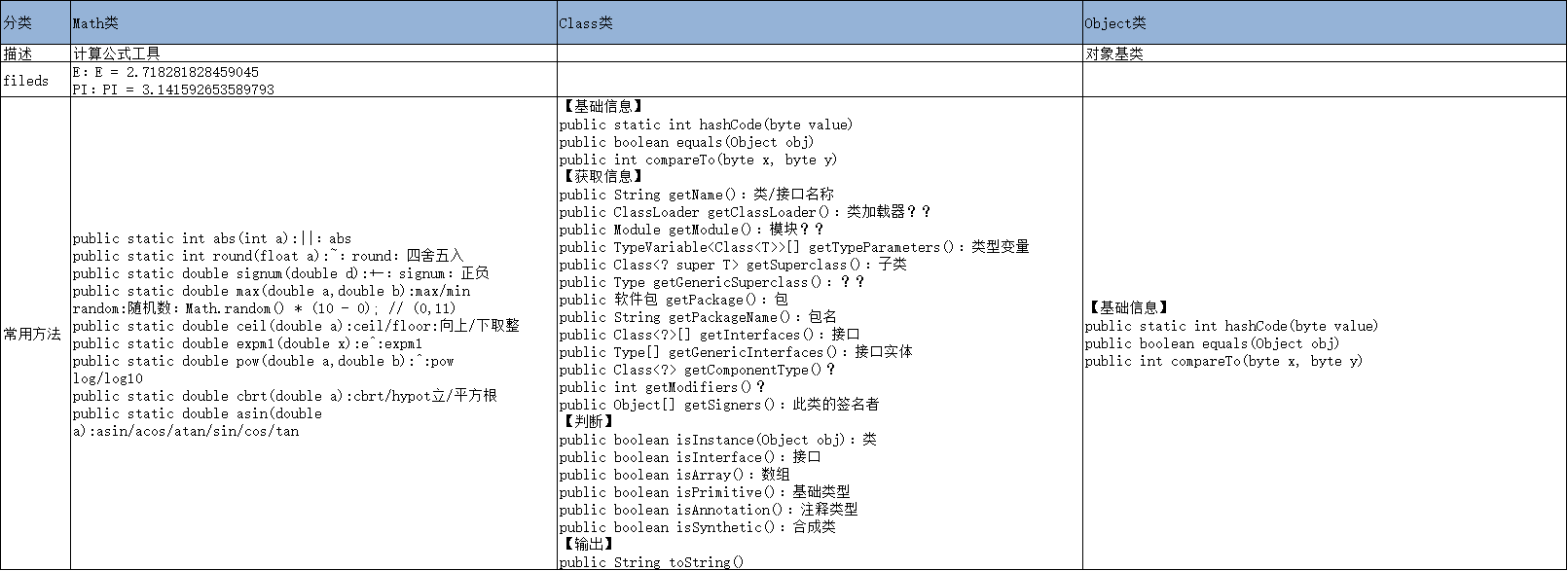
java.lang.Math类

public class MathTest { public static void main(String[] args) { int i1 = 2; float f1 = 0.5F; double d1 = 12.43; // java.lang.Math 字段 System.out.println(Math.E); // E = 2.718281828459045 System.out.println(Math.PI); // PI = 3.141592653589793 // java.lang.Math 方法 System.out.println(Math.abs(i1)); // || System.out.println(Math.round(f1)); // 四舍五入 System.out.println(Math.signum(f1)); // 正负? System.out.println(Math.max(i1, d1)); // max System.out.println(Math.min(i1, d1)); // min System.out.println(Math.random() * (10 - 0)); // (0,11) System.out.println(Math.ceil(f1)); // 向上取整 System.out.println(Math.floor(d1)); // 向下取整 System.out.println(Math.expm1(d1)); // e^x-1 System.out.println(Math.pow(i1, d1)); // x^y System.out.println(Math.log(d1)); // loge(d1) System.out.println(Math.log10(d1)); // log10(d1) System.out.println(Math.cbrt(f1)); // f1立方根 System.out.println(Math.hypot(f1, f1)); // 平方根 System.out.println(Math.sqrt(f1)); // 平方根 System.out.println(Math.ulp(f1)); // ?? System.out.println(Math.asin(f1)); // asin System.out.println(Math.acos(f1)); // acos System.out.println(Math.atan(f1)); // atan System.out.println(Math.sin(f1)); // sin System.out.println(Math.cos(f1)); // cos System.out.println(Math.tan(f1)); // tan } }
java.lang.Class类

import java.util.Arrays; public class ClassTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassTest ct1 = new ClassTest(); SubClass sct1 = new SubClass(); /* 创建Class对象 */ Class ct2 = ct1.getClass(); // getClass() Class sct2 = ct1.getClass(); Class<?> _class; _class = ClassTest.class; // T.class try { _class = Class.forName("java.lang.String"); // forName() } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } /* 常用方法 */ System.out.println("******"); System.out.println(ct2.getName()); // 类/接口名 System.out.println(ct2.getPackage()); // 类名 System.out.println(ct2.getTypeName()); // 类/接口名 System.out.println(sct2.asSubclass(ct2)); // 子类名称 System.out.println(ct2.getSimpleName()); // 类/接口简单名 // 类的修饰符 [1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024,2048] // [public,private,protected,static,final,synchronized,volatile,transient,native,interface,abstract,strict] System.out.println(ct2.getModifiers()); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ct2.getAnnotations())); // 注释 System.out.println(ct2.getProtectionDomain()); // ??? /* 还有一些方法待理解 */ } } class SubClass extends ClassTest { int field; public void method() { } }
java.lang.Object类

public class ObjectTest { public static void main(String[] args) { /* java.lang.Object 构造方法 */ Object obj = new Object(); Object obj1 = new Object(); /* java.lang.Object 方法-其他(计数,找位置,比较,哈希) */ System.out.println(obj.hashCode()); // hashCode值 /* java.lang.Object 方法-其他数据类型转换为Byte */ System.out.println(obj1.equals(obj1)); // obj1 == obj ? System.out.println(obj.getClass()); // Object /* java.lang.Object 方法-obj数据类型(进制)以String的类型输出 */ System.out.println(obj.toString()); // Object->String输出 } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号