Zephyr学习:DeviceTree学习
参考:
1.详解Zephyr设备树(DeviceTree)与驱动模型 - jayant97 - 博客园
2.Devicetree — Zephyr Project Documentation
硬件: 立创实战派开发板(esp32-s3)
看了大佬写的设备树教程,感觉收获颇丰,赶紧也来巩固一下,哈哈哈。
1. zephyr设备树构建流程
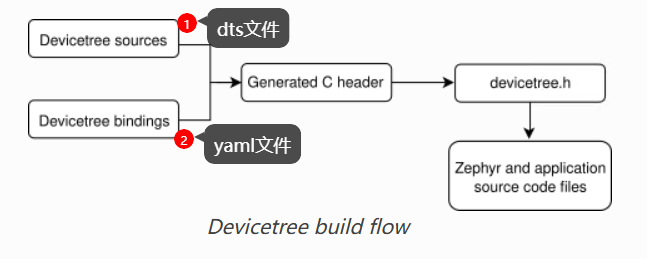
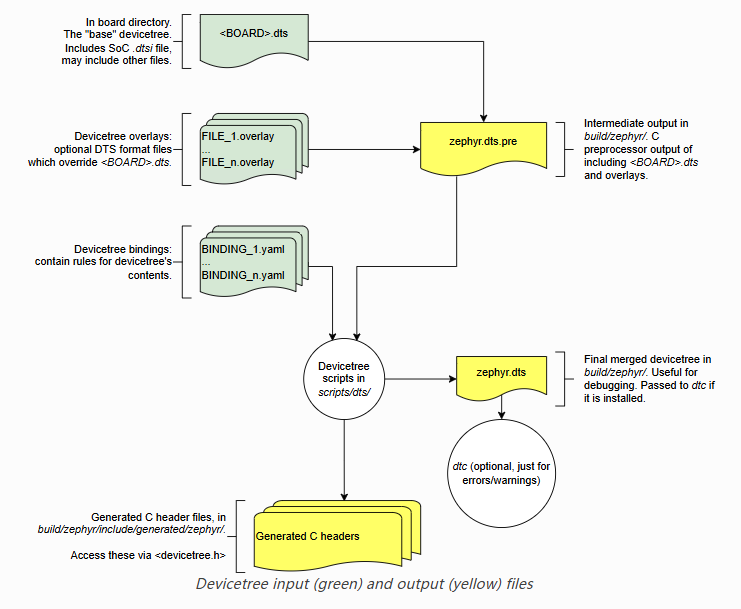
个人理解是我们在dts/overlay中写的硬件信息会通过yaml来确定和那个驱动绑定,然后生成C宏和执行驱动程序。
2. 设备树的结构和语法
参考文档:Syntax and structure — Zephyr Project Documentation
/dts-v1/; / { a-node { subnode_nodelabel: a-sub-node { foo = <3>; }; }; };
/ 表示根节点 ;
a-node 是根节点的一个子节点;
a-sub-node 是 a-node 的一个子节点;
foo 是 a-sub-node 的一个属性;
构建结构一般像这样,从上到下,树形结构:
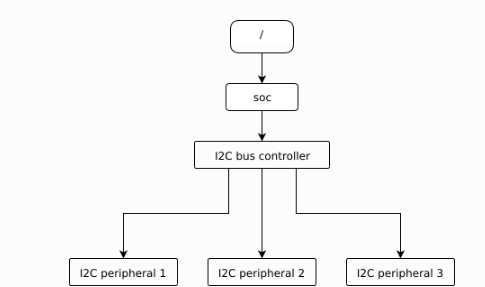
/dts-v1/; / { soc { i2c-bus-controller { i2c-peripheral-1 { }; i2c-peripheral-2 { }; i2c-peripheral-3 { }; }; }; };
一般和外设的地址相关联:
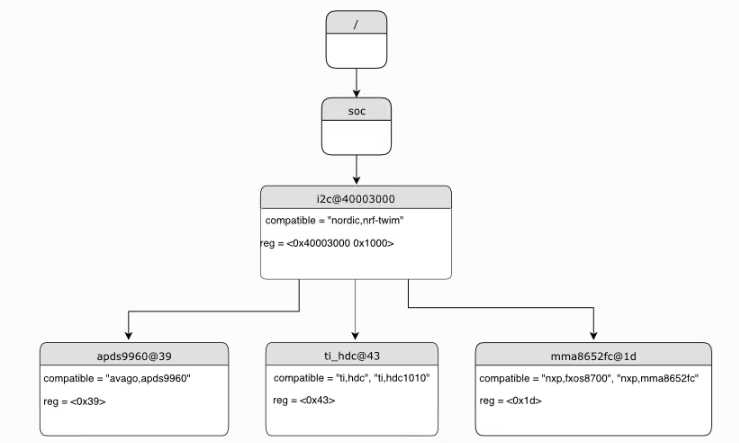
/dts-v1/; / { soc { i2c@40003000 { compatible = "nordic,nrf-twim"; reg = <0x40003000 0x1000>; apds9960@39 { compatible = "avago,apds9960"; reg = <0x39>; }; ti_hdc@43 { compatible = "ti,hdc", "ti,hdc1010"; reg = <0x43>; }; mma8652fc@1d { compatible = "nxp,fxos8700", "nxp,mma8652fc"; reg = <0x1d>; }; }; }; };
里面还有很多特殊的地方,需要用到的时候去看官方文档。
3. 设备树的绑定关系
比如我要定义一个按钮,DTS如下:
buttons { compatible = "gpio-keys"; button0: button_0 { gpios = <&gpio0 0 (GPIO_PULL_UP | GPIO_ACTIVE_HIGH)>; label = "BOOT Button"; zephyr,code = <INPUT_KEY_0>; }; };
该节点包含一个按钮0子节点,子节点控制一个IO,对应到 GPIO0 的 0 脚,配置成了上拉输入。通过 lable 知道是 Boot 按钮,对应到zephyr里面是第一个按钮。
compatible 属性是用来绑定硬件驱动的;可以知道这个按钮是绑定到 gpio-keys 这个驱动的,然后可以找到 yaml 文件和驱动文件。
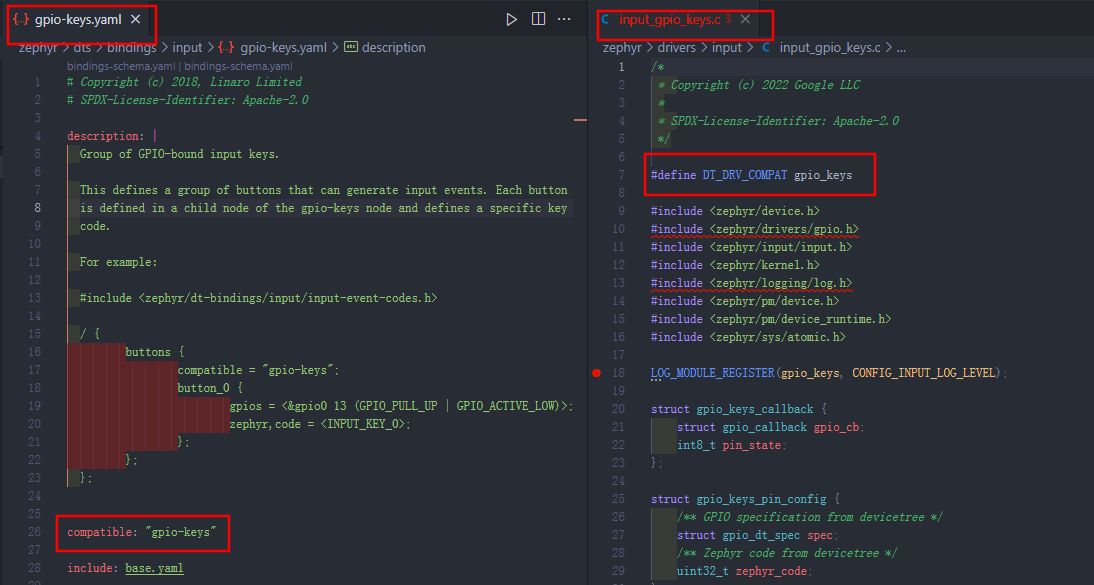
一般 yaml 文件和 compatible 名字是一样的, 驱动文件一般是把短横线变成下划线就可以了。
在gpio-keys.yaml 中可以看到:
compatible: "gpio-keys" include: base.yaml // 基于base.yaml properties: debounce-interval-ms: // 按键消抖时间 type: int default: 30 description: | Debouncing interval time in milliseconds. If not specified defaults to 30. polling-mode: // 使能轮询模式 type: boolean description: | Do not use interrupts for the key GPIOs, poll the pin periodically at the specified debounce-interval-ms instead. no-disconnect: // 断开引脚的功能,用于降低功耗 type: boolean description: | Do not try to disconnect the pin on suspend. Can be used if the GPIO controller does not support the GPIO_DISCONNECTED flag.
这些参数是可选的,这里没有配置这些参数。
child-binding: description: GPIO KEYS child node properties: gpios: // 配置按钮对应的gpio,上面是对应到GPIO0,上拉输入模式 type: phandle-array required: true // 这个选项是必须要有的 label: // 起个别名,上面是对应到boot按键 type: string description: Descriptive name of the key zephyr,code: // 对应到zephyr中key的编号,对应值0 type: int description: Key code to emit.
所以,在写dts的时候可以参考yaml的描述来写。
在驱动程序gpio_keys.c中可以看到以下的函数:
gpio_keys_poll_pin
gpio_keys_poll_pins
gpio_keys_change_deferred
gpio_keys_interrupt
gpio_keys_interrupt_configure
gpio_keys_init
gpio_keys_pm_action
这些函数实现了yaml中描述的消抖功能,轮询功能等等。
最终在初始化时调用宏函数GPIO_KEYS_INIT(i)执行初始化。
#define GPIO_KEYS_INIT(i) \ DT_INST_FOREACH_CHILD_STATUS_OKAY(i, GPIO_KEYS_CFG_CHECK); \ \ static const struct gpio_keys_pin_config gpio_keys_pin_config_##i[] = { \ DT_INST_FOREACH_CHILD_STATUS_OKAY_SEP(i, GPIO_KEYS_CFG_DEF, (,))}; \ \ static struct gpio_keys_pin_data \ gpio_keys_pin_data_##i[ARRAY_SIZE(gpio_keys_pin_config_##i)]; \ \ static const struct gpio_keys_config gpio_keys_config_##i = { \ .debounce_interval_ms = DT_INST_PROP(i, debounce_interval_ms), \ .num_keys = ARRAY_SIZE(gpio_keys_pin_config_##i), \ .pin_cfg = gpio_keys_pin_config_##i, \ .pin_data = gpio_keys_pin_data_##i, \ .handler = COND_CODE_1(DT_INST_PROP(i, polling_mode), \ (gpio_keys_poll_pins), (gpio_keys_change_deferred)), \ .polling_mode = DT_INST_PROP(i, polling_mode), \ .no_disconnect = DT_INST_PROP(i, no_disconnect), \ }; \ \ static struct gpio_keys_data gpio_keys_data_##i; \ \ PM_DEVICE_DT_INST_DEFINE(i, gpio_keys_pm_action); \ \ DEVICE_DT_INST_DEFINE(i, &gpio_keys_init, PM_DEVICE_DT_INST_GET(i), \ &gpio_keys_data_##i, &gpio_keys_config_##i, \ POST_KERNEL, CONFIG_INPUT_INIT_PRIORITY, NULL); DT_INST_FOREACH_STATUS_OKAY(GPIO_KEYS_INIT)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号