PTA第一阶段1~3次作业总结
1.前言
这三次作业的题量适中,总体上难度逐步上升,涵盖了基本的Java语法类的构造方法、方法的调用、参数传递、对象的构造与使用,以及选择结构,循环结构的运用
2.设计与分析
oop训练集一:
7-1计算年利率
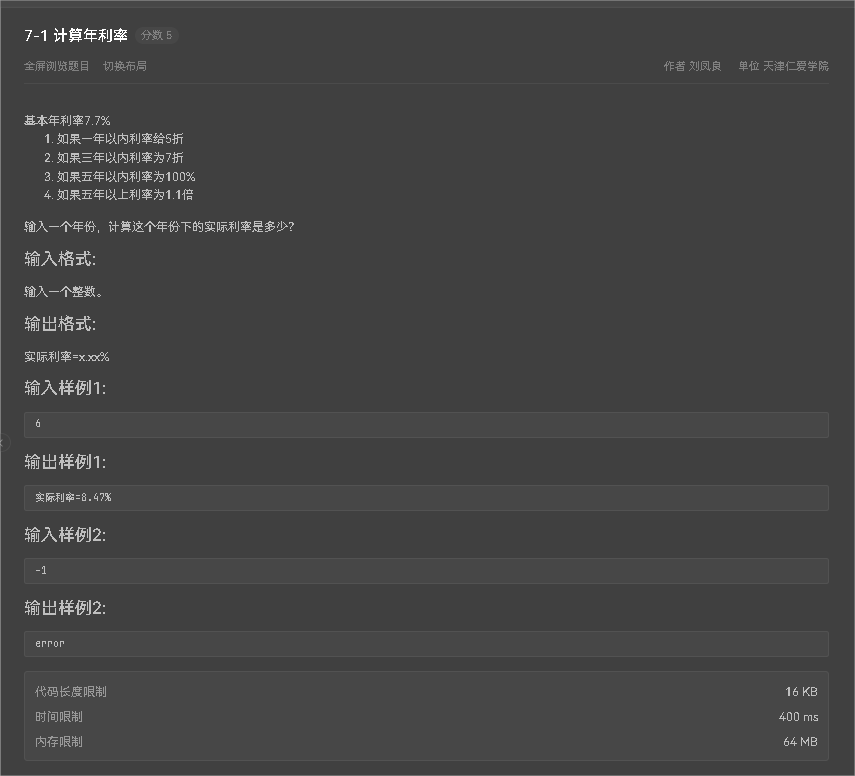
第一题较为简单只要掌握基本的输入输出方法,以及选择结构的运用就能轻松解题 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
double rate=7.7;
if(n<0)
System.out.printf("error");
else if(n<=1)
System.out.printf("实际利率=%.2f%%",rate*0.5);
else if(n<=3)
System.out.printf("实际利率=%.2f%%",rate*0.7);
else if(n<=5)
System.out.printf("实际利率=%.2f%%",rate);
else
System.out.printf("实际利率=%.2f%%",rate*1.1);
}
}
7-2身体质量指数(BMI)测算

第二题与第一题类似,只需注意边界条件即可轻松解题,源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main( String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
double bmi;
double hight;
double weight;
int flag=1;
weight=input.nextDouble();
hight=input.nextDouble();
if(weight>727||weight<0)
flag=0;
if(hight>2.72||hight<0)
flag=0;
bmi=(weight/hight)/hight;
if(flag==1){
if(bmi<18.5)
System.out.printf("thin");
else if(bmi<24)
System.out.printf("fit");
else if(bmi<28)
System.out.printf("overweight");
else
System.out.printf("fat");
}
if(flag==0)
System.out.printf("input out of range");
}
}
7-3 九九乘法表(双重循环)
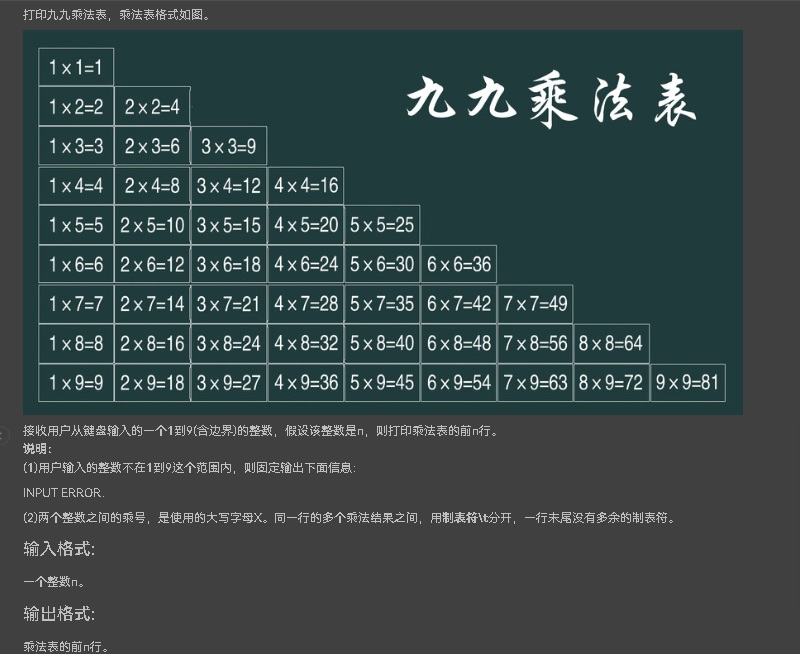
该题需掌握循环结构的使用,源码如下
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
int i,j;
if(n<1||n>9)
System.out.printf("INPUT ERROR.");
else{
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
if(j!=i)
System.out.printf("%dX%d=%d\t",i,j,i*j);
else
System.out.printf("%dX%d=%d",i,j,i*j);
}
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
7-4 快递运费

较为简单,只需掌握基本的输入输出方法,以及选择结构的运用就能轻松解题 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int fees;
double weight;
weight=input.nextDouble();
if(weight<20)
fees=(int)(12.0+(weight-1.0)*2.0+0.5);
else if(weight<60)
fees=(int)(39.0+(weight-20.0)*1.9+0.5);
else
fees=(int)(115.0+(weight-60.0)*1.3+0.5);
System.out.printf("%d",fees);
}
}
7-5 去掉重复的字符
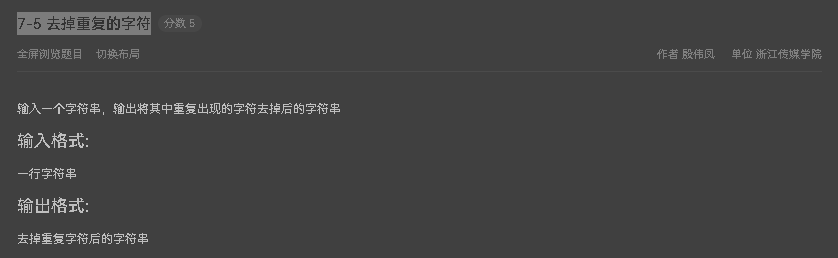
使用toCharArray将字符串转换为字符数组,再对数组进行操作即可 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
String str=input.nextLine();
int i,j,k;
int len=str.length();
char arr[]=str.toCharArray();
for(i=0;i<len-1;i++){
for(j=i+1;j<len;j++){
if(arr[i]==arr[j]){
for(k=j;k<len-1;k++){
arr[k]=arr[k+1];
}
len=len-1;
}
}
}
String str1=new String(arr,0,len);
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
7-6 统计一个子串在整串中出现的次数
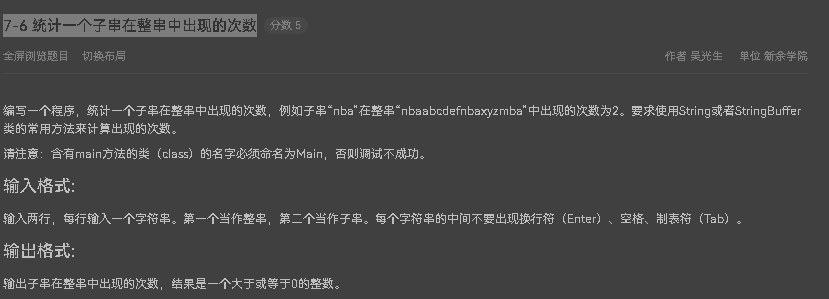
该题需掌握charAt()的用法,对字符串中的元素进行操作即可解题 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
String str1=input.nextLine();
String str2=input.nextLine();
int i,j;
int len=str2.length();
int s=0;
for(i=0;i<str1.length();i++){
if(str1.charAt(i)==str2.charAt(0)){
int flag=0;
for(j=1;j<len;j++)
if(str1.charAt(i+j)==str2.charAt(j))
flag++;
if(flag==len-1)
s++;
}
}
System.out.printf("%d",s);
}
}
7-7 有重复的数据

该题应先对输入的数据进行排序,在遍历数组比较相邻的数据是否相等,若存在相邻元素相等则说明存在重复数据 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
int[] arr=new int[n];
int flag=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i]=input.nextInt();
}
java.util.Arrays.sort(arr);
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
if(arr[i]==arr[i+1]){
flag=0;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
System.out.printf("YES");
else
System.out.printf("NO");
}
}
7-8 从一个字符串中移除包含在另一个字符串中的字符
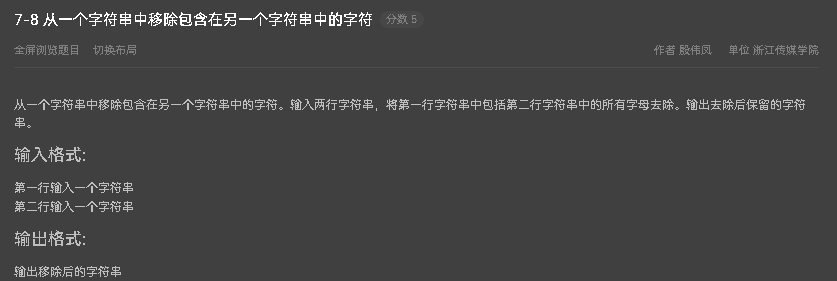
第5,6,7题的综合版 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
String str1=input.nextLine();
String str2=input.nextLine();
char arr1[]=str1.toCharArray();
char arr2[]=str2.toCharArray();
int len2=str2.length();
int len1=str1.length();
for(int i=0;i<len2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len1;j++){
if(arr2[i]==arr1[j]){
for(int k=j;k<len1-1;k++){
arr1[k]=arr1[k+1];
}
len1--;
j--;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<len1;i++)
System.out.printf("%c",arr1[i]);
}
}
7-9 Prime Numbers
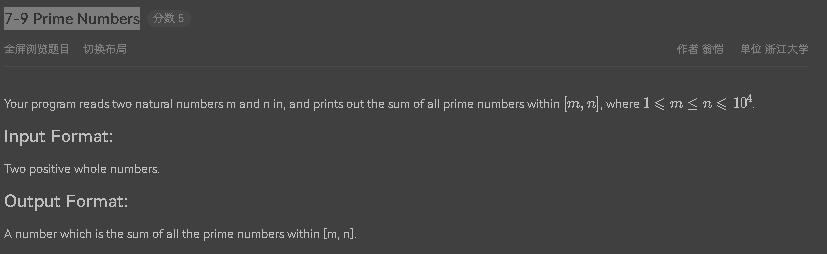
需要对方法的概念有初步的了解,并掌握基本的方法的写法 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int m=input.nextInt();
int n=input.nextInt();
int s=0;
for(int i=m;i<=n;i++){
if(is_prime(i)==1){
s+=i;
}
}
System.out.printf("%d",s);
}
public static int is_prime(int num){
int flag=1;
if(num==1)
flag=0;
int k=(int)Math.sqrt(num);
for(int i=2;i<=k;i++){
if(num%i==0){
flag=0;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
}
7-10 GPS数据处理
NMEA-0183协议是为了在不同的GPS(全球定位系统)导航设备中建立统一的BTCM(海事无线电技术委员会)标准,由美国国家海洋电子协会(NMEA-The National Marine Electronics Associa-tion)制定的一套通讯协议。GPS接收机根据 NMEA-0183协议的标准规范,将位置、速度等信息通过串口传送到PC机、PDA等设备。
NMEA-0183协议是GPS接收机应当遵守的标准协议,也是目前GPS接收机上使用最广泛的协议,大多数常见的GPS接收机、GPS数据处理软件、导航软件都遵守或者至少兼容这个协议。
NMEA-0183协议定义的语句非常多,但是常用的或者说兼容性最广的语句只有$GPGGA、$GPGSA、$GPGSV、$GPRMC、$GPVTG、$GPGLL等。
其中$GPRMC语句的格式如下:
$GPRMC,024813.640,A,3158.4608,N,11848.3737,E,10.05,324.27,150706,,,A*50
这里整条语句是一个文本行,行中以逗号“,”隔开各个字段,每个字段的大小(长度)不一,这里的示例只是一种可能,并不能认为字段的大小就如上述例句一样。
- 字段0:
$GPRMC,语句ID,表明该语句为Recommended Minimum Specific GPS/TRANSIT Data(RMC)推荐最小定位信息 - 字段1:UTC时间,hhmmss.sss格式
- 字段2:状态,A=定位,V=未定位
- 字段3:纬度ddmm.mmmm,度分格式(前导位数不足则补0)
- 字段4:纬度N(北纬)或S(南纬)
- 字段5:经度dddmm.mmmm,度分格式(前导位数不足则补0)
- 字段6:经度E(东经)或W(西经)
- 字段7:速度,节,Knots
- 字段8:方位角,度
- 字段9:UTC日期,DDMMYY格式
- 字段10:磁偏角,(000 - 180)度(前导位数不足则补0)
- 字段11:磁偏角方向,E=东W=西
- 字段16:校验值
这里,*为校验和识别符,其后面的两位数为校验和,代表了$和*之间所有字符(不包括这两个字符)的异或值的十六进制值。上面这条例句的校验和是十六进制的50,也就是十进制的80。
提示:^运算符的作用是异或。将$和*之间所有的字符做^运算(第一个字符和第二个字符异或,结果再和第三个字符异或,依此类推)之后的值对65536取余后的结果,应该和*后面的两个十六进制数字的值相等,否则的话说明这条语句在传输中 发生了错误。注意这个十六进制值中是会出现A-F的大写字母的。另外,在Java语言中,如果你需要的话,可以用Integer.parseInt(s)从String变量s中得到其所表达的整数数字;而Integer.parseInt(s, 16)从String变量s中得到其所表达 的十六进制数字
现在,你的程序要读入一系列GPS输出,其中包含$GPRMC,也包含其他语句。在数据的最后,有一行单独的END表示数据的结束。
你的程序要从中找出$GPRMC语句,计算校验和,找出其中校验正确,并且字段2表示已定位的语句,从中计算出时间,换算成北京时间。一次数据中会包含多条$GPRMC语句,以最后一条语句得到的北京时间作为结果输出。
你的程序一定会读到一条有效的$GPRMC语句。
输入格式:
多条GPS语句,每条均以回车换行结束。最后一行是END三个大写字母。
输出格式:
6位数时间,表达为:
hh:mm:ss
其中,hh是两位数的小时,不足两位时前面补0;mm是两位数的分钟,不足两位时前面补0;ss是两位数的秒,不足两位时前面补0。该题难度较大 需要对异或值的概念有深刻的理解,并掌握对字符串的处理技巧 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner inputScanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String strings;
int hh = 0, mm = 0, ss = 0;
while (true) {
strings = inputScanner.nextLine();
if (!strings.equals("END")) {
if (!strings.startsWith("$GPRMC")) {
continue;
}
int count = 0;
int k = 0;
for (k = 0; k < strings.length(); k++) {
if (strings.charAt(k) == ',' ) {
count++;
}
if (count == 2) {
break;
}
}
int sum = 0;
int j = 0;
if (strings.charAt(k+1) == 'A') {
for (j = 1; strings.charAt(j) != '*'; j++) {
sum ^= strings.charAt(j);
}
}else {
continue;
}
int check = Integer.parseInt(strings.substring(j + 1), 16);
if (check == sum%65536) {
hh = (int)(strings.charAt(7) - '0')*10 + (int)(strings.charAt(8) - '0');
mm = (int)(strings.charAt(9) - '0')*10 + (int)(strings.charAt(10) - '0');
ss = (int)(strings.charAt(11) - '0')*10 + (int)(strings.charAt(12) - '0');
}else {
continue;
}
}else{
hh = (hh + 8) % 24;
if (hh < 10) {
System.out.print("0");
}
System.out.print(hh +":"+ mm +":"+ ss);
break;
}
}
}
}
7-11 求定积分

该题看着挺复杂的,但实际上只要掌握定积分的概念以及算法则可以快速解答 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
double a=input.nextDouble();
double b=input.nextDouble();
double c=input.nextDouble();
double len=(b-a)/c;
a=a-len/2;
double s=0;
for(int i=1;i<=c;i++)
{
s+=len*(a+i*len)*(a+i*len);
}
System.out.printf("%.4f",s);
}
}
7-12 列出最简真分数序列

要掌握最小公倍数的求法(辗转相除法)即可轻松解题 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input =new Scanner(System.in);
int N=input.nextInt();
int t,a,b;
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
a=N;
b=i;
if(a%b==0)
;
else{
while(a%b!=0){
t=b;
b=a%b;
a=t;
}
}
if(b==1)
System.out.printf("%d/%d,",i,N);
}
}
}
oop训练集二
7-1 长度质量计量单位换算

该题较为简单注意输出格式即可 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double weight = input.nextDouble();
double len = input.nextDouble();
weight/=0.45359237;
len/=0.0254;
System.out.print((float)weight+" "+(float)len);
}
}
7-2 奇数求和
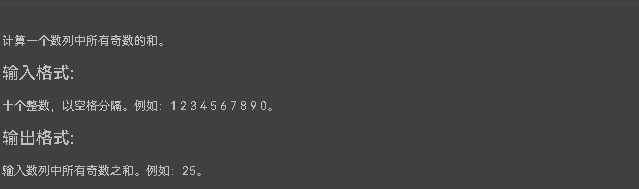
较为简单 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=10;
int[] arr=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
arr[i]=input.nextInt();
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
if(arr[i]%2==1||arr[i]%2==-1)
sum+=arr[i];
}
System.out.print(sum);
}
}
7-3 房产税费计算2022
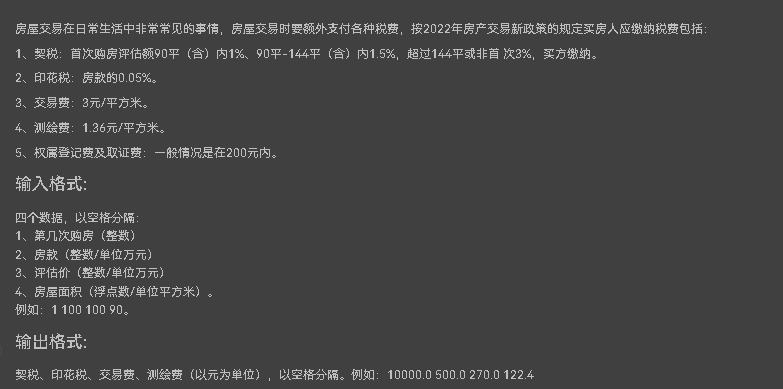
该题较为简单 注意输出时用强制类型转换为float型即可 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=input.nextInt();
int total=input.nextInt();
int e_price=input.nextInt();
float s=input.nextFloat();
double tax1,tax2,tax3,tax4;
if(n==1&&s<=90)
tax1=e_price*0.01*10000.0;
else if(n==1&&s<=144)
tax1=e_price*0.015*10000.0;
else
tax1=e_price*0.03*10000.0;
tax2=total*0.0005*10000.0;
tax3=3*s;
tax4=1.36*s;
System.out.print((float)tax1+" "+(float)tax2+" "+(float)tax3+" "+(float)tax4);
}
}
7-4 游戏角色选择

该题较为简单 只需掌握选择结构的运用即可 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int m=input.nextInt();
int n=input.nextInt();
if(m>4||m<1||n>3||n<1)
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
else{
if(m==1)
System.out.print("人类");
else if(m==2)
System.out.print("精灵");
else if(m==3)
System.out.print("兽人");
else if(m==4)
System.out.print("暗精灵");
System.out.print(" ");
if(n==1)
System.out.print("战士");
else if(n==2)
System.out.print("法师");
else if(n==3)
System.out.print("射手");
}
}
}
7-5 学号识别

程序解题思路上与上一题类似 ,但必上一题多了一个对输入数据的处理 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int num=input.nextInt();
int n=num;
int bit=0;
do{
n/=10;
bit+=1;
}while(n>0);
if(bit!=8){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
else{
int number;
int classroom;
int year;
int collage;
number=(num%100);
classroom=(num/100)%100;
collage=(num/10000)%100;
year=(num/1000000)%100;
if(collage!=1&&collage!=2&&collage!=3&&collage!=20){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else{
System.out.println("入学年份:"+(2000+year)+"年");
if(collage==1)
System.out.println("学院:"+"材料学院");
else if(collage==2)
System.out.println("学院:"+"机械学院");
else if(collage==3)
System.out.println("学院:"+"外语学院");
else
System.out.println("学院:"+"软件学院");
System.out.println("班级:"+classroom);
System.out.print("学号:");
System.out.printf("%02d",number);
}
}
}
}
7-6 巴比伦法求平方根近似值
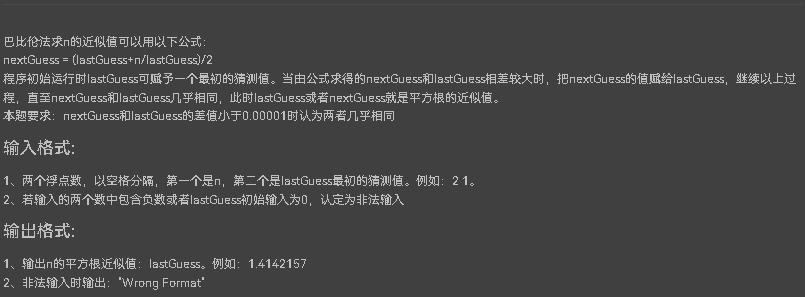
正确理解题目的意思以及巴比伦法求近似值即可完成求解 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
float n=input.nextFloat();
float lastGuess=input.nextFloat();
float nextGuess = (lastGuess+n/lastGuess)/2;
if(lastGuess<=0||n<=0){
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
}
else{
while(fab(lastGuess,nextGuess)>0.00001){
lastGuess=nextGuess;
nextGuess = (lastGuess+n/lastGuess)/2;
}
System.out.print(lastGuess);
}
}
public static float fab(float m,float n){
if(m-n>0)
return m-n;
else
return n-m;
}
}
7-7 二进制数值提取

该题较为简单 掌握charAt()的用法对字符串进行处理即可即可完成解答 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
String str=input.nextLine();
int n=str.length();
int flag=0;
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
if(str.charAt(i)=='-'&&str.charAt(i+1)=='1'){
flag=1;
j=i;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1){
for(int i=0;i<j;i++){
if(str.charAt(i)=='1'||str.charAt(i)=='0')
System.out.printf("%c",str.charAt(i));
}
}
else
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
7-8 判断三角形类型

要注意无法直接判定两个浮点数相等,应判断两个数的差小于某个范围 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
float a=input.nextFloat();
float b=input.nextFloat();
float c=input.nextFloat();
float temp=0;
if(a<1||a>200||b<1||b>200||c<1||c>200){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
else{
if(a>b){
temp=a;
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if(b>c){
temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
if(a>c){
temp=a;
a=c;
c=temp;
}
float x=a*a+b*b-c*c;
if(a+b<=c){
System.out.print("Not a triangle");
}
else{
if(a==b&&b==c)
System.out.print("Equilateral triangle");
else if(a==b||b==c){
if(Math.abs(x)<=0.0001)
System.out.print("Isosceles right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.print("Isosceles triangle");
}
else if(Math.abs(x)<=0.0001)
System.out.print("Right-angled triangle");
else
System.out.print("General triangle");
}
}
}
}
7-9求下一天

这里的处理技巧较为粗糙,下一次作业中用了数组存放每个月的天数简化了代码 本次作业的源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year=input.nextInt();
int month=input.nextInt();
int day=input.nextInt();
if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)){
nextDate(year,month,day);
}
else
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){
if(year<1820||year>2020)
return false;
if(month<1||month>12)
return false;
if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12){
if(day<1||day>31)
return false;
else
return true;
}
else if(month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11){
if(day<1||day>30)
return false;
else
return true;
}
else{
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if(day<1||day>29)
return false;
else
return true;
}
else{
if(day<1||day>28)
return false;
else
return true;
}
}
}
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day){
if(month==12&&day==31){
day=1;
month=1;
year+=1;
}
else if((month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10)&&day==31){
day=1;
month+=1;
}
else if((month==4||month==6||month==9||month==11)&&day==30){
day=1;
month+=1;
}
else if(month==2){
if(isLeapYear(year)){
if(day==29){
day=1;
month+=1;
}
else
day++;
}
else{
if(day==28){
day=1;
month+=1;
}
else
day++;
}
}
else
day+=1;
System.out.print("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day);
}
}
oop训练集三
7-1 创建圆形类

该题要求理解类的概念,掌握构造方法的技巧 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
class Circle{
private double radius=0;
public Circle(){
}
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return this.radius;
}
public double getArea(){
return this.radius*this.radius*Math.PI;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double r = input.nextDouble();
if(r>=0) {
Circle circle=new Circle(r);
System.out.print("The"+" "+"circle's"+" "+"radius"+" "+"is:");
System.out.printf("%.2f",circle.getRadius());
System.out.println();
System.out.print("The"+" "+"circle's"+" "+"area"+" "+"is:");
System.out.printf("%.2f",circle.getArea());
}
else{
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
7-2 创建账户类Account
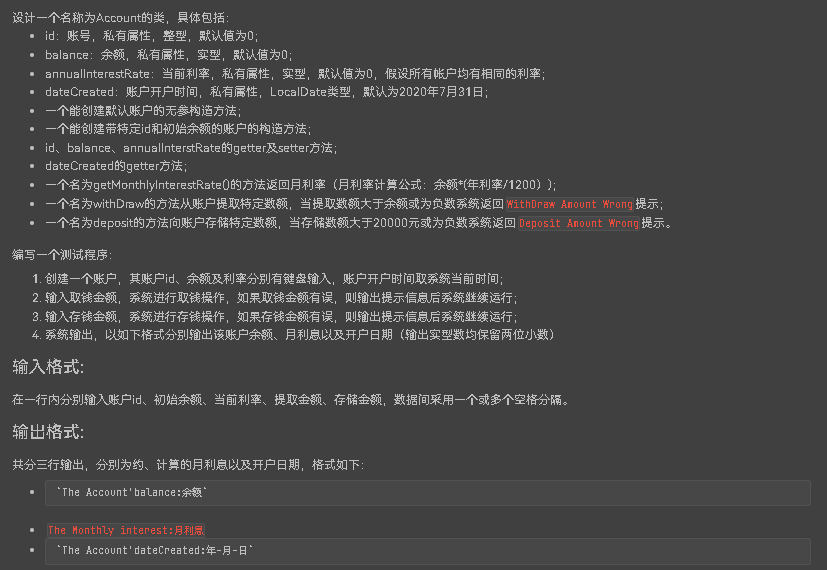
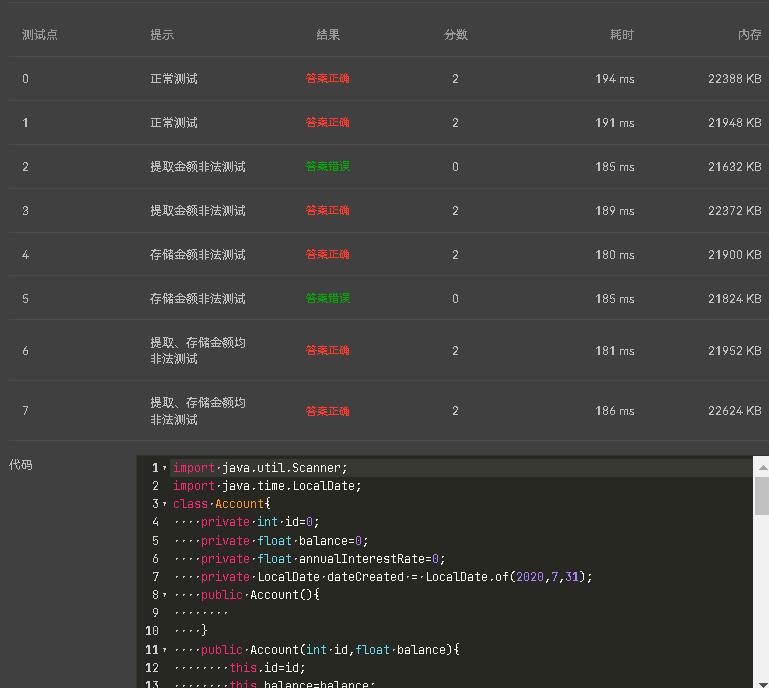
该题要求理解private 以及public 的意义,明白两者的区别以及性质用法 源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.time.LocalDate;
class Account{
private int id=0;
private double balance=0;
private double annualInterestRate=0;
private LocalDate dateCreated = LocalDate.of(2020,7,31);
public Account(){
}
public Account(int id,double balance){
this.id=id;
this.balance=balance;
}
public void setId(int id){
this.id=id;
}
public void setBalance(double balance){
this.balance=balance;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate){
this.annualInterestRate=annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId(){
return this.id;
}
public double getBalance(){
return this.balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate(){
return this.annualInterestRate;
}
public LocalDate getDateCreated(){
return this.dateCreated;
}
public double getMonthlyInterestRate(){
return this.balance*(annualInterestRate/1200);
}
public void withDraw(double money){
if(money<0||money>getBalance())
System.out.println("WithDraw Amount Wrong");
else
this.balance-=money;
}
public void deposit(double money){
if(money<0||money>20000)
System.out.println("Deposit Amount Wrong");
else
this.balance+=money;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Account user = new Account();
user.setId(input.nextInt());
user.setBalance(input.nextDouble());
user.setAnnualInterestRate(input.nextDouble());
user.withDraw(input.nextDouble());
user.deposit(input.nextDouble());
System.out.print("The"+" "+"Account'balance:");
System.out.printf("%.2f",user.getBalance());
System.out.println();
System.out.print("The"+" "+"Monthly"+" "+"interest:");
System.out.printf("%.2f",user.getMonthlyInterestRate());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("The"+" "+"Account'dateCreated:"+user.getDateCreated());
}
}
7-3 定义日期类
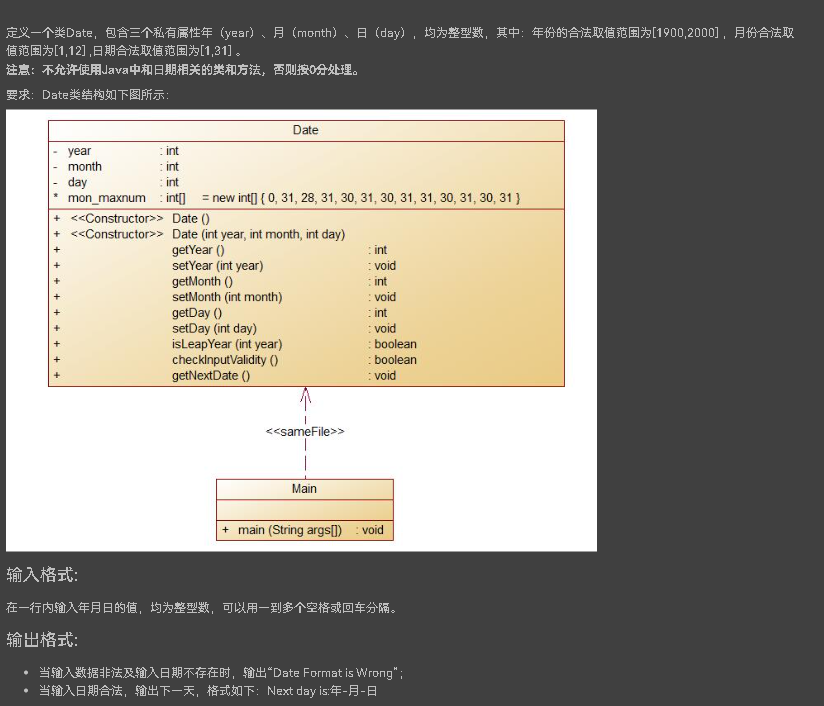
与第二次作业集中某题类似
类图如下:
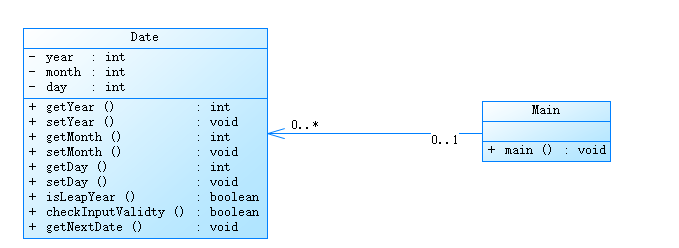
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
class Date{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public Date(){
}
public Date(int year,int month,int day){
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public int getYear(){
return this.year;
}
public void setYear(int year){
this.year=year;
}
public int getMonth(){
return this.month;
}
public void setMonth(int month){
this.month=month;
}
public int getDay(){
return this.day;
}
public void setDay(int day){
this.day=day;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
if(this.year<1900||this.year>2000)
return false;
if(this.month<1||this.month>12)
return false;
if(this.month==1||this.month==3||this.month==5||this.month==7||this.month==8||this.month==10||this.month==12){
if(this.day<1||this.day>31)
return false;
else
return true;
}
else if(this.month==4||this.month==6||this.month==9||this.month==11){
if(this.day<1||this.day>30)
return false;
else
return true;
}
else{
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
if(this.day<1||this.day>29)
return false;
else
return true;
}
else{
if(this.day<1||this.day>28)
return false;
else
return true;
}
}
}
public void getNextDate(){
if(this.month==12&&this.day==31){
this.day=1;
this.month=1;
this.year+=1;
}
else if((this.month==1||this.month==3||this.month==5||this.month==7||this.month==8||this.month==10)&&this.day==31){
this.day=1;
this.month+=1;
}
else if((this.month==4||this.month==6||this.month==9||this.month==11)&&this.day==30){
this.day=1;
this.month+=1;
}
else if(this.month==2){
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
if(this.day==29){
this.day=1;
this.month+=1;
}
else
this.day++;
}
else{
if(this.day==28){
this.day=1;
this.month+=1;
}
else
this.day++;
}
}
else
this.day+=1;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Date date = new Date();
int year=input.nextInt();
int month=input.nextInt();
int day=input.nextInt();
int flag;
date.setYear(year);
date.setMonth(month);
date.setDay(day);
if(date.checkInputValidity()){
date.getNextDate();
System.out.print("Next"+" "+"day"+" "+"is:"+date.getYear()+"-"+date.getMonth()+"-"+date.getDay());
}
else{
System.out.print("Date Format is Wrong");
}
}
}
7-4 日期类设计

上一题的迭代升级,其中求两个日期所相差的天数是通过计算两个合法日期到1820,1,1的天数,再进行作差比较;
类图如下:
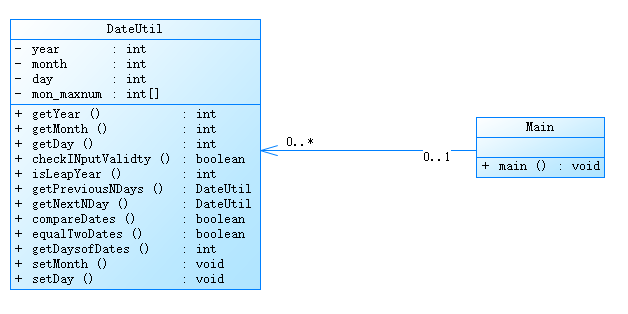
源码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
class DateUtil{
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
private int[] mon_maxnum1=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
private int[] mon_maxnum2=new int[]{0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil(int year,int month,int day) {
this.year=year;
this.month=month;
this.day=day;
}
public int getYear() {
return this.year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return this.month;
}
public int getDay() {
return this.day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity(){
if(this.year<1820||this.year>2020)
return false;
if(this.month<1||this.month>12)
return false;
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
if(this.day<1||this.day>mon_maxnum2[this.month])
return false;
else
return true;
}
else{
if(this.day<1||this.day>mon_maxnum2[this.month])
return false;
else
return true;
}
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year){
if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(this.year,this.month,this.day);
int[] max=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(;n>0;n--){
if(isLeapYear(date.year))
max[2]=29;
else
max[2]=28;
if(date.month==12){
if(date.day==max[date.month]){
date.year++;
date.month=1;
date.day=1;
}
else if(day>0&&day<max[date.month])
date.day++;
}
else if(date.month<12){
if(date.day==max[date.month]){
date.month++;
date.day=1;
}
else if(date.day>0&&date.day<max[date.month])
date.day++;
}
}
return date;
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(this.year,this.month,this.day);
int[] max=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(;n>0;n--){
if(isLeapYear(date.year))
max[2]=29;
else
max[2]=28;
if(date.month==1){
if(date.day==1){
date.year--;
date.month=12;
date.day=31;
}
else
date.day--;
}
else if(date.month!=1){
if(date.day==1){
date.month--;
date.day=max[date.month];
}
else
date.day--;
}
}
return date;
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date){
if(date.year<this.year)
return true;
else if(date.year>this.year)
return false;
else{
if(date.month<this.month)
return true;
else if(date.month>this.month)
return false;
else{
if(date.day<this.day)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date){
if(date.year==this.year && date.month==this.month && date.day==this.day)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date){
if(equalTwoDates(date))
return 0;
int day1=0;
int day2=0;
for(int i=1820;i<date.year;i++){
if(isLeapYear(i))
day1+=366;
else
day1+=365;
}
for(int i=1;i<date.month;i++){
if(isLeapYear(date.year)){
day1+=this.mon_maxnum2[i];
}
else
day1+=this.mon_maxnum1[i];
}
day1+=date.day;
for(int i=1820;i<this.year;i++){
if(isLeapYear(i))
day2+=366;
else
day2+=365;
}
for(int i=1;i<this.month;i++){
if(isLeapYear(this.year)){
day2+=this.mon_maxnum2[i];
}
else
day2+=this.mon_maxnum1[i];
}
day2+=this.day;
if(compareDates(date))
return day2-day1;
else
return day1-day2;
}
public String showDate(){
String Date = Integer.toString(this.year);
Date+="-";
Date+=Integer.toString(this.month);
Date+="-";
Date+=Integer.toString(this.day);
return Date;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
3.踩坑心得
(1).oop训练集1第7题 判断是否有重复数据时若直接遍历数组找是否存在相同数据则会运行超时
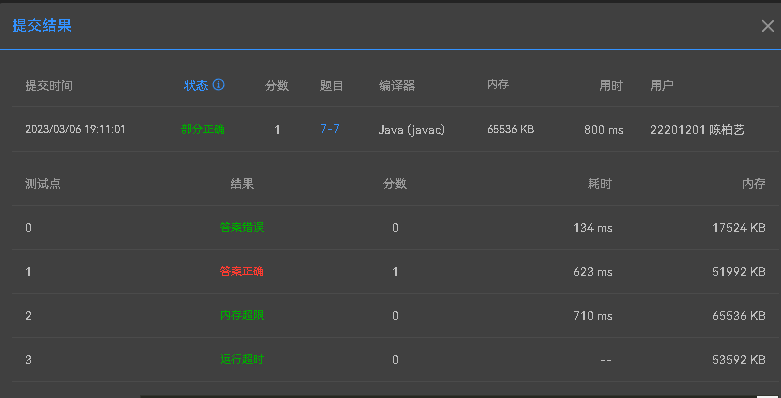
应该先对数据进行排序再比较相邻元素是否相等才能节约运行时长
(2).oop训练集二中第三题 若输出时不将税转换成float类型则会出现错误
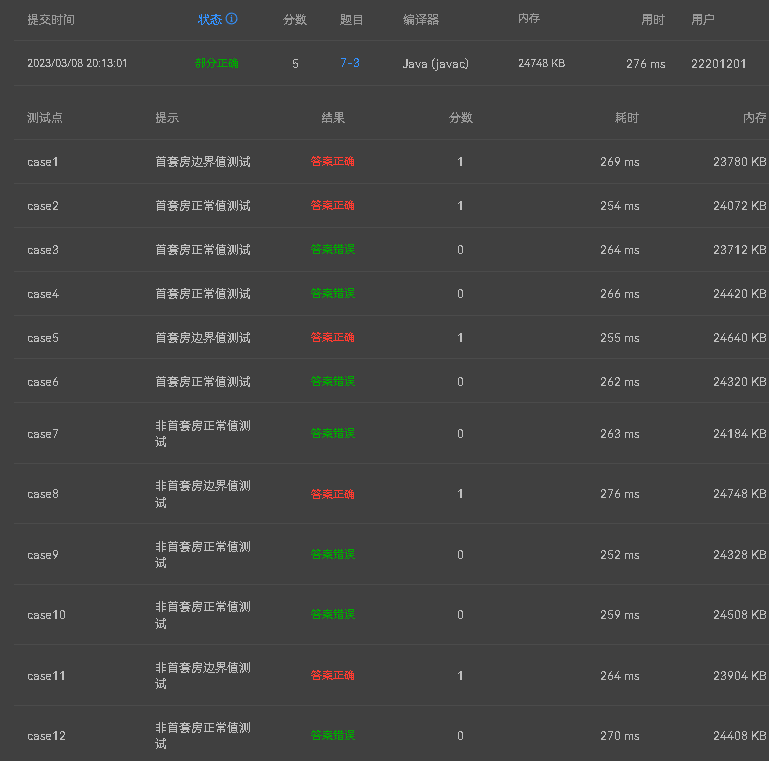
应用(float)强制类型转换将数据转换为float类型输出
(3).oop训练集二第八题 若直接判定a*a+b*b与c*c是否相等则无法得出真确结论,因为两个浮点数无法直接比较相等
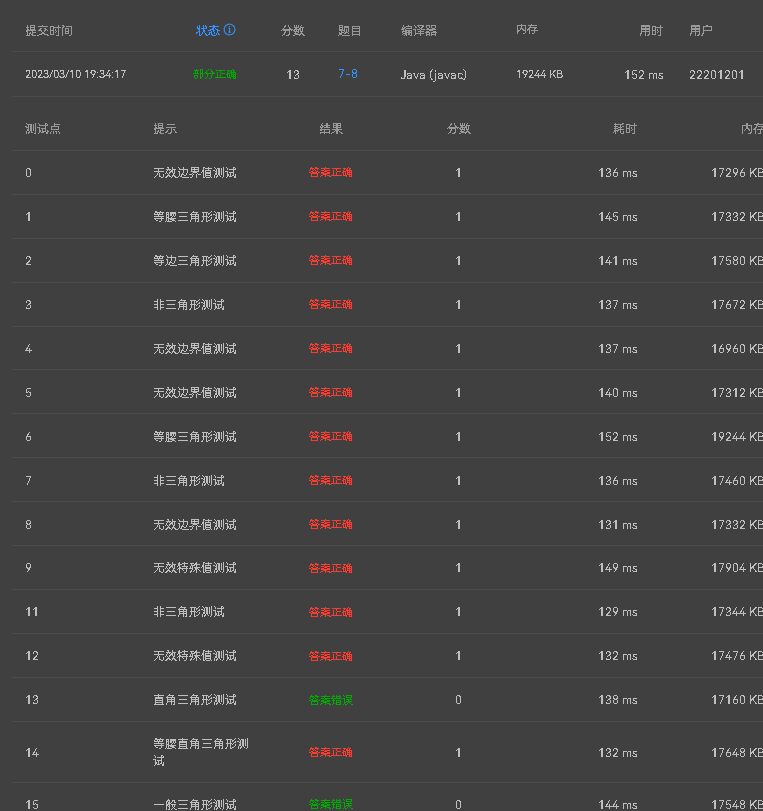
应转而比较两者的差值是否在某一范围内
(4).oop训练集三第二题用户余额以及利率应设为double类型
4.改进建议
题目集三第四题还有许多可优化的地方,如计算两个日期的天数差时可以改为直接计算而不是计算到1820.1.1的天数之差,可以减少运行时长。
写代码的格式还不够规范,经常容易忽视边界值的情况。
5.总结
这一阶段的三次题目集让我对Java有一初步的了解。熟悉最基本的Java语法,熟悉编译环境。经过这三次的PTA练习,我基本掌握了Java中数据的输入输出的方法,练习了类的构造方法、方法的调用、参数传递、对象的构造与使用。练习了循环结构、控制结构。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号