金融量化分析
第一部分:金融与量化投资
股票:
- 股票是股份公司发给出资人的一种凭证,股票的持有者就是股份公司的股东。
股票的面值与市值
- 面值表示票面金额
- 市值表示市场价值
上市/IPO:
- 企业通过证券交易所公开向社会增发股票以募集资金
股票的作用:
- 出资证明、证明股东身份、对公司经营发表意见
- 公司分红、交易获利
股票的分类
股票按业绩分类:
- 蓝筹股:资本雄厚、信誉优良的公司的股票
- 绩优股:业绩优良公司的股票
- ST股:特别处理股票,连续两年亏损或每股净资产低于股票面值
股票按上市地区分类:
- A股:中国大陆上市,人民币认购买卖(T+1,涨跌幅10%)
- B股:中国大陆上市,外币认购买卖(T+1,T+3)
- H股:中国香港上市(T+0,涨跌幅不设限制)
- N股:美国纽约上市
- S股:新加坡上市
股票市场的构成
- 上市公司
- 投资者(包括机构投资者)
- 证监会、证券业协会、交易所
- 证券中介机构
交易所
- 上海证券交易所:只有一个主板(沪指)
- 深圳证券交易所:
- 主板:大型成熟企业(深成指)
- 中小板:经营规模较小
- 创业板:尚处于成长期的创业企业
影响股价的因素
- 公司自身因素:股票自身价值是决定股价最基本的因素,而这主要取决于发行公司的经营业绩、资信水平以及连带而来的股息红利派发状况、发展前景、股票预期收益水平等。
- 行业因素:行业在国民经济中地位的变更,行业的发展前景和发展潜力,新兴行业引来的冲击等,以及上市公司在行业中所处的位置,经营业绩,经营状况,资金组合的改变及领导层人事变动等都会影响相关股票的价格。
- 市场因素:投资者的动向,大户的意向和操纵,公司间的合作或相互持股,信用交易和期货交易的增减,投机者的套利行为,公司的增资方式和增资额度等,均可能对股价形成较大影响。
- 心理因素:情绪波动,判断失误,盲目追随大户、狂抛抢购
- 经济因素:经济周期,国家的财政状况,金融环境,国际收支状况,行业经济地位的变化,国家汇率的调整等
- 政治因素
股票买卖(A股)
- 委托买卖股票 : 个人不能直接买卖,需要在券商开户,进行委托购买
- 股票交易日:周一到周五(非法定节假日和交易所休市日)
- 股票交易时间:
- 9:15-9:25 开盘集合竞价时间
- 9:30-11:30 前市,连续竞价时间
- 13:00-15:00 后市,连续竞价时间
- 14:57-15:00 深交所收盘集合竞价时间
- T+1交易制度:股票买入后当天不能卖出,要在买入后的下一个交易日才能卖出
- 涨停、跌停限制
金融分析
基本面分析
- 宏观经济面分析:国家的财政政策、货币政策等
- 行业分析
- 公司分析:财务数据、业绩报告等
技术面分析:各项技术指标
- K线
- MA(均线)
- KDJ(随机指标)
- MACD(指数平滑移动平均线)
- ……
K线
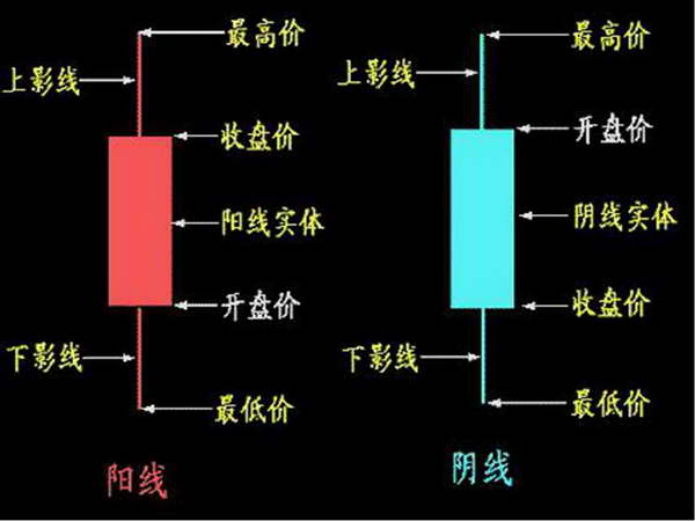
金融量化投资
- 量化投资:利用计算机技术并且采用一定的数学模型去实践投资理念,实现投资策略的过程。
- 量化投资的优势:
- 避免主观情绪、人性弱点和认知偏差,选择更加客观
- 能同时包括多角度的观察和多层次的模型
- 及时跟踪市场变化,不断发现新的统计模型,寻找交易机会
- 在决定投资策略后,能通过回测验证其效果
量化策略
- 量化策略:通过一套固定的逻辑来分析、判断和决策,自动化地进行股票交易。
- 核心内容
- 选股
- 择时
- 仓位管理
- 止盈止损
- 策略的周期
- 产生想法/学习知识
- 实现策略:Python
- 检验策略:回测/模拟交易
- 实盘交易
- 优化策略/放弃策略
第二部分:量化投资与Python
量化投资与Python
- 为什么选择Python?
- 其他选择:Excel、SAS/SPSS、R
- 量化投资第三方相关模块
- NumPy:数值计算
- pandas:数据分析
- Matplotlib:图标绘制
- 如何使用Python进行量化投资
- 自己编写:NumPy+pandas+Matplotlib+……
- 在线平台:聚宽、优矿、米筐、Quantopian、……
- 开源框架:RQAlpha、QUANTAXIS、……
Ipython:交互式的Python命令行
- IPython:安装:pip install ipython
- TAB键自动完成
- ?命令(内省、命名空间搜索)
- 执行系统命令(!)
- %run命令执行文件代码
- %paste %cpaste命令执行剪贴板代码
- 与编辑器和IDE交互
- 魔术命令:%timeit %pdb …
- 使用命令历史
- 输入与输出变量(_, __, _2, _i2)
- 目录书签系统 %bookmark
- Ipython Notebook
Ipython常用的魔术命令


Python调试器命令


Ipython快捷键

NumPy:数组计算
- NumPy是高性能科学计算和数据分析的基础包。它是pandas等其他各种工具的基础。
- NumPy的主要功能:
- ndarray,一个多维数组结构,高效且节省空间
- 无需循环对整组数据进行快速运算的数学函数
- *读写磁盘数据的工具以及用于操作内存映射文件的工具
- *线性代数、随机数生成和傅里叶变换功能
- *用于集成C、C++等代码的工具
- 安装方法:pip install numpy
- 引用方式:import numpy as np
NumPy:ndarray-多维数组对象
- 创建ndarray:np.array()
- 为什么要使用ndarray:
- 例1:已知若干家跨国公司的市值(美元),将其换算为人民币
- 例2:已知购物车中每件商品的价格与商品件数,求总金额
- ndarray还可以是多维数组,但元素类型必须相同
- 常用属性:
- T 数组的转置(对高维数组而言)
- dtype 数组元素的数据类型
- size 数组元素的个数
- ndim 数组的维数
- shape 数组的维度大小(以元组形式)
NumPy:ndarray-多维数组对象
- dtype:
- bool_, int(8,16,32,64), uint(8,16,32,64), float(16,32,64)
- 类型转换:astype()
- 创建ndarray:
- array() 将列表转换为数组,可选择显式指定dtype
- arange() range的numpy版,支持浮点数
- linspace() 类似arange(),第三个参数为数组长度
- zeros() 根据指定形状和dtype创建全0数组
- ones() 根据指定形状和dtype创建全1数组
- empty() 根据指定形状和dtype创建空数组(随机值)
- eye() 根据指定边长和dtype创建单位矩阵
NumPy:索引和切片
- 数组和标量之间的运算
- a+1 a*3 1//a a**0.5
- 同样大小数组之间的运算
- a+b
- a/b
- a**b
- 数组的索引
- a[5]
- a2[2][3]
- a2[2,3]
- 数组的切片
- a[5:8]
- a[:3] = 1
- a2[1:2, :4]
- a2[:,:1]
- a2[:,1]
- 与列表不同,数组切片时并不会自动复制,在切片数组上的修改会影响原数组。
- b = a[:4]
- b[-1] = 250
- 解决方法:
- copy()】 b = a[:4] b[-1] = 250
NumPy:布尔型索引
- 问题:给一个数组,选出数组中所有大于5的数。
- 答案:a[a>5]
- 原理: a>5会对a中的每一个元素进行判断,返回一个布尔数组 布尔型索引:将同样大小的布尔数组传进索引,会返回一个由所有True对应位置的元素的数组
- 问题2:给一个数组,选出数组中所有大于5的偶数。
- 问题3:给一个数组,选出数组中所有大于5的数和偶数。
- 答案: a[(a>5) & (a%2==0)] a[(a>5) | (a%2==0)]
NumPy:花式索引*
- 问题1:对于一个数组,选出其第1,3,4,6,7个元素,组成新的二维数组。
- 答案:a[[1,3,4,6,7]]
- 问题2:对一个二维数组,选出其第一列和第三列,组成新的二维数组。
- 答案:a[:,[1,3]]
NumPy:通用函数
- 通用函数:能同时对数组中所有元素进行运算的函数
- 常见通用函数:
- 一元函数:abs, sqrt, exp, log, ceil, floor, rint, trunc, modf, isnan, isinf, cos, sin, tan
- 二元函数:add, substract, multiply, divide, power, mod, maximum, mininum,
NumPy:数学和统计方法
- 常用函数:
- sum 求和
- mean 求平均数
- std 求标准差 v
- ar 求方差
- min 求最小值
- max 求最大值
- argmin 求最小值索引
- argmax 求最大值索引
NumPy:随机数生成
- 常用函数
- rand 给定形状产生随机数组(0到1之间的数)
- randint 给定形状产生随机整数
- choice 给定形状产生随机选择
- shuffle 与random.shuffle相同
- uniform 给定形状产生随机数组
pandas:数据分析
- pandas是一个强大的Python数据分析的工具包。
- pandas是基于NumPy构建的。
- pandas的主要功能
- 具备对其功能的数据结构DataFrame、Series
- 集成时间序列功能
- 提供丰富的数学运算和操作
- 灵活处理缺失数据
- 安装方法:pip install pandas
- 引用方法:import pandas as pd
pandas:Series
- Series是一种类似于一位数组的对象,由一组数据和一组与之相关的数据标签(索引)组成。
- Series比较像列表(数组)和字典的结合体
- 创建方式:
- pd.Series([4,7,-5,3])
- pd.Series([4,7,-5,3],index=['a','b','c','d'])
- pd.Series({'a':1, 'b':2})
- pd.Series(0, index=['a','b','c','d'])
- 获取值数组和索引数组:
- values属性
- index属性
pandas:Series特性
- Series支持NumPy模块的特性(下标):
- 从ndarray创建Series:Series(arr)
- 与标量运算:sr*2
- 两个Series运算:sr1+sr2
- 索引:sr[0], sr[[1,2,4]]
- 切片:sr[0:2](切片依然是视图形式)
- 通用函数:np.abs(sr)
- 布尔值过滤:sr[sr>0]
- 统计函数:mean() sum() cumsum()
pandas:整数索引
- 整数索引的pandas对象往往会使新手抓狂。
- 例:
- sr = np.Series(np.arange(4.))
- sr[-1]
- 如果索引是整数类型,则根据整数进行数据操作时总是面向标签的。
- loc属性 以标签解释
- iloc属性 以下标解释
pandas:Series数据对齐
- pandas在运算时,会按索引进行对齐然后计算。如果存在不同的索引,则结果的索引是两个操作数索引的并集。
- 例:
- sr1 = pd.Series([12,23,34], index=['c','a','d'])
- sr2 = pd.Series([11,20,10], index=['d','c','a',])
- sr1+sr2
- sr3 = pd.Series([11,20,10,14], index=['d','c','a','b'])
- sr1+sr3
- 如何在两个Series对象相加时将缺失值设为0?
- sr1.add(sr2, fill_value=0)
- 灵活的算术方法:add, sub, div, mul
pandas:Series缺失数据
- 缺失数据:使用NaN(Not a Number)来表示缺失数据。其值等于np.nan。内置的None值也会被当做NaN处理。
- 处理缺失数据的相关方法:
- dropna() 过滤掉值为NaN的行
- fillna() 填充缺失数据
- isnull() 返回布尔数组,缺失值对应为True
- notnull() 返回布尔数组,缺失值对应为False
- 过滤缺失数据:
- sr.dropna()
- sr[data.notnull()]
- 填充缺失数据:fillna(0)
pandas:DataFrame
- DataFrame是一个表格型的数据结构,含有一组有序的列。
- DataFrame可以被看做是由Series组成的字典,并且共用一个索引。
- 创建方式:
- pd.DataFrame({'one':[1,2,3,4],'two':[4,3,2,1]})
- pd.DataFrame({'one':pd.Series([1,2,3],index=['a','b','c']), 'two':pd.Series([1,2,3,4],index=['b','a','c','d'])})
- ……
- csv文件读取与写入:
- df.read_csv('filename.csv')
- df.to_csv()
pandas:DataFrame查看数据
- 查看数据常用属性及方法:
- index 获取索引
- T 转置
- columns 获取列索引
- values 获取值数组
- describe() 获取快速统计
- DataFrame各列name属性:列名
- rename(columns={})
pandas:DataFrame索引和切片
- DataFrame有行索引和列索引。
- 通过标签获取:
- df['A']
- df[['A', 'B']]
- df['A'][0]
- df[0:10][['A', 'C']]
- df.loc[:,['A','B']]
- df.loc[:,'A':'C']
- df.loc[0,'A']
- df.loc[0:10,['A','C']]
- 通过位置获取:
- df.iloc[3]
- df.iloc[3,3]
- df.iloc[0:3,4:6]
- df.iloc[1:5,:]
- df.iloc[[1,2,4],[0,3]]
- 通过布尔值过滤:
- df[df['A']>0]
- df[df['A'].isin([1,3,5])]
- df[df<0] = 0
pandas:DataFrame数据对齐与缺失数据
- DataFrame对象在运算时,同样会进行数据对其,结果的行索引与列索引分别为两个操作数的行索引与列索引的并集。
- DataFrame处理缺失数据的方法:
- dropna(axis=0,how='any',…)
- fillna()
- isnull()
- notnull()
pandas:其他常用方法
- pandas常用方法(适用Series和DataFrame):
- mean(axis=0,skipna=False)
- sum(axis=1)
- sort_index(axis, …, ascending) 按行或列索引排序
- sort_values(by, axis, ascending) 按值排序
- NumPy的通用函数同样适用于pandas
- apply(func, axis=0) 将自定义函数应用在各行或者各列上 ,func可返回标量或者Series
- applymap(func) 将函数应用在DataFrame各个元素上
- map(func) 将函数应用在Series各个元素上
*pandas:层次化索引
- 层次化索引是Pandas的一项重要功能,它使我们能够在一个轴上拥有多个索引级别。
- 例:data=pd.Series(np.random.rand(9), index=[['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'c'], [1,2,3,1,2,3,1,2,3]])
pandas:时间对象处理
- 时间序列类型:
- 时间戳:特定时刻
- 固定时期:如2017年7月
- 时间间隔:起始时间-结束时间
- Python标准库:datetime
- date time datetime timedelta
- dt.strftime()
- strptime()
- 第三方包:dateutil
- dateutil.parser.parse()
- 成组处理日期:pandas
- pd.to_datetime(['2001-01-01', '2002-02-02'])
- 产生时间对象数组:date_range
- start 开始时间
- end 结束时间
- periods 时间长度
- freq 时间频率,默认为'D',可选H(our),W(eek),B(usiness),S(emi-)M(onth),(min)T(es), S(econd), A(year),…
pandas:时间序列
- 时间序列就是以时间对象为索引的Series或DataFrame。
- datetime对象作为索引时是存储在DatetimeIndex对象中的。
- 时间序列特殊功能:
- 传入“年”或“年月”作为切片方式
- 传入日期范围作为切片方式
pandas:从文件读取
- 读取文件:从文件名、URL、文件对象中加载数据
- read_csv 默认分隔符为csv
- read_table 默认分隔符为\t
- read_excel 读取excel文件
- 读取文件函数主要参数:
- sep 指定分隔符,可用正则表达式如'\s+'
- header=None 指定文件无列名
- names 指定列名
- index_col 指定某列作为索引
- skip_row 指定跳过某些行
- na_values 指定某些字符串表示缺失值
- parse_dates 指定某些列是否被解析为日期,布尔值或列表
pandas:写入到文件
- 写入到文件: to_csv
- 写入文件函数的主要参数:
- sep
- na_rep 指定缺失值转换的字符串,默认为空字符串
- header=False 不输出列名一行
- index=False 不输出行索引一列
- cols 指定输出的列,传入列表
- 其他文件类型:json, XML, HTML, 数据库
- pandas转换为二进制文件格式(pickle):
- save
- load
Matplotlib:绘图和可视化
- Matplotlib是一个强大的Python绘图和数据可视化的工具包。
- 安装方法:pip install matplotlib
- 引用方法:import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- 绘图函数:plt.plot()
- 显示图像:plt.show()
Matplotlib:plot函数
- plot函数:
- 线型linestyle(-,-.,--,..)
- 点型marker(v,^,s,*,H,+,x,D,o,…)
- 颜色color(b,g,r,y,k,w,…)
- plot函数绘制多条曲线
- 标题:title
- x轴:xlabel
- y轴:ylabel
- 其他类型图像:
- hist 频数直方图
*Matplotlib:画布与图
- 画布:figure
- fig = plt.figure()
- 图:subplot
- ax1 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,1)
- 调节子图间距:
- subplots_adjust(left, bottom, right, top, wspace, hspace)
第三部分 实现简单的量化框架
框架内容:
- 开始时间、结束时间、现金、持仓数据
- 获取历史数据
- 交易函数
- 计算并绘制收益曲线
- 回测主体框架
- 计算各项指标
- 用户待写代码:初始化、每日处理函数
第四部分 在线平台与量化投资
本节内容:
- 第一个简单的策略(了解平台)
- 双均线策略
- 因子选股策略
- 多因子选股策略
- 小市值策略
- 海龟交易法则
- 均值回归策略
- 动量策略
- 反转策略
- 羊驼交易法则
- PEG策略
- 鳄鱼交易法则
JoinQuant平台
- 主要框架
- initialize
- handle_data
- ……
- 获取历史数据
- 交易函数
- 回测频率:
- 按天回测
- 按分钟回测
- 风险指标
双均线策略
- 均线:对于每一个交易日,都可以计算出前N天的移动平均值,然后把这些移动平均值连起来,成为一条线,就叫做N日移动平均线。
- 移动平均线常用线有5天、10天、30天、60天、120天和240天的指标。 5天和10天的是短线操作的参照指标,称做日均线指标; 30天和60天的是中期均线指标,称做季均线指标; 120天、240天的是长期均线指标,称做年均线指标。
- 金叉:短期均线上穿长期均线
- 死叉:短期均线下穿长期均线

1 # 导入函数库 2 import jqdata 3 4 # 初始化函数,设定基准等等 5 def initialize(context): 6 set_benchmark('000300.XSHG') 7 set_option('use_real_price', True) 8 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 9 10 g.security = ['601318.XSHG'] 11 g.p1 = 5 12 g.p2 = 60 13 14 15 def handle_data(context, data): 16 cash = context.portfolio.available_cash 17 for stock in g.security: 18 hist = attribute_history(stock, g.p2) 19 ma60 = hist['close'].mean() 20 ma5 = hist['close'][-5:].mean() 21 if ma5 > ma60 and stock not in context.portfolio.positions: 22 order_value(stock, cash/len(g.security)) 23 elif ma5 < ma60 and stock in context.portfolio.positions: 24 order_target(stock, 0
因子选股策略
- 因子:
- 标准 增长率,市值,ROE,……
- 选股策略:
- 选取该因子最大(或最小)的N只股票持仓
- 多因子选股:如何同时考虑多个因子?

1 # 导入函数库 2 import jqdata 3 4 # 初始化函数,设定基准等等 5 def initialize(context): 6 set_benchmark('000300.XSHG') 7 set_option('use_real_price', True) 8 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 9 g.N= 10 10 g.days = 0 11 12 #获取成分股 13 14 15 def handle_data(context, data): 16 g.days+=1 17 if g.days % 30 == 0: 18 g.security = get_index_stocks('000300.XSHG') 19 df = get_fundamentals(query(valuation).filter(valuation.code.in_(g.security))) 20 df = df.sort(columns='market_cap') 21 df = df.iloc[:g.N,:] 22 tohold = df['code'].values 23 24 for stock in context.portfolio.positions: 25 if stock not in tohold: 26 order_target(stock, 0) 27 28 tobuy = [stock for stock in tohold if stock not in context.portfolio.positions] 29 30 if len(tobuy)>0: 31 cash = context.portfolio.available_cash 32 cash_every_stock = cash / len(tobuy) 33 for stock in tobuy: 34 order_value(stock, cash_every_stock)
均值回归理论

1 import jqdata 2 import math 3 import numpy as np 4 import pandas as pd 5 6 def initialize(context): 7 set_option('use_real_price', True) 8 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 9 10 g.benchmark = '000300.XSHG' 11 set_benchmark(g.benchmark) 12 13 g.ma_days = 30 14 g.stock_num = 10 15 16 run_monthly(handle, 1) 17 #run_monthly(handle, 11) 18 19 def handle(context): 20 tohold = get_hold_list(context) 21 for stock in context.portfolio.positions: 22 if stock not in tohold: 23 order_target_value(stock, 0) 24 25 tobuy = [stock for stock in tohold if stock not in context.portfolio.positions] 26 27 if len(tobuy)>0: 28 cash = context.portfolio.available_cash 29 cash_every_stock = cash / len(tobuy) 30 31 for stock in tobuy: 32 order_value(stock, cash_every_stock) 33 34 def get_hold_list(context): 35 stock_pool = get_index_stocks(g.benchmark) 36 stock_score = pd.Series(index=stock_pool) 37 for stock in stock_pool: 38 df = attribute_history(stock, g.ma_days, '1d', ['close']) 39 ma = df.mean()[0] 40 current_price = get_current_data()[stock].day_open 41 ratio = (ma - current_price) / ma 42 stock_score[stock] = ratio 43 return stock_score.nlargest(g.stock_num).index.value
- 均值回归:“跌下去的迟早要涨上来”
- 均值回归的理论基于以下观测:价格的波动一般会以它的均线为中心。也就是说,当标的价格由于波动而偏离移动均线时,它将调整并重新归于均线。
- 偏离程度:(MA-P)/MA
- 策略:在每个调仓日进行(每月调一次仓)
- 计算池内股票的N日移动均线;
- 计算池内所有股票价格与均线的偏离度;
- 选取偏离度最高的num_stocks支股票并进行调仓。
布林带策略
- 布林带/布林线/保利加通道(Bollinger Band):由三条轨道线组成,其中上下两条线分别可以看成是价格的压力线和支撑线,在两条线之间是一条价格平均线。
- 计算公式:
- 中间线=20日均线
- up线=20日均线+N*SD(20日收盘价)
- down线=20日均线-N*SD(20日收盘价)

1 import talib 2 #import numpy as np 3 #import pandas as pd 4 5 def initialize(context): 6 set_option('use_real_price', True) 7 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 8 set_benchmark('000300.XSHG') 9 10 g.security = ['600036.XSHG']#,'601328.XSHG','600196.XSHG','600010.XSHG'] 11 g.N = 2 12 13 # 初始化此策略 14 def handle_data(context, data): 15 cash = context.portfolio.cash / len(g.security) 16 for stock in g.security: 17 df = attribute_history(stock, 20) 18 middle = df['close'].mean() 19 upper = df['close'].mean() + g.N * df['close'].std() 20 lower = df['close'].mean() - g.N * df['close'].std() 21 22 current_price = get_current_data()[stock].day_open 23 # 当价格突破阻力线upper时,且拥有的股票数量>=0时,卖出所有股票 24 if current_price >= upper and stock in context.portfolio.positions: 25 order_target(stock, 0) 26 # 当价格跌破支撑线lower时, 且拥有的股票数量<=0时,则全仓买入 27 elif current_price <= lower and stock not in context.portfolio.positions: 28 order_value(stock, cash)
PEG策略
- 彼得·林奇:任何一家公司股票如果定价合理的话,市盈率就会与收益增长率相等。
- 每股收益(EPS)
- 股价(P)
- 市盈率(PE)= P/EPS
- 收益增长率(G)= (EPSi – EPSi-1)/ EPSi-1
- PEG = PE / G / 100
- PEG越低,代表股价被低估的可能性越大,股价会涨的可能性越大。
- PEG是一个综合指标,既考察价值,又兼顾成长性。PEG估值法适合应用于成长型的公司。
- 注意:过滤掉市盈率或收益增长率为负的情况

1 def initialize(context): 2 set_benchmark('000300.XSHG') 3 set_option('use_real_price', True) 4 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 5 6 g.security = get_index_stocks('000300.XSHG') 7 g.days = 0 8 g.N = 10 9 10 def handle_data(context, data): 11 g.days+=1 12 if g.days%30!=0: 13 return 14 df = get_fundamentals(query(valuation.code, valuation.pe_ratio, indicator.inc_net_profit_year_on_year).filter(valuation.code.in_(g.security))) 15 df = df[(df['pe_ratio']>0)&(df['inc_net_profit_year_on_year']>0)] 16 df['PEG'] = df['pe_ratio']/df['inc_net_profit_year_on_year']/100 17 df = df.sort(columns='PEG')[:g.N] 18 tohold = df['code'].values 19 20 for stock in context.portfolio.positions: 21 if stock not in tohold: 22 order_target_value(stock, 0) 23 24 tobuy = [stock for stock in tohold if stock not in context.portfolio.positions] 25 26 if len(tobuy)>0: 27 print('Buying') 28 cash = context.portfolio.available_cash 29 cash_every_stock = cash / len(tobuy) 30 31 for stock in tobuy: 32 order_value(stock, cash_every_stock)
羊驼交易法则
- 起始时随机买入N只股票,每天卖掉收益率最差的M只,再随机买入剩余股票池的M只。

1 import jqdata 2 import pandas as pd 3 4 def initialize(context): 5 set_benchmark('000300.XSHG') 6 set_option('use_real_price', True) 7 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 8 9 g.security = get_index_stocks('000300.XSHG') 10 g.period = 30 11 g.N = 10 12 g.change = 1 13 g.init = True 14 15 stocks = get_sorted_stocks(context, g.security)[:g.N] 16 cash = context.portfolio.available_cash * 0.9 / len(stocks) 17 for stock in stocks: 18 order_value(stock, cash) 19 run_monthly(handle, 2) 20 21 22 def get_sorted_stocks(context, stocks): 23 df = history(g.period, field='close', security_list=stocks).T 24 df['ret'] = (df.iloc[:,-1] - df.iloc[:,0]) / df.iloc[:,0] 25 df = df.sort(columns='ret', ascending=False) 26 return df.index.values 27 28 def handle(context): 29 if g.init: 30 g.init = False 31 return 32 stocks = get_sorted_stocks(context, context.portfolio.positions.keys()) 33 34 for stock in stocks[-g.change:]: 35 order_target(stock, 0) 36 37 stocks = get_sorted_stocks(context, g.security) 38 39 for stock in stocks: 40 if len(context.portfolio.positions) >= g.N: 41 break 42 if stock not in context.portfolio.positions: 43 order_value(stock, context.portfolio.available_cash * 0.9)
海龟交易法则
- 唐奇安通道:
- 上线=Max(前N个交易日的最高价)
- 下线=Min(前N个交易日的最低价)
- 中线=(上线+下线)/2
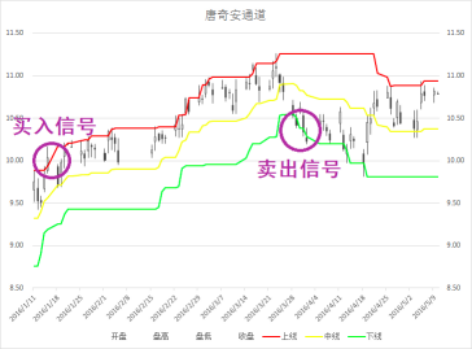

分钟回测
- 入市:若当前价格高于过去20日的最高价,则买入一个Unit
- 加仓:若股价在上一次买入(或加仓)的基础上上涨了0.5N,则加仓一个Unit
- 止盈:当股价跌破10日内最低价时(10日唐奇安通道下沿),清空头寸
- 止损:当价格比最后一次买入价格下跌2N时,则卖出全部头寸止损(损失不会超过2%)

1 import jqdata 2 import math 3 import numpy as np 4 import pandas as pd 5 from collections import deque 6 7 def initialize(context): 8 9 set_option('use_real_price', True) 10 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 11 12 g.security = '000060.XSHE' 13 set_benchmark(g.security) 14 g.in_day = 20 15 g.out_day = 10 16 g.today_units = 0 17 g.current_units = 0 18 g.N=deque(maxlen=19) 19 g.current_N = 0 20 g.last_buy_price = 0 21 22 price = attribute_history(g.security, g.N.maxlen*2+1, '1d', ('high', 'low', 'close')) 23 24 for i in range(g.N.maxlen+1, g.N.maxlen*2+1): 25 li = [] 26 for j in range(i-19,i+1): 27 a = price['high'][j]-price['low'][j] 28 b = abs(price['high'][j]-price['close'][j-1]) 29 c = abs(price['low'][j]-price['close'][j-1]) 30 li.append(max(a,b,c)) 31 current_N = np.array(li).mean() 32 g.N.append(current_N) 33 34 35 def before_trading_start(context): 36 g.current_N = cal_N() 37 g.today_units = 0 38 39 40 def handle_data(context, data): 41 dt = context.current_dt 42 current_price = data[g.security].price #上一分钟价格 43 value = context.portfolio.total_value 44 cash = context.portfolio.available_cash 45 46 unit = math.floor(value * 0.01 / g.current_N) 47 48 49 if g.current_units == 0: 50 buy(current_price, cash, unit) 51 else: 52 if stop_loss(current_price): 53 return 54 if sell(current_price): 55 return 56 addin(current_price, cash, unit) 57 58 def cal_N(): 59 # if len(g.N) < g.N.maxlen: 60 # price = attribute_history(g.security, g.N.maxlen+2, '1d', ('high', 'low', 'close')) 61 # li = [] 62 # for i in range(1, g.N.maxlen+2): 63 # a = price['high'][i]-price['low'][i] 64 # b = abs(price['high'][i]-price['close'][i-1]) 65 # c = abs(price['low'][i]-price['close'][i-1]) 66 # li.append(max(a,b,c)) 67 # current_N = np.array(li).mean() 68 # else: 69 price = attribute_history(g.security, 2, '1d', ('high', 'low', 'close')) 70 a = price['high'][1]-price['low'][1] 71 b = abs(price['high'][1]-price['close'][0]) 72 c = abs(price['low'][1]-price['close'][0]) 73 current_N = (max(a,b,c) + np.array(g.N).sum())/(g.N.maxlen+1) 74 g.N.append(current_N) 75 return current_N 76 77 def buy(current_price, cash, unit): 78 price = attribute_history(g.security, g.in_day, '1d', ('high',)) 79 if current_price > max(price['high']): 80 shares = cash / current_price 81 if shares >= unit: 82 print("buying %d" % unit) 83 o = order(g.security, unit) 84 g.last_buy_price = o.price 85 g.current_units += 1 86 g.today_units += 1 87 return True 88 return False 89 90 91 def addin(current_price, cash, unit): 92 if current_price >= g.last_buy_price + 0.5 * g.current_N: 93 shares = cash / current_price 94 if shares >= unit: 95 print("adding %d" % unit) 96 o = order(g.security, unit) 97 g.last_buy_price = o.price 98 g.current_units += 1 99 g.today_units += 1 100 return True 101 return False 102 103 def sell(current_price): 104 price = attribute_history(g.security, g.out_day, '1d', ('low',)) 105 if current_price < min(price['low']): 106 print("selling") 107 order_target(g.security, 0) 108 g.current_units = g.today_units 109 return True 110 return False 111 112 def stop_loss(current_price): 113 if current_price < g.last_buy_price - 2 * g.current_N: 114 print("stop loss") 115 order_target(g.security, 0) 116 g.current_units = g.today_units 117 return True 118 return False
鳄鱼法则交易系统
https://www.joinquant.com/post/595?tag=new

1 # 导入函数库 2 import jqdata 3 import numpy as np 4 5 # 初始化函数,设定基准等等 6 def initialize(context): 7 set_option('use_real_price', True) 8 set_order_cost(OrderCost(close_tax=0.001, open_commission=0.0003, close_commission=0.0003, min_commission=5), type='stock') 9 set_benchmark('000300.XSHG') 10 11 g.up_price = {} #向上碎形最高价 12 g.low_price = {} #向下碎形最低价 13 g.up_fractal_exists = {} #判断有效向上碎形 14 g.down_fractal_exists = {} #判断有效向下碎形 15 g.AO_index = {} #存放连续的AO指标数据 16 g.cal_AC_index = {} #计算AC指标中转存储 17 g.AC_index = {} #存放连续的AC指标数据 18 g.amount = {} #满仓仓位 19 g.stock = get_index_stocks('000300.XSHG') 20 g.buy_stock = [] 21 g.month = context.current_dt.month 22 run_monthly(select_universe,1,'open') 23 24 #重置全局变量 25 def reset_global(): 26 g.up_price = {} #向上碎形最高价 27 g.low_price = {} #向下碎形最低价 28 g.up_fractal_exists = {} #判断有效向上碎形 29 g.down_fractal_exists = {} #判断有效向下碎形 30 g.AO_index = {} #存放连续的AO指标数据 31 g.cal_AC_index = {} #计算AC指标中转存储 32 g.AC_index = {} #存放连续的AC指标数据 33 g.amount = {} #满仓仓位 34 g.buy_stock = [] 35 36 def initial_stock_global(stock): 37 g.up_price[stock] = 0 38 g.low_price[stock] = 0 39 g.up_fractal_exists[stock] = False 40 g.down_fractal_exists[stock] = False #判断有效向下碎形 41 g.AO_index[stock] = [0] #存放连续的AO指标数据 42 g.cal_AC_index[stock] = [0] #计算AC指标中转存储 43 g.AC_index[stock] = [0] #存放连续的AC指标数据 44 g.amount[stock] = 0 #满仓仓位 45 46 #轮换选股后清空持仓 47 def reset_position(context): 48 for stock in g.buy_stock: 49 order_target(stock,0) 50 log.info("sell %s for reset position"%stock) 51 52 #选股 53 def select_universe(context): 54 #每三个月操作一次 55 month = context.current_dt.month 56 if month%6 != g.month%6: 57 return 58 #清空全局变量 59 reset_position(context) 60 reset_global() 61 hist = history(30,'1d','close',g.stock,df = False) 62 for stock in g.stock: 63 if is_sleeping_alligator(stock,hist,20): 64 g.buy_stock.append(stock) 65 #初始化该股票全局变量 66 initial_stock_global(stock) 67 print g.buy_stock 68 return None 69 70 #睡着的鳄鱼 71 def is_sleeping_alligator(stock,hist,nday): 72 for i in range(nday): 73 if is_struggle(stock,hist,i) == False: 74 return False 75 return True 76 77 #均线纠缠,BRG三线非常接近 78 def is_struggle(stock,hist,delta): 79 blue_line = hist[stock][-21-delta:-8-delta].mean() 80 red_line = hist[stock][-13-delta:-5-delta].mean() 81 green_line = hist[stock][-8-delta:-3-delta].mean() 82 if abs(blue_line/red_line-1)<0.02 and abs(red_line/green_line-1)<0.02: 83 return True 84 else: 85 return False 86 87 #判断 向上 或 向下 碎形 88 def is_fractal(stock,direction): 89 hist = attribute_history(stock, 5, fields=[direction]) 90 if direction == 'high': 91 if np.all(hist.iloc[:2] < hist.iloc[2]) and np.all(hist.iloc[3:] < hist.iloc[2]): 92 g.up_price[stock] = hist.iloc[2].values 93 return True 94 elif direction == 'low': 95 if np.all(hist.iloc[:2] > hist.iloc[2]) and np.all(hist.iloc[3:] > hist.iloc[2]): 96 g.low_price[stock] = hist.iloc[2].values 97 return True 98 return False 99 100 #通过比较碎形与红线位置,判断碎形是否有效 101 def is_effective_fractal(stock, direction): 102 if is_fractal(stock,direction): 103 hist = attribute_history(stock, 11) 104 red_line = hist['close'][:-3].mean() 105 close_price = hist['close'][-1] 106 if direction == 'high': 107 if close_price > red_line: 108 g.up_fractal_exists[stock] = True 109 else: 110 g.up_fractal_exists[stock] = False 111 elif direction == 'low': 112 if close_price < red_line: 113 g.down_fractal_exists[stock] = True 114 else: 115 g.down_fractal_exists[stock] = False 116 117 118 #N日内最高价格的N日线 119 def nday_high_point(stock,n): 120 hist = history(2*n,'1d','high',[stock],df = False)[stock] 121 high_point = [] 122 for i in range(n): 123 high_point.append(max(hist[-5-i:-1-i])) 124 return np.array(high_point).mean() 125 126 #N日内最低价格的N日线 127 def nday_low_point(stock,n): 128 hist = history(2*n,'1d','low',[stock],df = False)[stock] 129 low_point = [] 130 for i in range(n): 131 low_point.append(max(hist[-5-i:-1-i])) 132 return np.array(low_point).mean() 133 134 #AO=5日内(最高-最低)/2的5日移动平均-34日内(最高-最低)/2的34日移动平均 135 def AO_index(stock): 136 g.AO_index[stock].append(nday_high_point(stock,5)/2 + nday_low_point(stock,5)/2\ 137 - nday_high_point(stock,34)/2 - nday_low_point(stock,34)/2) 138 return None 139 140 #AO-AO的5日平均值的5日平均 141 def AC_index(stock): 142 AO_index(stock) 143 if len(g.AO_index[stock]) >= 5: 144 g.cal_AC_index[stock].append(g.AO_index[stock][-1] - np.array(g.AO_index[stock][-5:]).mean()) 145 if len(g.cal_AC_index[stock]) >=5: 146 g.AC_index[stock].append(np.array(g.cal_AC_index[stock][-5:]).mean()) 147 148 #判断序列n日上行 149 def is_up_going(alist,n): 150 if len(alist) < n: 151 return False 152 for i in range(n-1): 153 if alist[-(1+i)] <= alist[-(2+i)]: 154 return False 155 return True 156 157 #判断序列n日下行 158 def is_down_going(alist,n): 159 if len(alist) < n: 160 return False 161 for i in range(n-1): 162 if alist[-(1+i)] >= alist[-(2+i)]: 163 return False 164 return True 165 166 #碎形被突破 167 def active_fractal(stock,direction): 168 close_price = history(1,'1d','close',[stock],df=False)[stock][0] 169 if direction == 'up' and close_price > g.up_price[stock]: 170 return True 171 elif direction == 'down' and close_price < g.low_price[stock]: 172 return True 173 return False 174 175 #进场,初始仓位 176 def set_initial_position(stock,context): 177 close_price = history(1,'1d','close',[stock],df=False)[stock][0] 178 g.amount[stock] = context.portfolio.cash/close_price/len(g.buy_stock)*3 179 order(stock, g.amount[stock]) 180 log.info("buying %s 股数为 %s"%(stock,g.amount[stock])) 181 g.down_fractal_exists[stock] = False 182 183 #卖出 184 def sell_all_stock(stock,context): 185 order_target(stock,0) 186 log.info("selling %s"%stock) 187 g.up_fractal_exists[stock] = False 188 189 #加仓 190 def adjust_position(stock,context,position): 191 order(stock,g.amount[stock]*position) 192 log.info("adjust position buying %s 股数为 %s"%(stock,g.amount[stock]*position)) 193 194 # 计算股票前n日收益率 195 def security_return(days,security_code): 196 hist1 = attribute_history(security_code, days + 1, '1d', 'close',df=False) 197 security_returns = (hist1['close'][-1]-hist1['close'][0])/hist1['close'][0] 198 return security_returns 199 200 # 止损,根据前n日收益率 201 def conduct_nday_stoploss(context,security_code,days,bench): 202 if security_return(days,security_code)<= bench: 203 for stock in g.buy_stock: 204 order_target_value(stock,0) 205 log.info("Sell %s for stoploss" %stock) 206 return True 207 else: 208 return False 209 210 # 计算股票累计收益率(从建仓至今) 211 def security_accumulate_return(context,data,stock): 212 current_price = data[stock].price 213 cost = context.portfolio.positions[stock].avg_cost 214 if cost != 0: 215 return (current_price-cost)/cost 216 else: 217 return None 218 219 # 个股止损,根据累计收益 220 def conduct_accumulate_stoploss(context,data,stock,bench): 221 if security_accumulate_return(context,data,stock) != None\ 222 and security_accumulate_return(context,data,stock) < bench: 223 order_target_value(stock,0) 224 log.info("Sell %s for stoploss" %stock) 225 return True 226 else: 227 return False 228 229 # 个股止盈,根据累计收益 230 def conduct_accumulate_stopwin(context,data,stock,bench): 231 if security_accumulate_return(context,data,stock) != None\ 232 and security_accumulate_return(context,data,stock) > bench: 233 order_target_value(stock,0) 234 log.info("Sell %s for stopwin" %stock) 235 return True 236 else: 237 return False 238 239 def handle_data(context,data): 240 #大盘止损 241 if conduct_nday_stoploss(context,'000300.XSHG',3,-0.03): 242 return 243 for stock in g.buy_stock: 244 #个股止损 245 if conduct_accumulate_stopwin(context,data,stock,0.3)\ 246 or conduct_accumulate_stoploss(context,data,stock,-0.1): 247 return 248 #计算AO,AC指标 249 AC_index(stock) 250 #空仓时,寻找机会入场 251 if context.portfolio.positions[stock].amount == 0: 252 #计算向上碎形 253 is_effective_fractal(stock,'high') 254 #有效向上碎形存在,并被突破,买入 255 if g.up_fractal_exists and active_fractal(stock,'up'): 256 close_price = history(5, '1d', 'close', [stock],df = False) 257 if is_up_going(g.AO_index[stock],5)\ 258 and is_up_going(g.AC_index[stock],3)\ 259 and is_up_going(close_price[stock],2): 260 set_initial_position(stock,context) 261 #有持仓时,加仓或离场 262 else: 263 #计算向下碎形 264 is_effective_fractal(stock,'low') 265 #出场条件1:有效向下碎形存在,并被突破,卖出 266 if g.down_fractal_exists and active_fractal(stock,'down'): 267 sell_all_stock(stock,context) 268 return



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号