assignment1 knn
可视化部分样本,显示部分训练数据样本的图像
# Visualize some examples from the dataset. # We show a few examples of training images from each class. classes = ['plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'] #类别列表 num_classes = len(classes) #类别数目 samples_per_class = 7 # 每个类别采样个数 for y, cls in enumerate(classes): # 对列表的元素位置和元素进行循环,y表示元素位置(0,num_class),cls元素本身'plane'等 idxs = np.flatnonzero(y_train == y) #找出标签中y类的位置 idxs = np.random.choice(idxs, samples_per_class, replace=False) #从中选出我们所需的7个样本 for i, idx in enumerate(idxs): #对所选的样本的位置和样本所对应的图片在训练集中的位置进行循环 plt_idx = i * num_classes + y + 1 # 在子图中所占位置的计算 plt.subplot(samples_per_class, num_classes, plt_idx) # 说明要画的子图的编号 plt.imshow(X_train[idx].astype('uint8')) # 画图 plt.axis('off') if i == 0: plt.title(cls) # 写上标题,也就是类别名 plt.show() # 显示
要求实现的代码:
two loops
for i in range(num_test): for j in range(num_train): dists[i][j] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(X[i]-self.X_train[j]))) return dists
one loop
做减法时,numpy会使用广播机制
x[i] (3072,0)
self.X_train[i] (5000,3072)
X[i]-self.X_train[i]
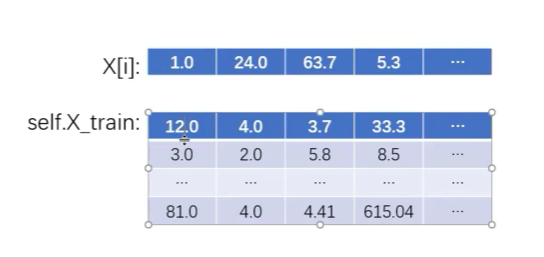 每一行减去x【i】
每一行减去x【i】
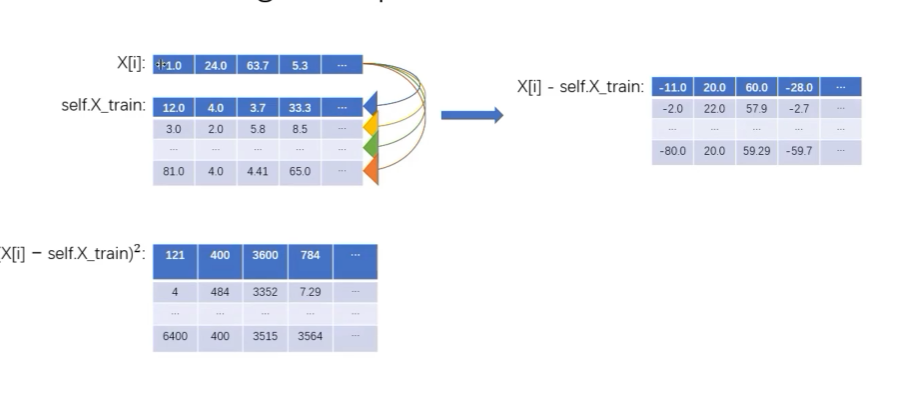
for i in range(num_test):#循环500词次,每次拿到一张图片
dists[i] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.X_train - X[i]), axis=1))
#每一行都求和
#r如果直接使用np.sum那么会对所有的结果求和,得到一个,而我们需要5000个结果,每个结果是这3072个值的和,因此需要axis轴
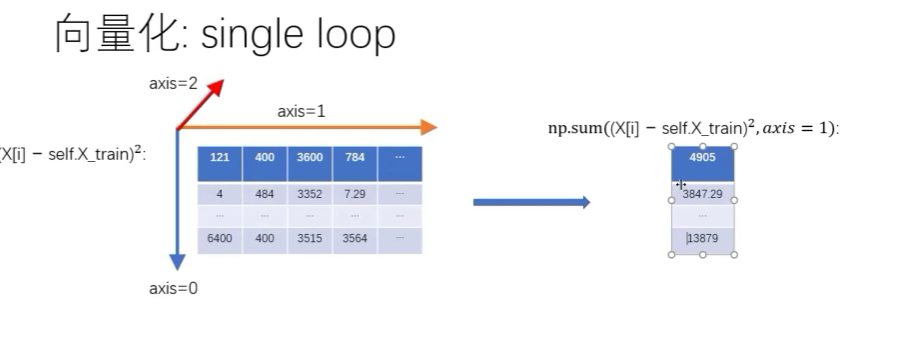
return dists
no loops
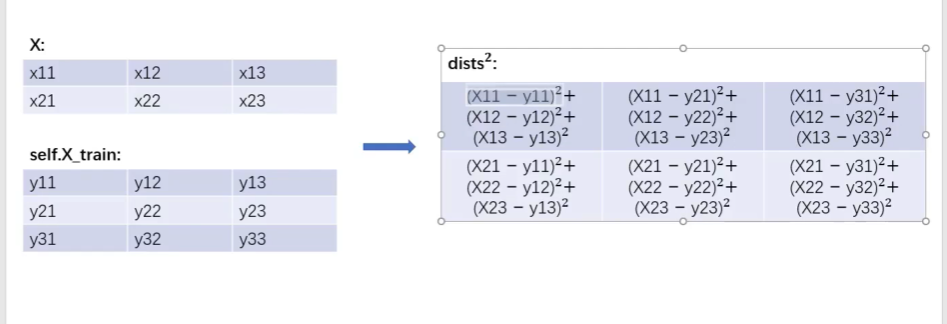

dists += np.sum(X**2,axis = 1,keepdims=True)#(500,1) dists += np.sum(self.X_train**2,axis = 1,keepdims=True).T#转置成行,(1,5000)
#keepdims=True是NumPy中的一个参数,用于控制在进行某些操作(如求和、平均值等)时是否保持原始数组的维度。
#如果设置为True,那么即使结果只有一个维度也要保留原始数组的维度;如果设置为False(默认值),则结果将降低一个维度。 dists -= 2*np.dot(X,self.X_train.T)(500,3072)(3072,5000) dists = np.sqrt(dists)(500,5000)
predict_labels预测
def predict_labels(self, dists, k=1): """ Given a matrix of distances between test points and training points, predict a label for each test point. 给一个dist矩阵,500行5000列 Inputs: - dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j] gives the distance betwen the ith test point and the jth training point. Returns: - y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i]. """ num_test = dists.shape[0] y_pred = np.zeros(num_test) for i in range(num_test): # A list of length k storing the labels of the k nearest neighbors to # the ith test point. closest_y = [] # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** dist = dists[i]#每一行 idx = np.argsort(dist)#每张图片最近的到最远的排列,长度为5000的向量,类型为整数 closest_y = self.y_train[idx]#每张图片最近的到最远的排列的类别放入closest_y中
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
######################################################################### # TODO: # # Now that you have found the labels of the k nearest neighbors, you # # need to find the most common label in the list closest_y of labels. # # Store this label in y_pred[i]. Break ties by choosing the smaller # # label. # ######################################################################### # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** #将closest_y中出现频率最高的类别作为当前训练图片的标签,如果两个类别频次一样高,就使用标签更小的值 count = Counter(closest_y)#对cloest_y中出现的标签进行投票 _y_pres = count.most_common(1)#返回列表,有两个元组,一个是类别,一个是出现的频次,返回出现频次最高的x个,这里是1个 y_pred[i] = _y_pres[0][0]#y—pred是长度为500的向量 # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** return y_pred
完成后在knn.ipynb中测试,得到

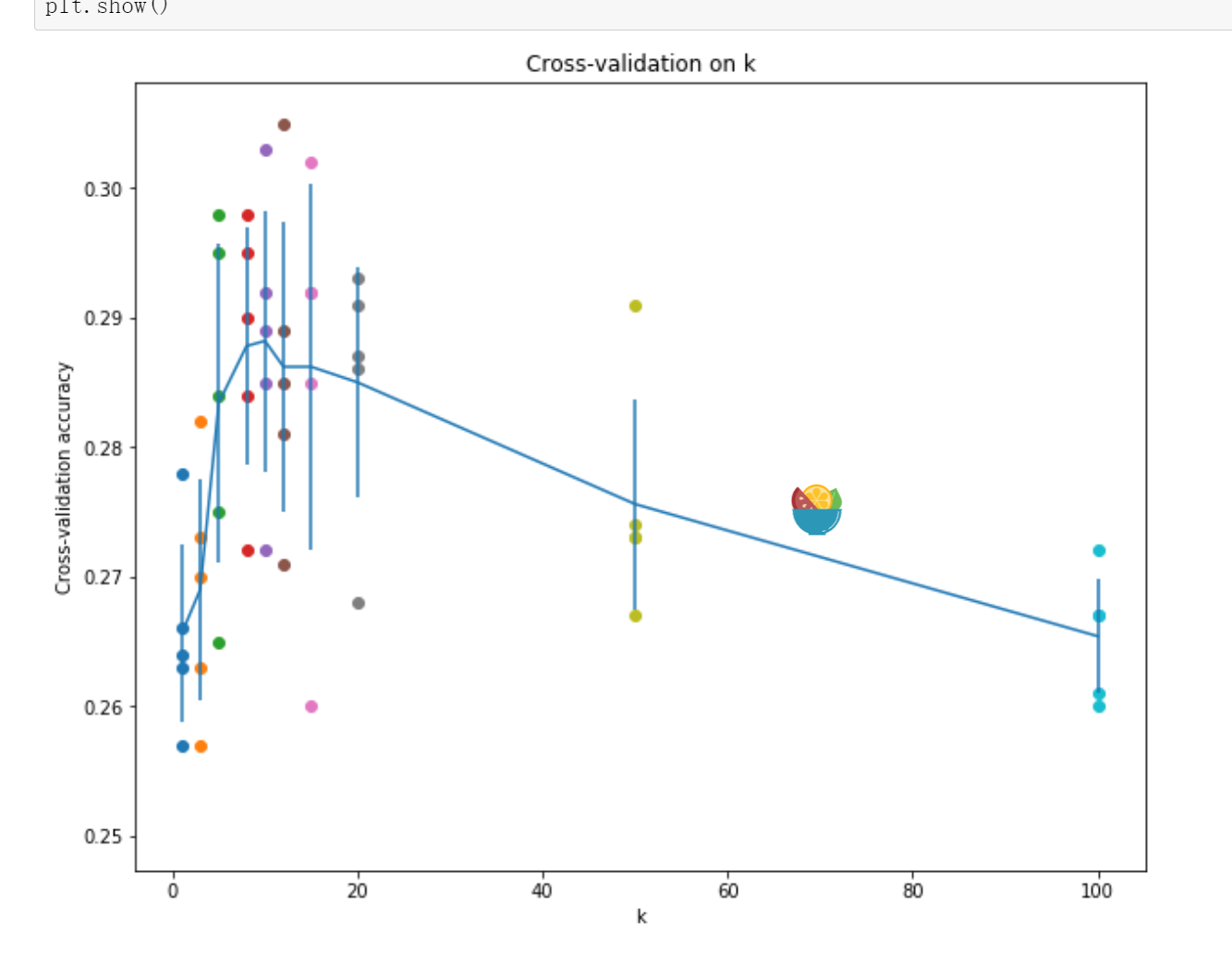
交叉验证Cross-validation
num_folds = 5 k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100] X_train_folds = [] y_train_folds = [] ################################################################################ # TODO: # # Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and # # y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where # # y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. # # Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. # ################################################################################ # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** X_train_folds = np.array_split(X_train, num_folds) y_train_folds = np.array_split(y_train, num_folds) # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** # A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find # when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation, # k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different # accuracy values that we found when using that value of k. k_to_accuracies = {} ################################################################################ # TODO: # # Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each # # possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, # # where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the # # last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all # # values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. # ################################################################################ # *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** for k in k_choices: k_to_accuracies[k]=[]#{k1:[],k2:[],...} for i in range(num_folds): _x_val = X_train_folds[i] _y_val = y_train_folds[i] _x_train = np.vstack([X_train_folds[j] for j in range(num_folds)if j!=i])#(4000,3072) _y_train = np.hstack([y_train_folds[j] for j in range(num_folds)if j!=i])#(4000) classifier = KNearestNeighbor() classifier.train(_x_train,_y_train) dists = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(_x_val)#(1000,4000),欧几里得计算得到这个大小的矩阵 y_val_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists,k=k) num_correct = np.sum(y_val_pred==_y_val) acc = float(num_correct)/len(_y_val) k_to_accuracies[k].append(acc) pass # *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)***** # Print out the computed accuracies for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies): for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]: print('k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy))
参考:[博客入坑]CS231N assignment 1 _ KNN 知识 & 详细解析 - 360MEMZ - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
assignment1-Q1.2-knn-向量化_哔哩哔哩_bilibili




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号