raissi2019 Allen-Cahn方程 (待更新...)
离散形式,与连续时间模型大同小异。
离散时间与连续时间的区别仅在于数据采样的数据间隔(物理定律方程本身是连续的)
文中是用t=0.1时的数据,来预测t=0.9时的数据,时间间隔为0.8
Our training data-set consists of \(N_n\) = 200 initial data points that are randomly sub-sampled from the exact solution at time t = 0.1, and our goal is to predict the solution at time t = 0.9 using a single time-step with size \(\Delta\) t = 0.8.
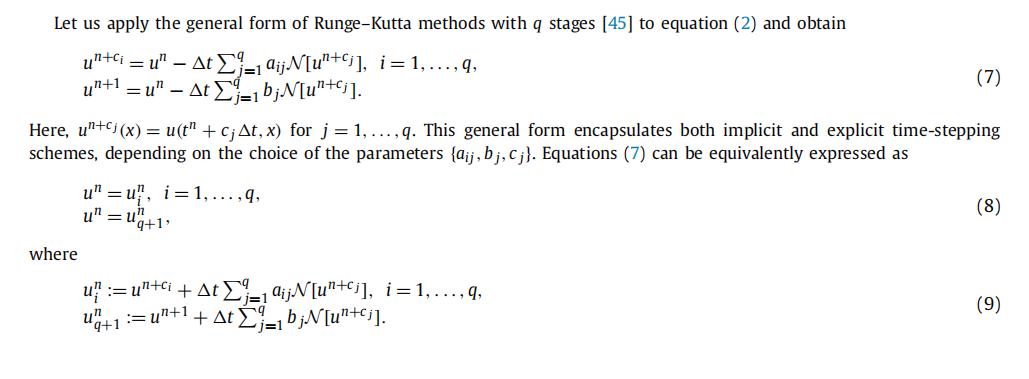
这种方法的误差为\(o(\Delta t^{2q})\),q为龙格库塔方法的阶数。因此控制离散时间模型算法精度的参数就是时间间隔\(\Delta t\)和龙格库塔阶数q.
但是龙格库塔方法看不懂的具体推导看不懂。
龙格库塔
龙格库塔算法理论形式:
论文中的应用:
# 放进神经网络里进行训练
self.U0_pred = self.net_U0(self.x0_tf) # N x (q+1) #conrresonds to the data at time-step t^n
self.U1_pred, self.U1_x_pred= self.net_U1(self.x1_tf) # N1 x (q+1)
构建神经网络的计算框架
def neural_net(self, X, weights, biases):
num_layers = len(weights) + 1
H = 2.0*(X - self.lb)/(self.ub - self.lb) - 1.0 # 归一化
for l in range(0,num_layers-2):
W = weights[l]
b = biases[l]
H = tf.tanh(tf.add(tf.matmul(H, W), b))
W = weights[-1]
b = biases[-1]
Y = tf.add(tf.matmul(H, W), b)
return Y
核心在这儿
def net_U0(self, x):
U1 = self.neural_net(x, self.weights, self.biases)
U = U1[:,:-1] #去掉U1的最后一列
U_x = self.fwd_gradients_0(U, x)
U_xx = self.fwd_gradients_0(U_x, x)
F = 5.0*U - 5.0*U**3 + 0.0001*U_xx # 加入了物理方程信息
U0 = U1 - self.dt*tf.matmul(F, self.IRK_weights.T)
return U0
def net_U1(self, x):
U1 = self.neural_net(x, self.weights, self.biases)
U1_x = self.fwd_gradients_1(U1, x)
return U1, U1_x # N x (q+1)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号