实验4
源代码
task.4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
int ch;
int line_count = 0;
int char_count = 0;
// 以只读方式打开文件data4.txt
fp = fopen("data4.txt", "r");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file\n");
return 1;
}
// 逐字符读取文件
// 逻辑说明:
// 1. 统计不包含空白符(空格、换行、制表符等)的字符数
// 2. 统计行数(通过检测换行符 '\n')
int last_char = -1; // 用于记录上一个读取的字符,辅助判断最后一行
while((ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF) {
// 统计字符数:排除空白符
if(ch != ' ' && ch != '\n' && ch != '\t' && ch != '\r' && ch != '\v' && ch != '\f') {
char_count++;
}
// 统计行数:遇到换行符行数+1
if(ch == '\n') {
line_count++;
}
last_char = ch;
}
// 特殊处理:如果文件非空且最后一个字符不是换行符,说明最后一行未被换行符计数,需要补加1
if(last_char != -1 && last_char != '\n') {
line_count++;
}
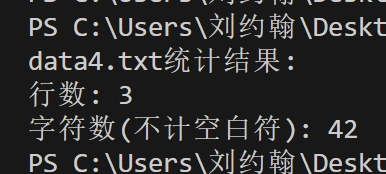
printf("data4.txt统计结果:\n");
printf("行数: %d\n", line_count);
printf("字符数(不计空白符): %d\n", char_count);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![image]()
实验5
源代码
task.5
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 10
typedef struct {
long id; // 准考证号
char name[20]; // 姓名
float objective; // 客观题得分
float subjective; // 操作题得分
float sum; // 总分
char result[10]; // 考试结果
} STU;
// 函数声明
void read(STU st[], int n);
void write(STU st[], int n);
void output(STU st[], int n);
int process(STU st[], int n, STU st_pass[]);
int main() {
STU stu[N], stu_pass[N];
int cnt;
double pass_rate;
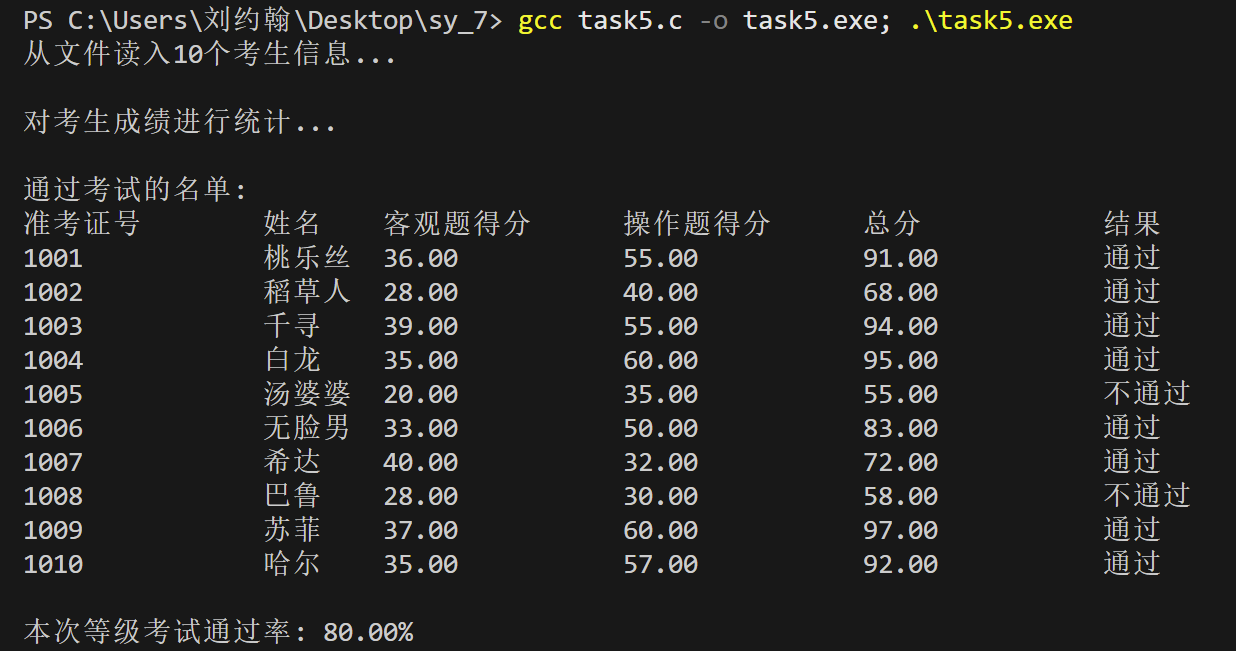
printf("从文件读入%d个考生信息...\n", N);
read(stu, N);
printf("\n对考生成绩进行统计...\n");
cnt = process(stu, N, stu_pass);
printf("\n通过考试的名单:\n");
output(stu, N); // 输出所有考生完整信息到屏幕
write(stu, N); // 输出考试通过的考生信息到文件
pass_rate = 1.0 * cnt / N;
printf("\n本次等级考试通过率: %.2f%%\n", pass_rate*100);
return 0;
}
// 把所有考生完整信息输出到屏幕上
void output(STU st[], int n) {
int i;
printf("准考证号\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t结果\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n",
st[i].id, st[i].name, st[i].objective, st[i].subjective, st[i].sum, st[i].result);
}
// 从文本文件examinee.txt读入考生信息
void read(STU st[], int n) {
int i;
FILE *fin;
fin = fopen("examinee.txt", "r");
if (!fin) {
printf("fail to open file\n");
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
fscanf(fin, "%ld %s %f %f", &st[i].id, st[i].name, &st[i].objective, &st[i].subjective);
fclose(fin);
}
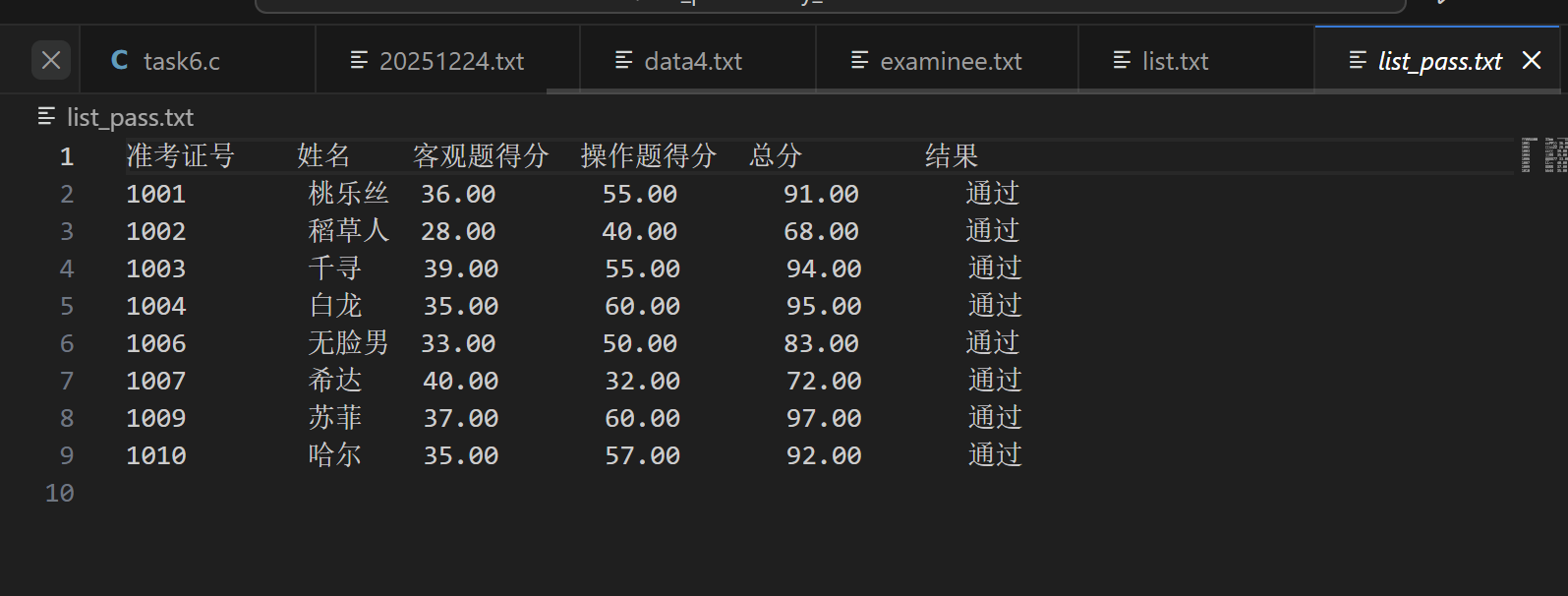
// 把通过考试的考生完整信息写入文件list_pass.txt
void write(STU s[], int n) {
FILE *fout;
int i;
fout = fopen("list_pass.txt", "w");
if (!fout) {
printf("fail to open file to write\n");
return;
}
// 写入表头,保持格式一致
fprintf(fout, "准考证号\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t结果\n");
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 只有 result 为 "通过" 的考生才写入文件
if(strcmp(s[i].result, "通过") == 0) {
fprintf(fout, "%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n",
s[i].id, s[i].name, s[i].objective, s[i].subjective, s[i].sum, s[i].result);
}
}
fclose(fout);
}
// 对考生信息进行处理:计算每位考生考试总分、结果;统计考试通过的人数
int process(STU st[], int n, STU st_pass[]) {
int i;
int count = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st[i].sum = st[i].objective + st[i].subjective;
if(st[i].sum >= 60) {
strcpy(st[i].result, "通过");
st_pass[count] = st[i];
count++;
} else {
strcpy(st[i].result, "不通过");
}
}
return count;
}
实验结果截图
![image]()
![image]()
实验6
源代码
task.6
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 80
#define M 5
typedef struct {
char id[20];
char name[20];
char className[40];
} Student;
int main() {
Student stus[N];
Student lucky[M];
FILE *fp;
int i, j;
int index;
int indices[M];
int found;
fp = fopen("list.txt", "r");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open list.txt\n");
return 1;
}
for(i = 0; i < N; i++) {
fscanf(fp, "%s %s %s", stus[i].id, stus[i].name, stus[i].className);
}
fclose(fp);
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(i = 0; i < M; i++) {
do {
index = rand() % N;
found = 0;
for(j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if(indices[j] == index) {
found = 1;
break;
}
}
} while(found);
indices[i] = index;
lucky[i] = stus[index];
}
for(i = 0; i < M - 1; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < M - 1 - i; j++) {
if(strcmp(lucky[j].id, lucky[j+1].id) > 0) {
Student temp = lucky[j];
lucky[j] = lucky[j+1];
lucky[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
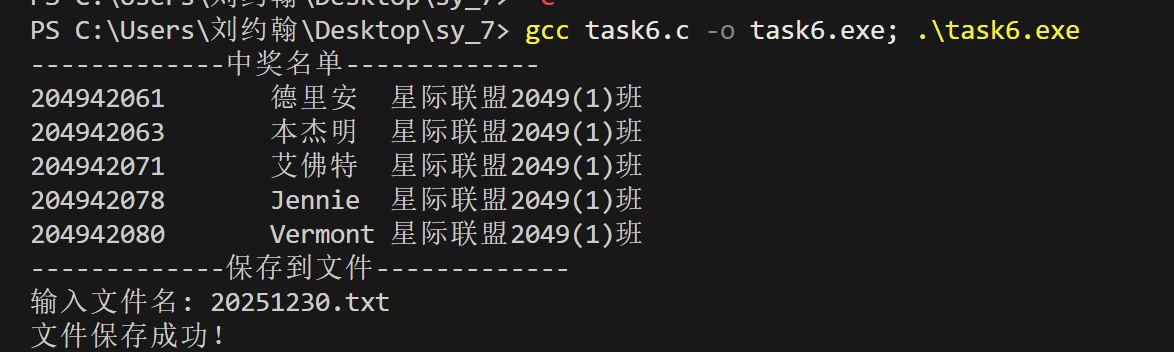
printf("-------------中奖名单-------------\n");
for(i = 0; i < M; i++) {
printf("%s\t%s\t%s\n", lucky[i].id, lucky[i].name, lucky[i].className);
}
char filename[50];
time_t now = time(NULL);
struct tm *t = localtime(&now);
sprintf(filename, "%04d%02d%02d.txt", t->tm_year + 1900, t->tm_mon + 1, t->tm_mday);
printf("-------------保存到文件-------------\n");
printf("输入文件名: %s\n", filename);
fp = fopen(filename, "w");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to write\n");
return 1;
}
for(i = 0; i < M; i++) {
fprintf(fp, "%s\t%s\t%s\n", lucky[i].id, lucky[i].name, lucky[i].className);
}
fclose(fp);
printf("文件保存成功!\n");
return 0;
}
实验结果截图
![image]()
![image]()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号